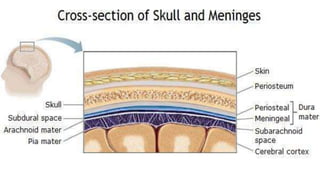
Meningitis is an inflammation of the protective membranes (meninges) surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It is usually caused by a viral or bacterial infection. The meninges have three layers (dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater) that are separated by fluid-filled spaces. Meningitis is a medical emergency because it can be life-threatening. It most commonly affects children and young adults. Bacterial meningitis is usually preceded by a mild respiratory infection that allows bacteria to enter the bloodstream and meninges. Diagnosis involves examination of cerebrospinal fluid obtained via lumbar puncture for signs of infection.