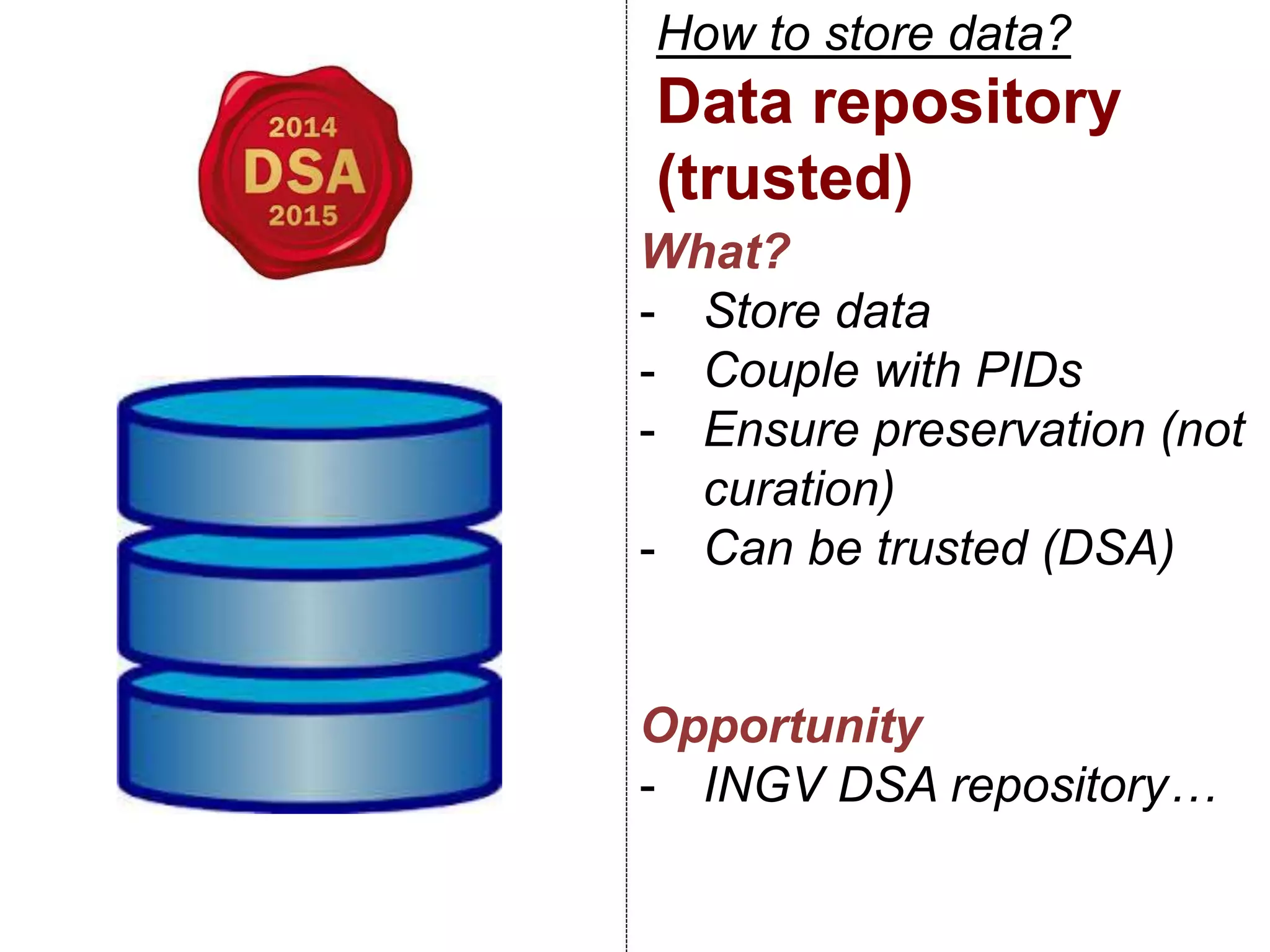
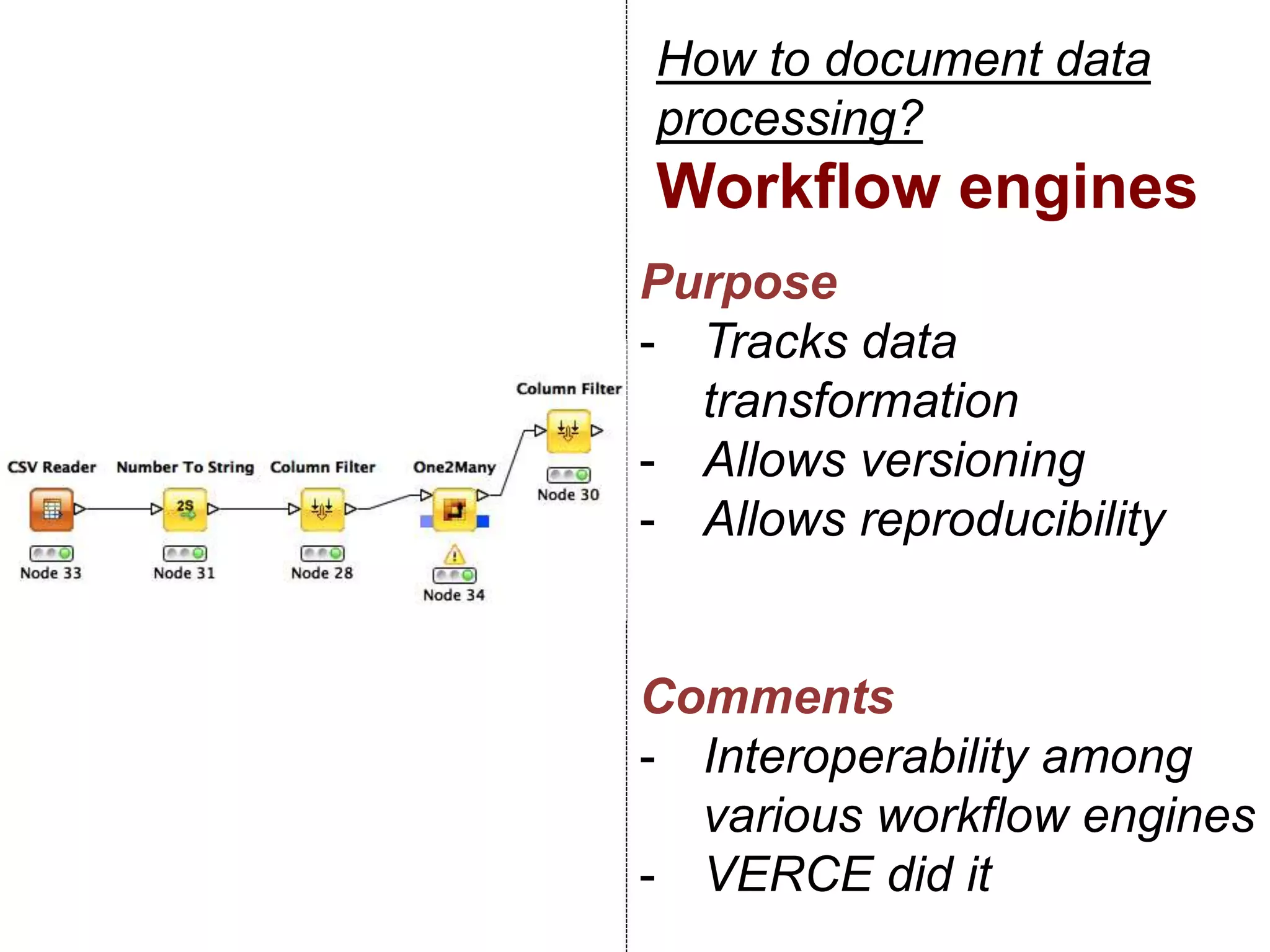
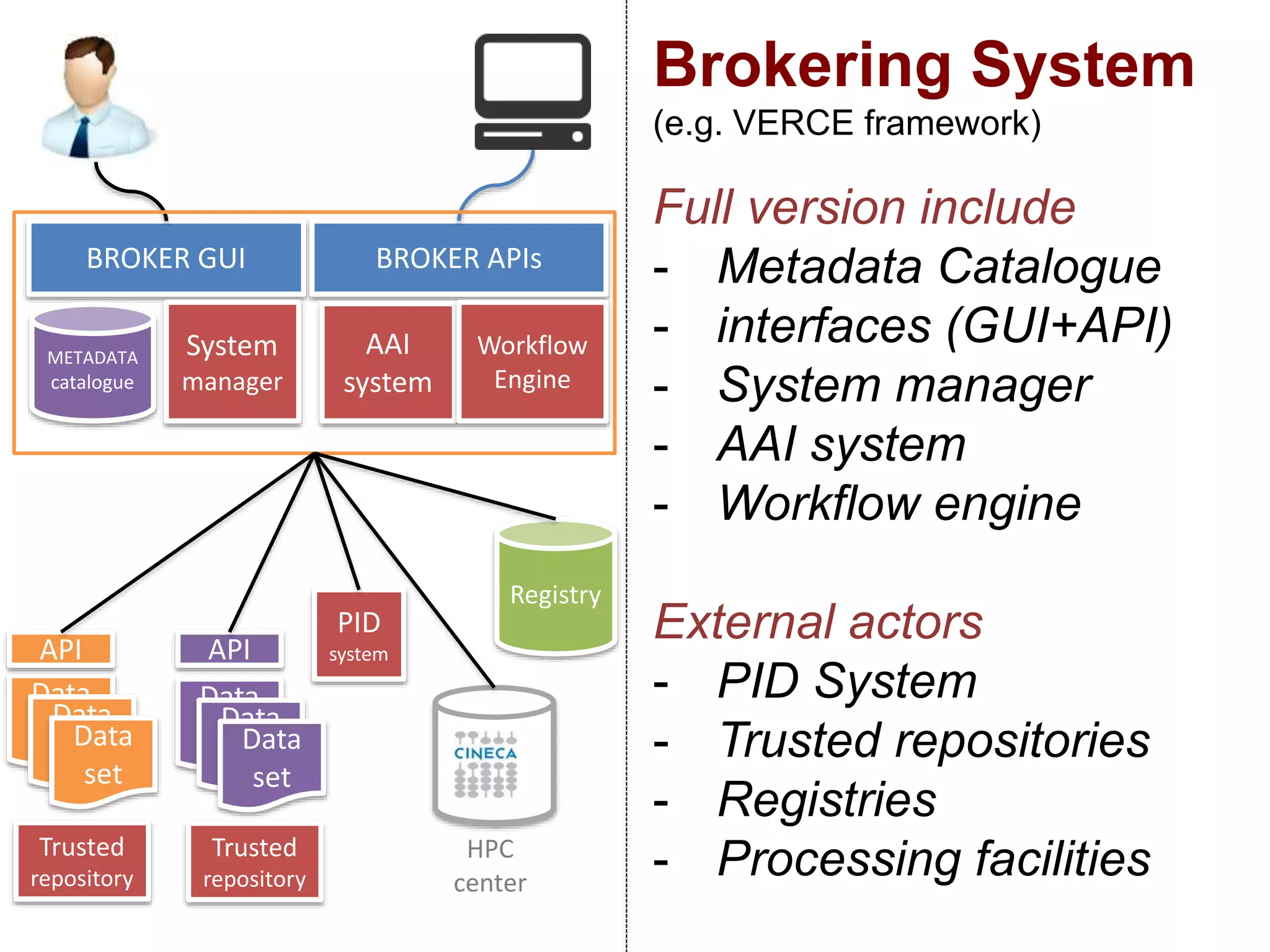
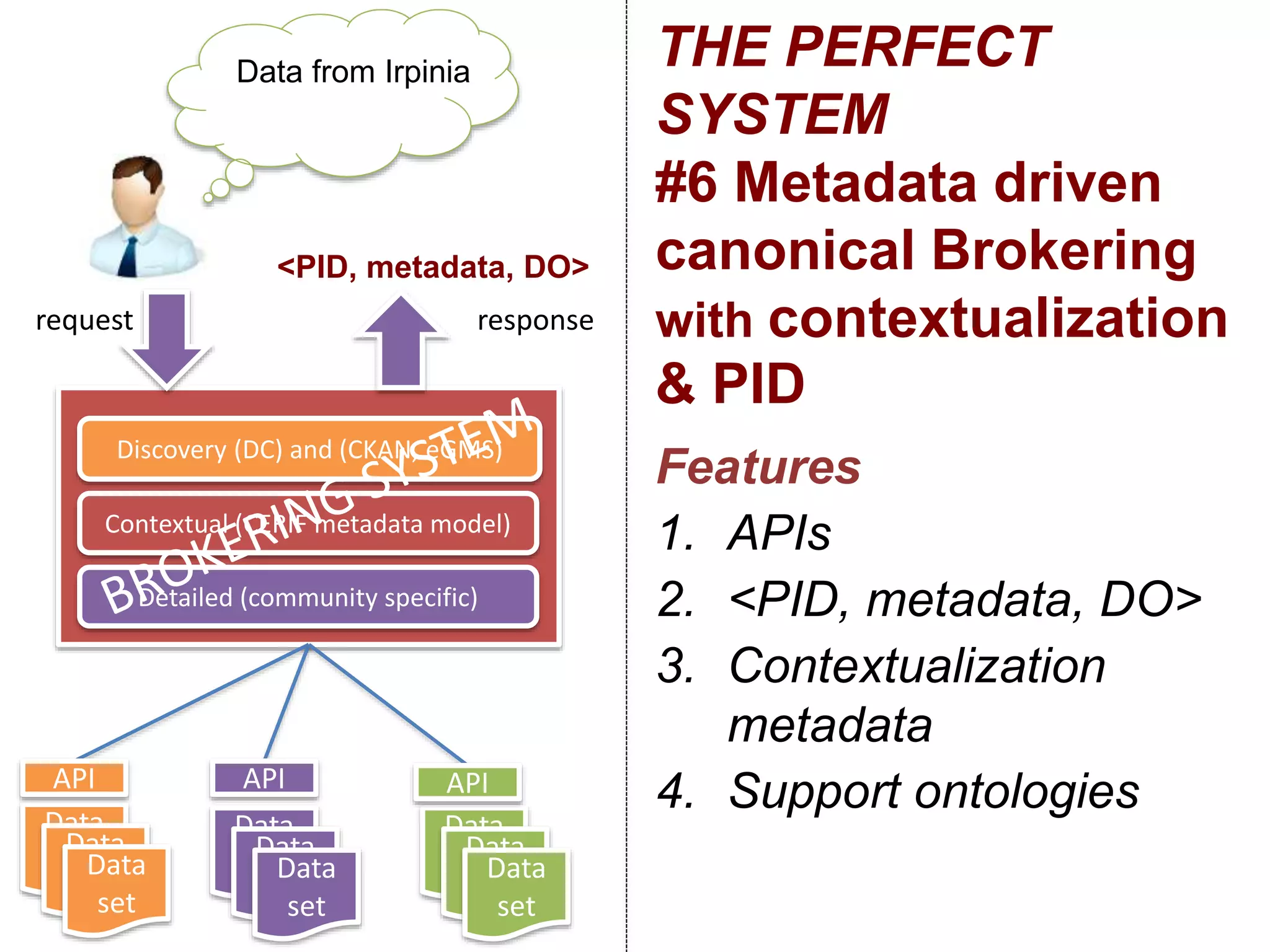
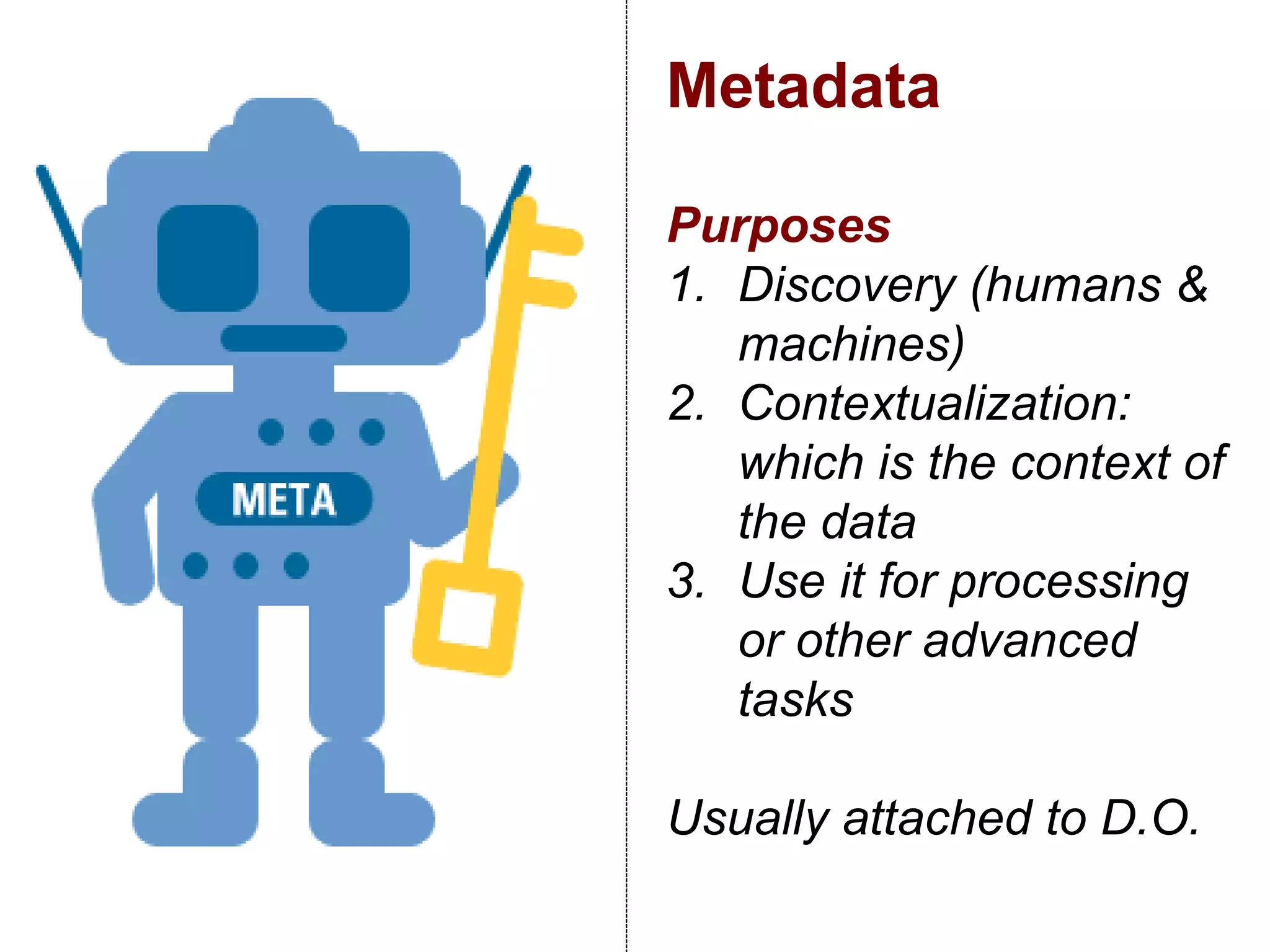
