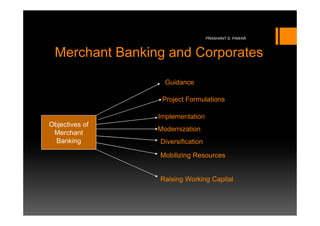
The document defines and discusses merchant banking. Merchant banks originated in medieval Italy as family-owned businesses that financed trade using excess capital. They facilitate business processes and transferring capital funds. In India, merchant banking provides non-fund based services like managing securities issuance, providing corporate advisory services, and mobilizing resources. The objectives of merchant banks are to provide guidance, raise capital, diversify companies, and help with projects, modernization, and working capital. Their activities include project counseling, feasibility studies, licensing assistance, and advice on mergers and acquisitions.