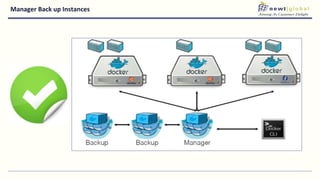
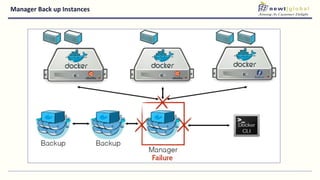
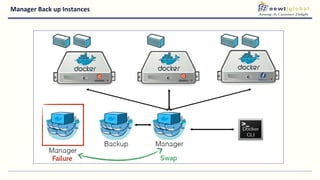
- Venkat is the DevOps Practice Leader at NewtGlobal with over 16 years of experience delivering enterprise projects.
- The webinar will discuss microservices and include a Q&A session. Questions can be asked in the chat window.
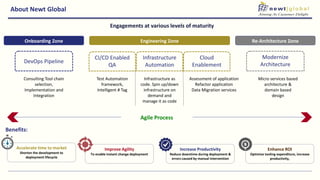
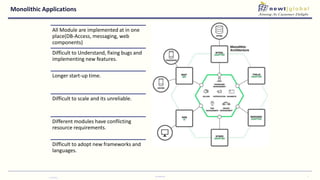
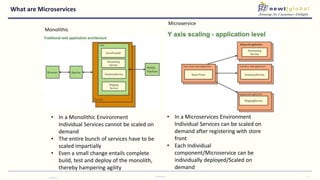
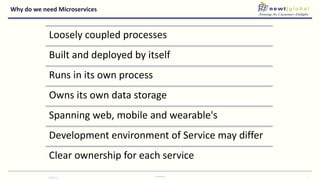
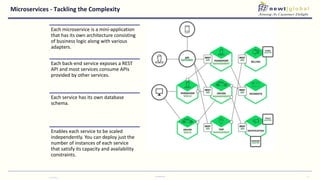
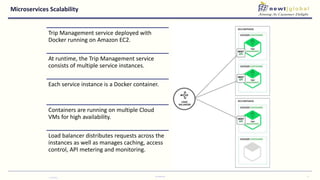
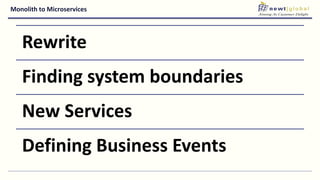
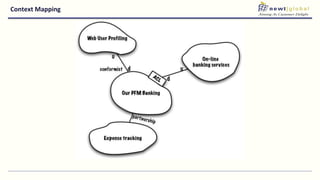
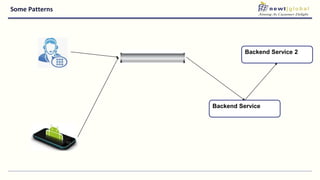
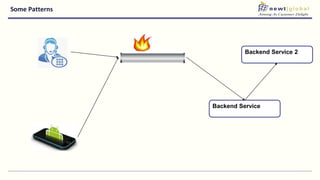
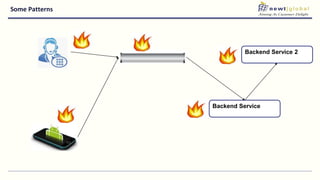
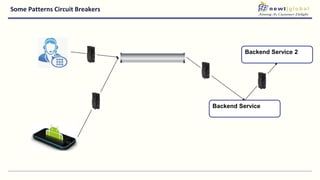
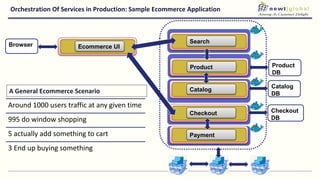
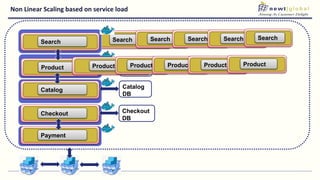
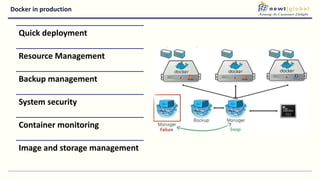
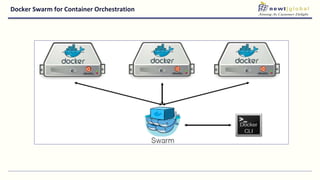
