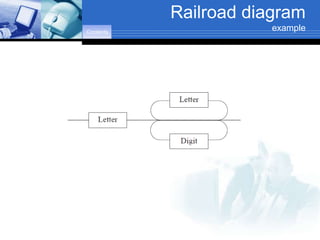
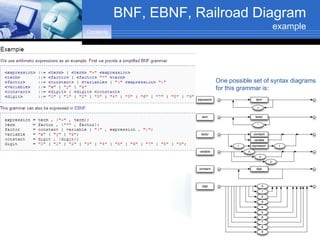
The document discusses software design and development meta languages, specifically focusing on Backus-Naur Form (BNF), Extended Backus-Naur Form (EBNF), and railroad diagrams. It defines these metalanguages and explains their usage in describing programming language syntax through various examples. The document includes visual representations and interpretations of how these languages work, highlighting components such as terminal and non-terminal symbols.