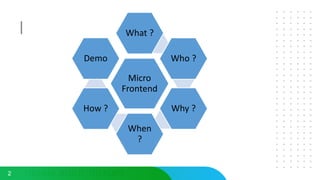
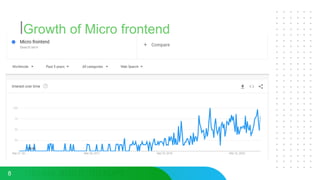
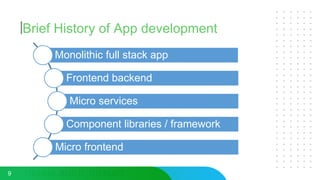
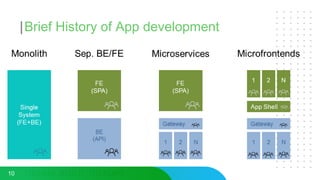
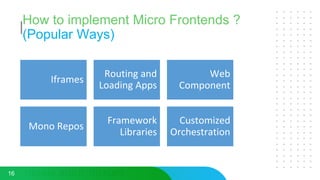
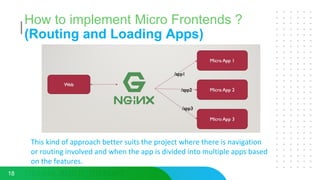
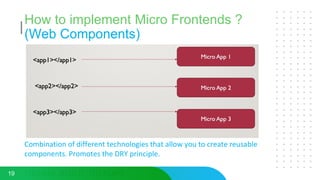
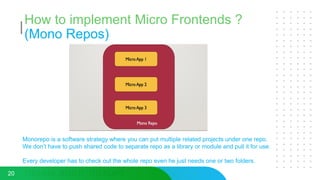
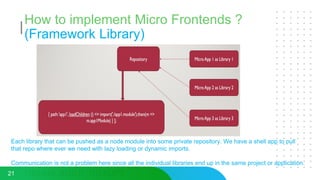
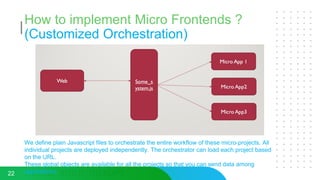
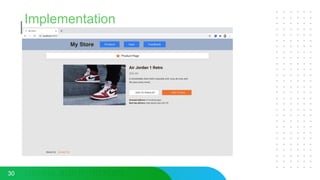
This document discusses micro frontends, which extend the microservices architecture approach to frontend web development. It defines micro frontends as distinct slices of a web application that encompass the frontend, backend service, and database. The document then discusses why companies are using micro frontends and when they should be used. It provides examples of how companies like Walmart and Emtec Digital have implemented micro frontends. Finally, it covers popular ways to implement micro frontends such as using iframes, routing, web components, monorepos, and framework libraries.