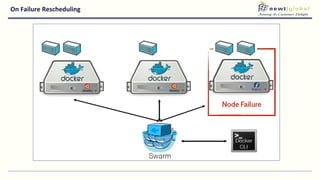
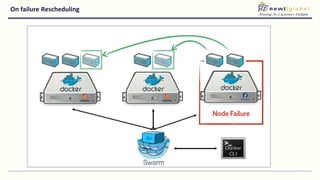
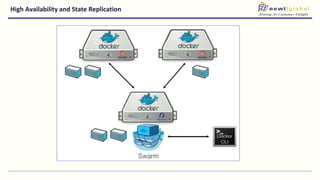
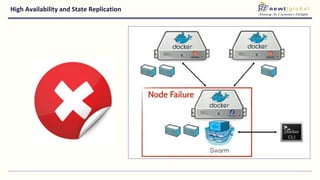
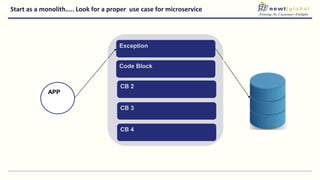
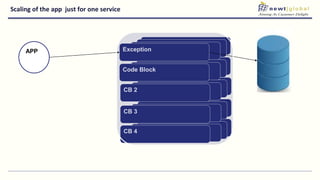
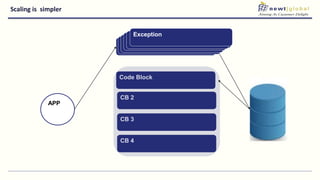
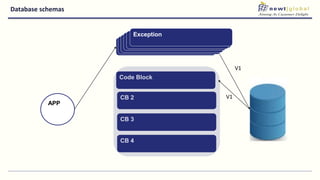
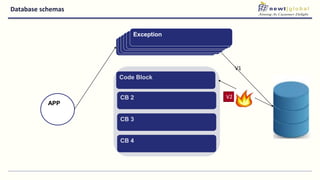
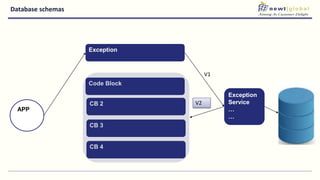
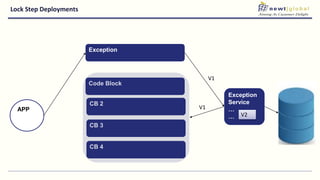
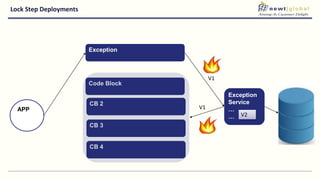
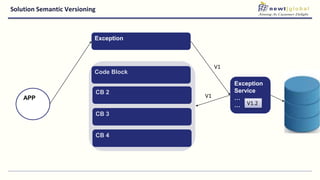
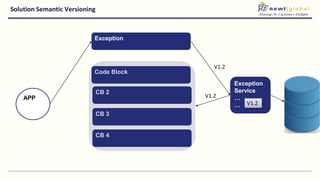
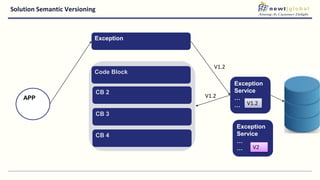
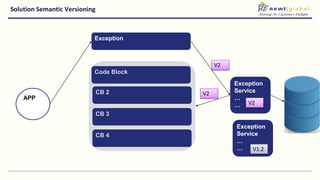
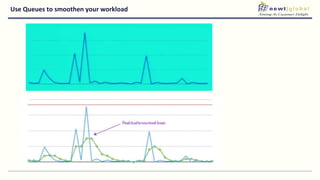
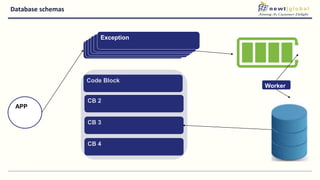
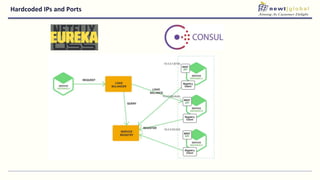
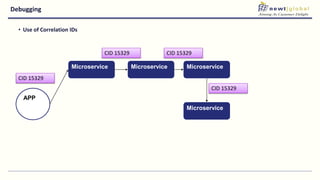
- Moving from monolithic to microservices architecture allows individual components to be independently deployed, scaled, and developed using different technologies. This improves agility but also increases complexity.