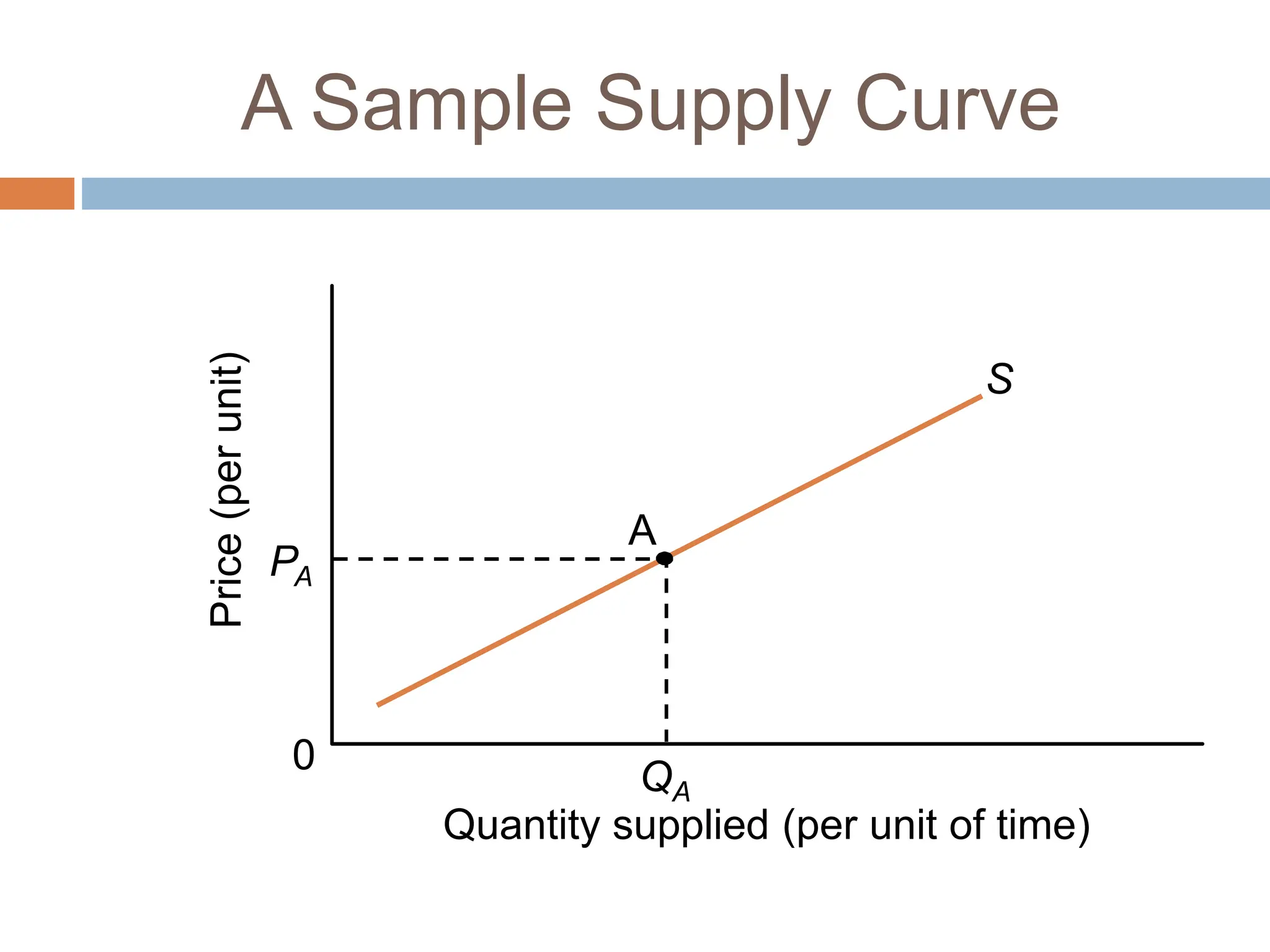
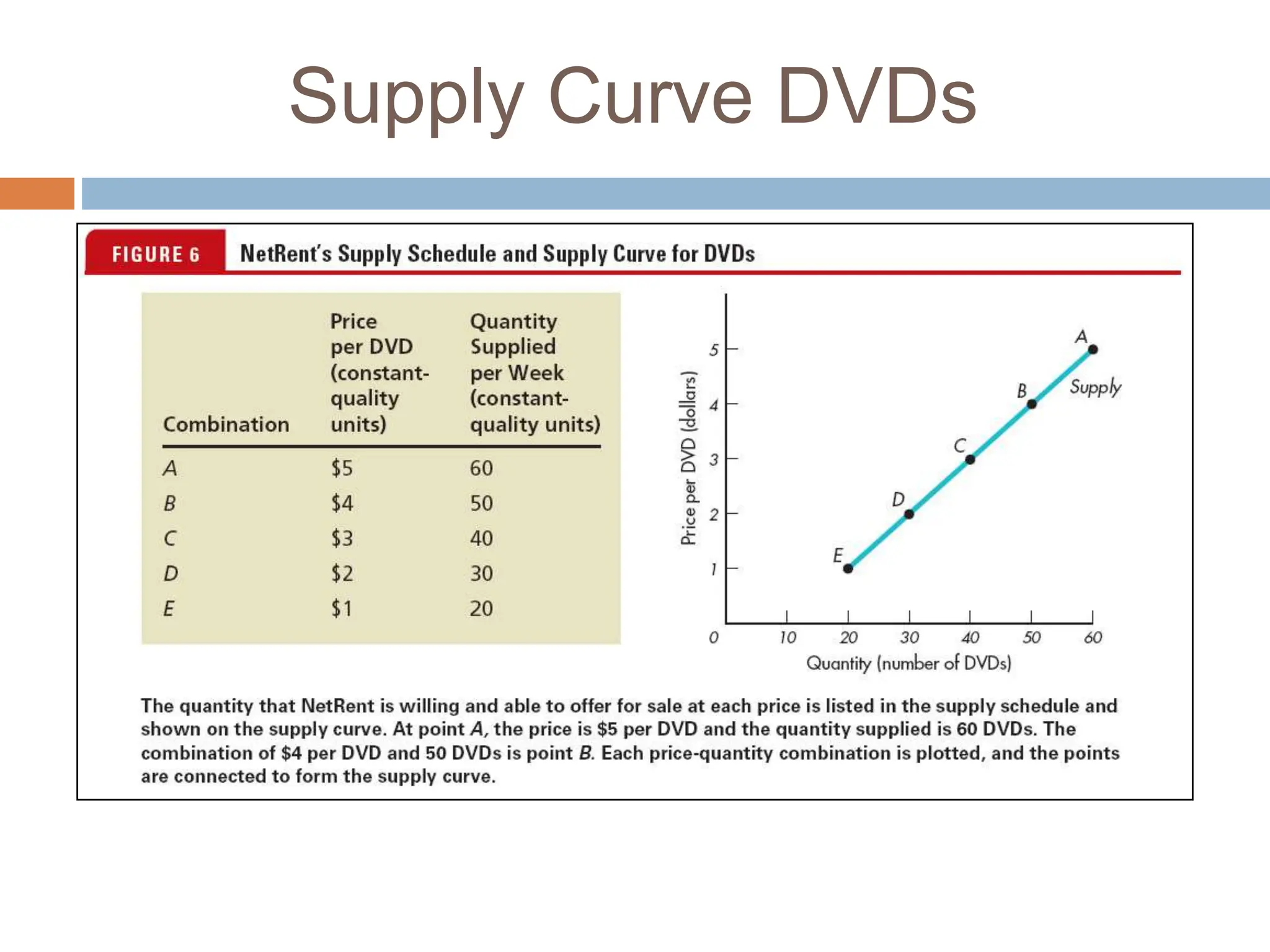
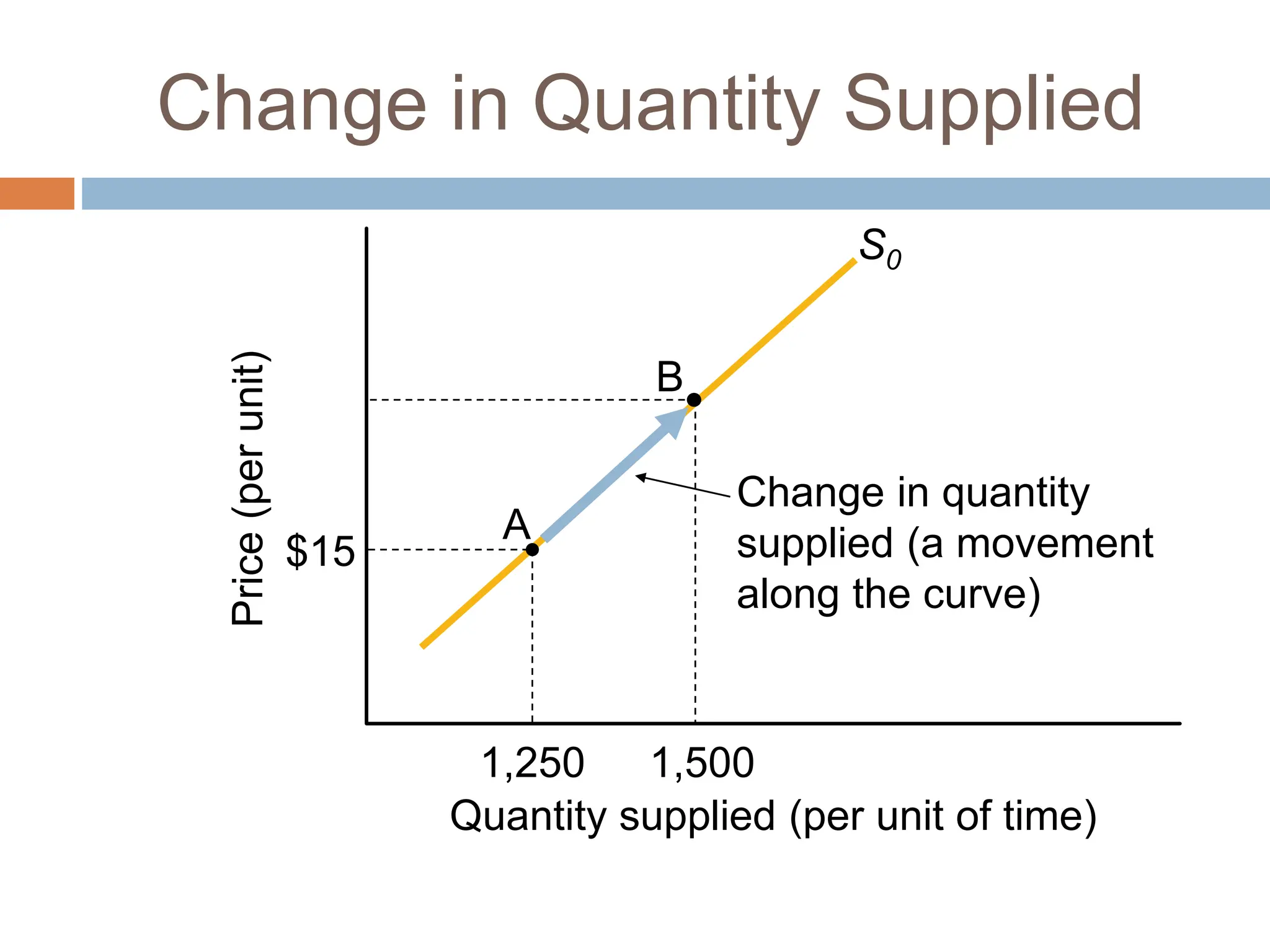
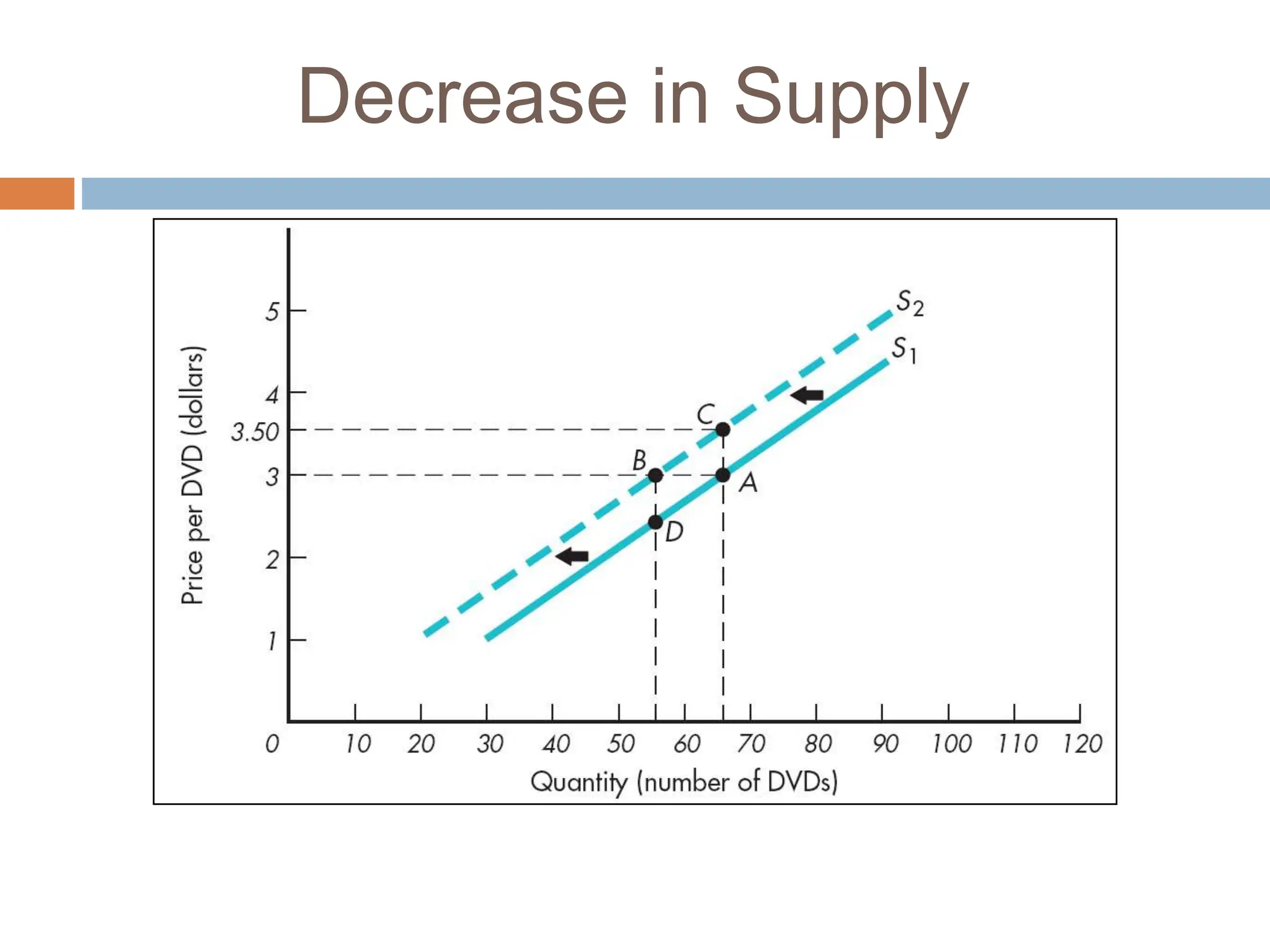
Chapter 3 of microeconomics covers supply theory, focusing on the law of demand and the determinants of supply, which include price, resource costs, technology, expectations, the number of sellers, and taxes. It is explained that there is a direct relationship between price and quantity supplied, illustrated through the upward-sloping supply curve. The chapter also discusses factors leading to shifts in supply, such as production costs, technological changes, government policies, and climate impacts.