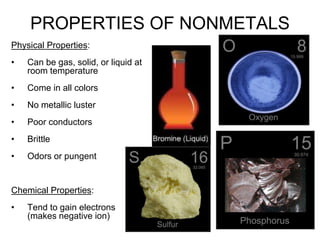
The document discusses the properties, occurrence, and processing of metals and nonmetals, including their physical and chemical characteristics. It outlines the differences in reactivity, metallurgy processes, and practical applications of various metals and nonmetals, as well as the significance of alloys and corrosion prevention methods. Key points include the activity series of metals and specific uses for common elements like iron, sulfur, and gold.