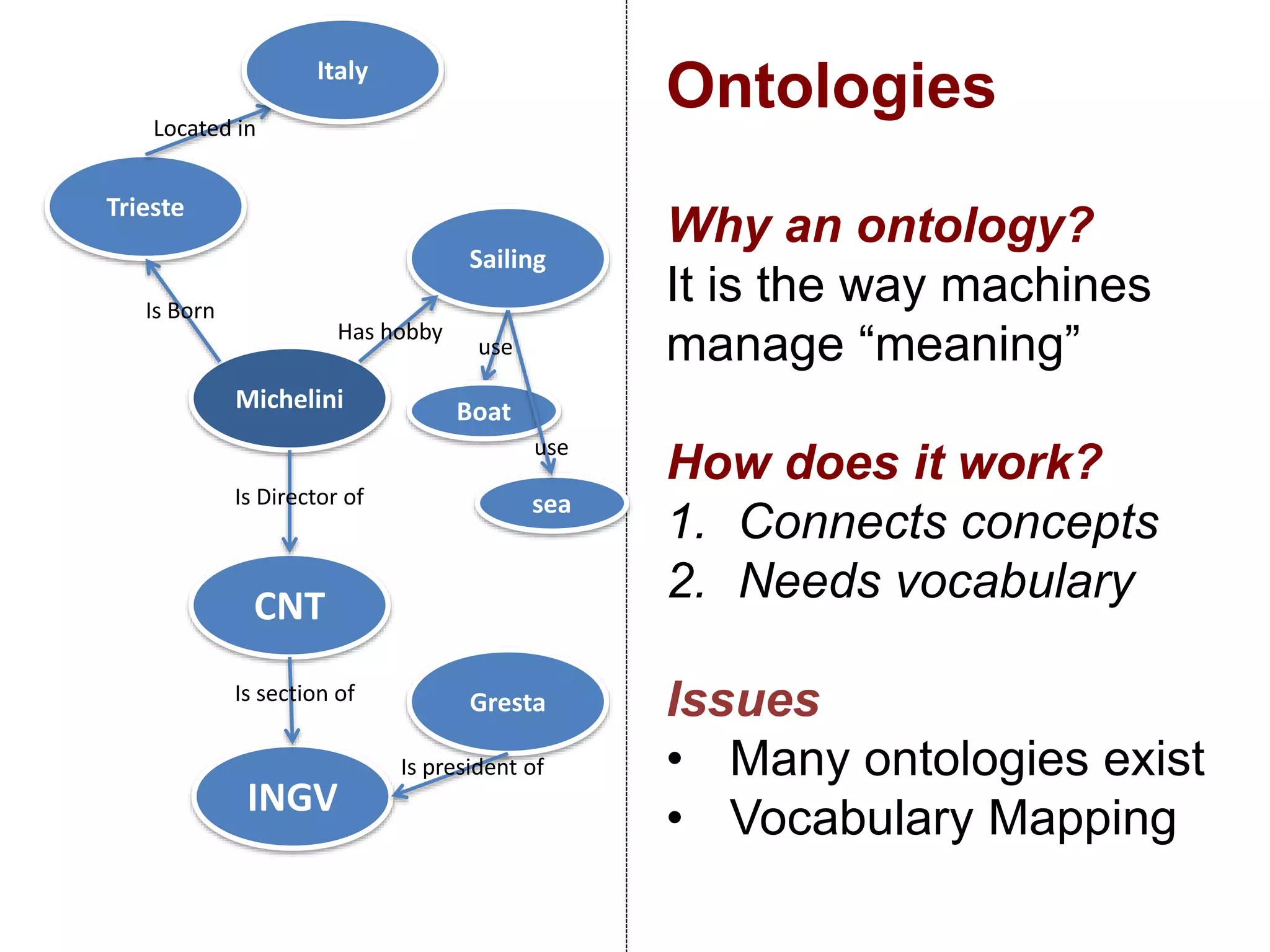
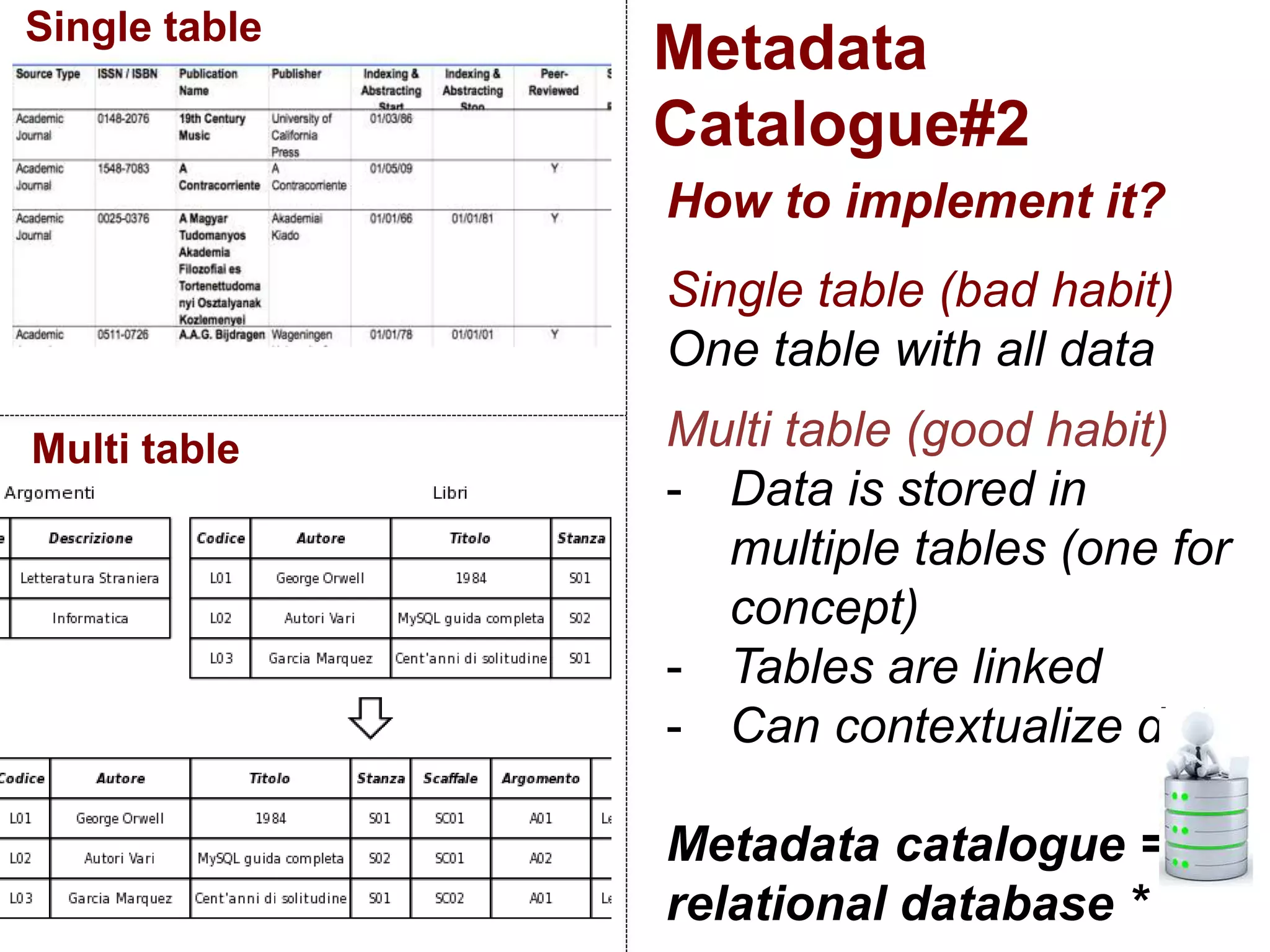
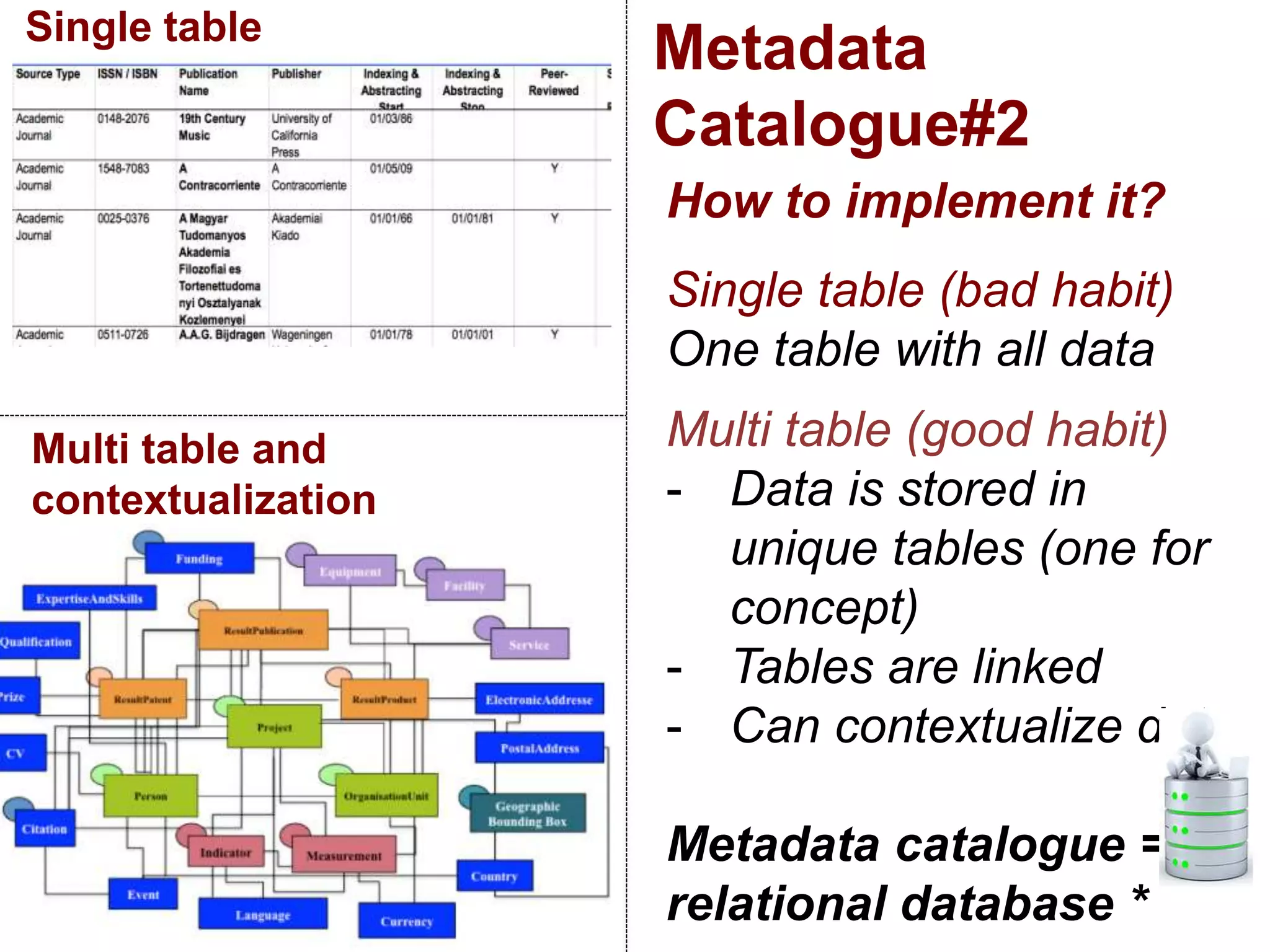
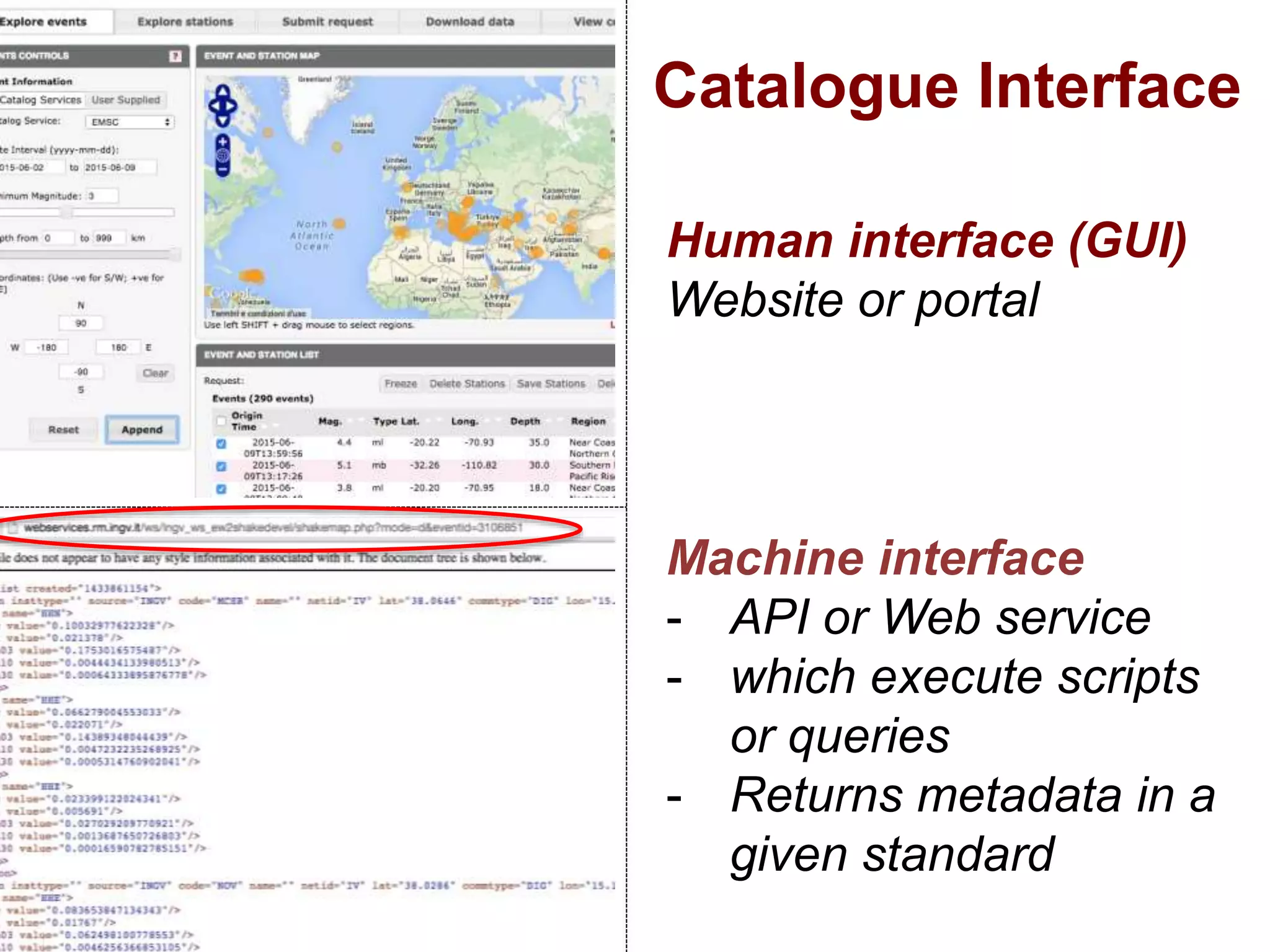
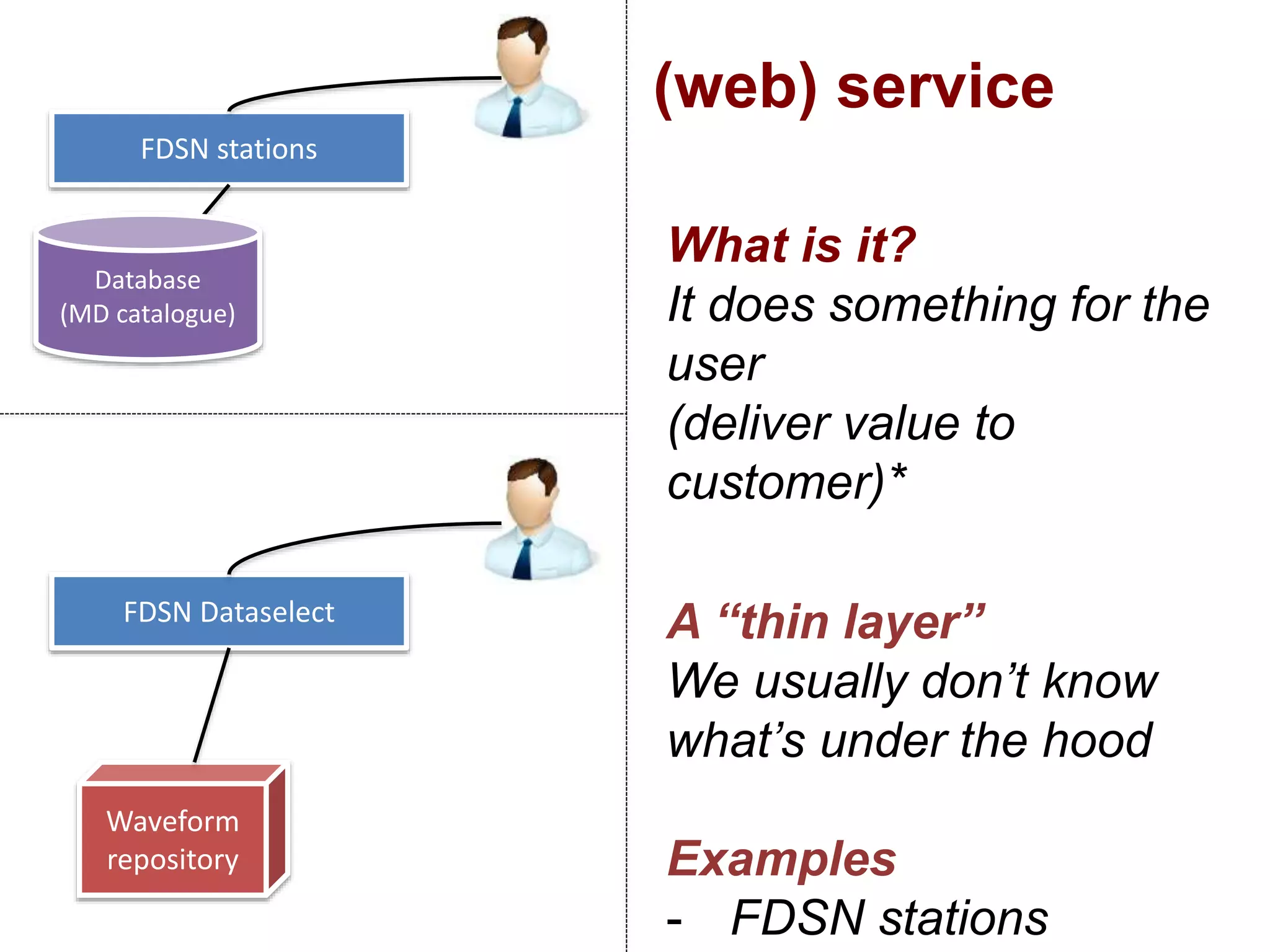
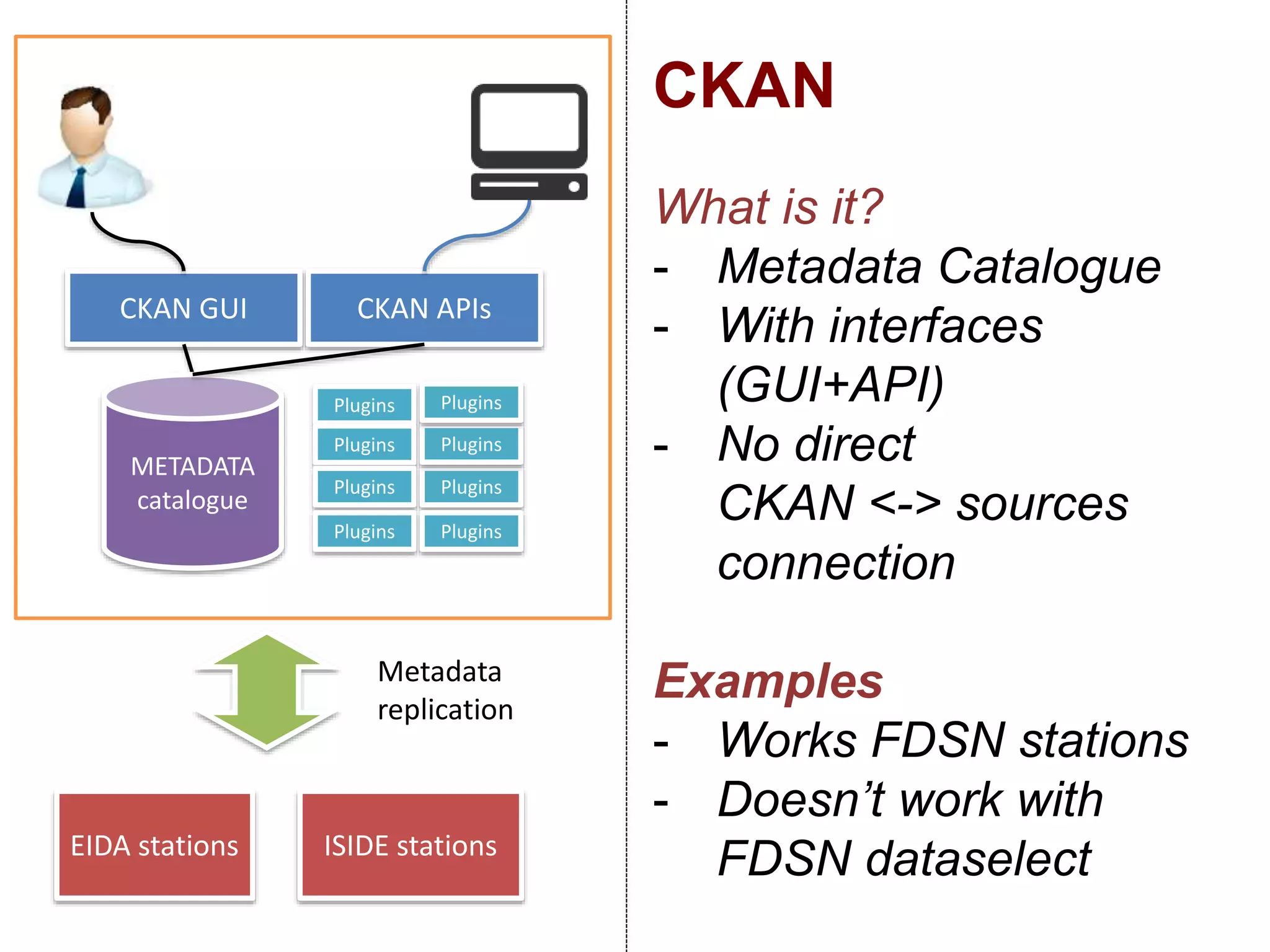
