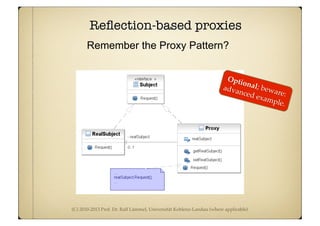
This document discusses metaprograms and metadata in Java. Metaprograms are programs that manipulate other programs, where programs correspond to data of metaprograms. Metadata is data that provides additional information about programs or other data. The document provides examples of using reflection and annotations in Java to implement metaprogramming and work with metadata. It also discusses using proxies to implement the proxy pattern reflectively in Java.








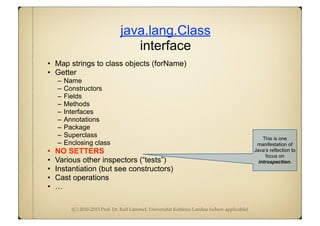













![(C) 2010-2013 Prof. Dr. Ralf Lämmel, Universität Koblenz-Landau (where applicable)
Annotation declaration
for sample annotation
/**
* Describes a Request-For-Enhancement(RFE)
* for the API element at hand
*/
public @interface RequestForEnhancement {
int id();
String synopsis();
String engineer() default "[unassigned]";
String date(); default "[unimplemented]";
}
Thus, annotation declarations are
somewhat specific interface declarations.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meta-130528025242-phpapp01/85/Metaprograms-and-metadata-as-part-of-the-the-PTT-lecture-26-320.jpg)