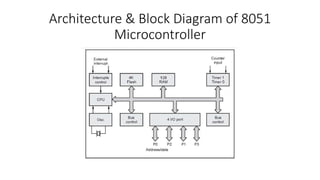
The 8051 microcontroller has a central processing unit that monitors and controls all operations. It contains RAM, ROM, I/O ports, timers, and ADCs on a single chip. The CPU reads programs stored in ROM memory and executes instructions to perform tasks. It can be interrupted by other important subroutines. The microcontroller uses memory to store programs that tell it what specific tasks to perform. It has address and data buses that function as communication channels to transfer addresses and data between the CPU and memory.