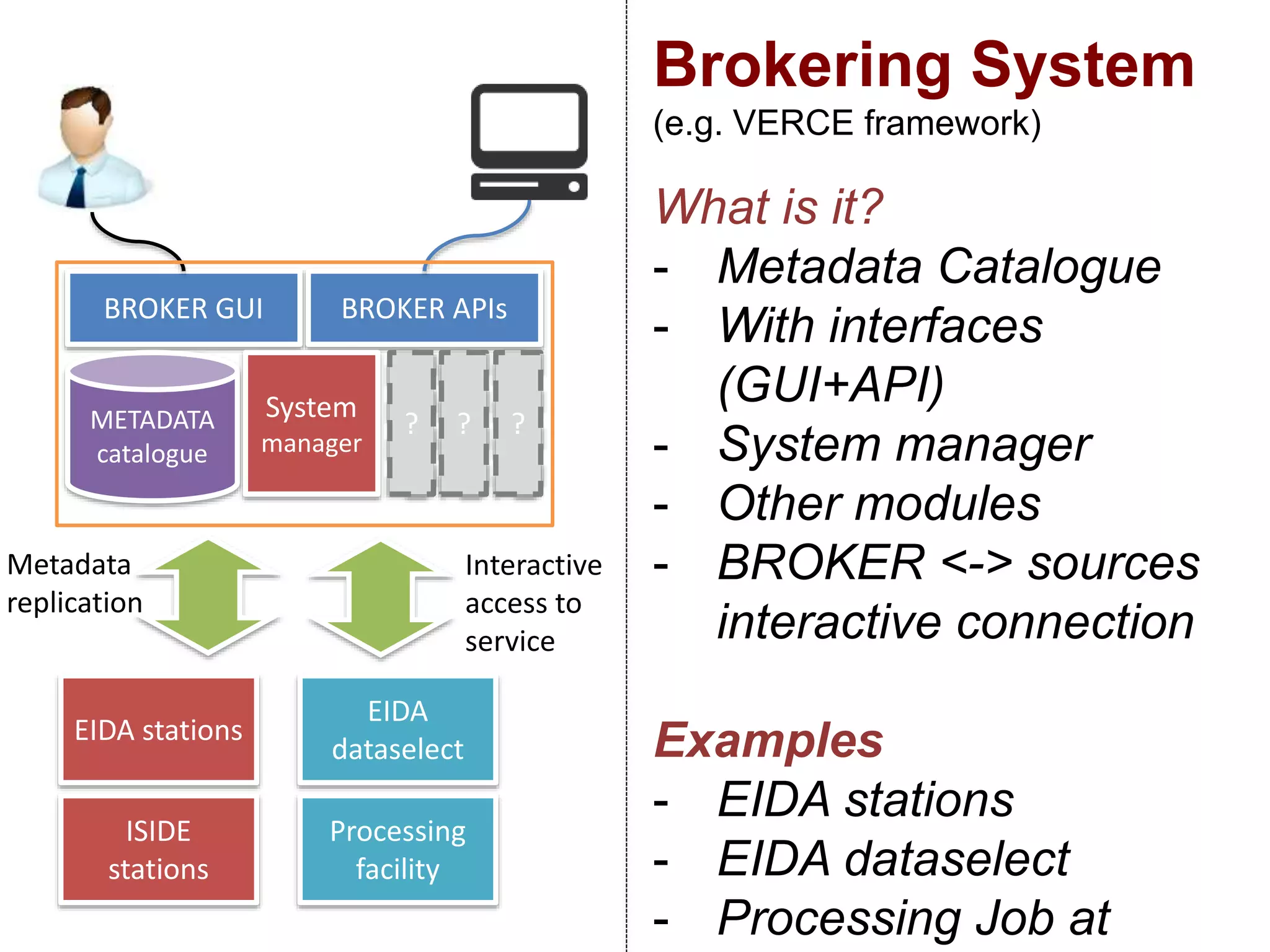
The document discusses metadata and brokering in data systems, emphasizing the importance of digital data, metadata, and interoperability. It outlines the functionalities of metadata catalogs, the role of APIs in data discovery and contextualization, and the use of ontologies for machine understanding. Additionally, it addresses the challenges of data sharing, storage, and management within various frameworks and systems.







![RDA concepts
Data Fabric
What?
Identifies mechanisms,
standard, components and
interfaces making data
science efficient and cost
effective
Data Management Plan
• Data management
• Data analysis
• Data preservation
• Data publication
• Data sharing
[UK data Archive http://www.data-archive.ac.uk/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-150612214633-lva1-app6891/75/Metadata-brokering-a-modern-approach-2-18-2048.jpg)
![RDA concepts
Data Fabric
[RDA WG outputs https://indico.cern.ch/event/370271/session/2/contribution/6/material/0/0.pdf]
How to store?How to register?
How to discover?
How to cite?
How to document
processing?
How to integrate?
How to collect
new DP?
How to
access?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015-150612214633-lva1-app6891/75/Metadata-brokering-a-modern-approach-2-19-2048.jpg)