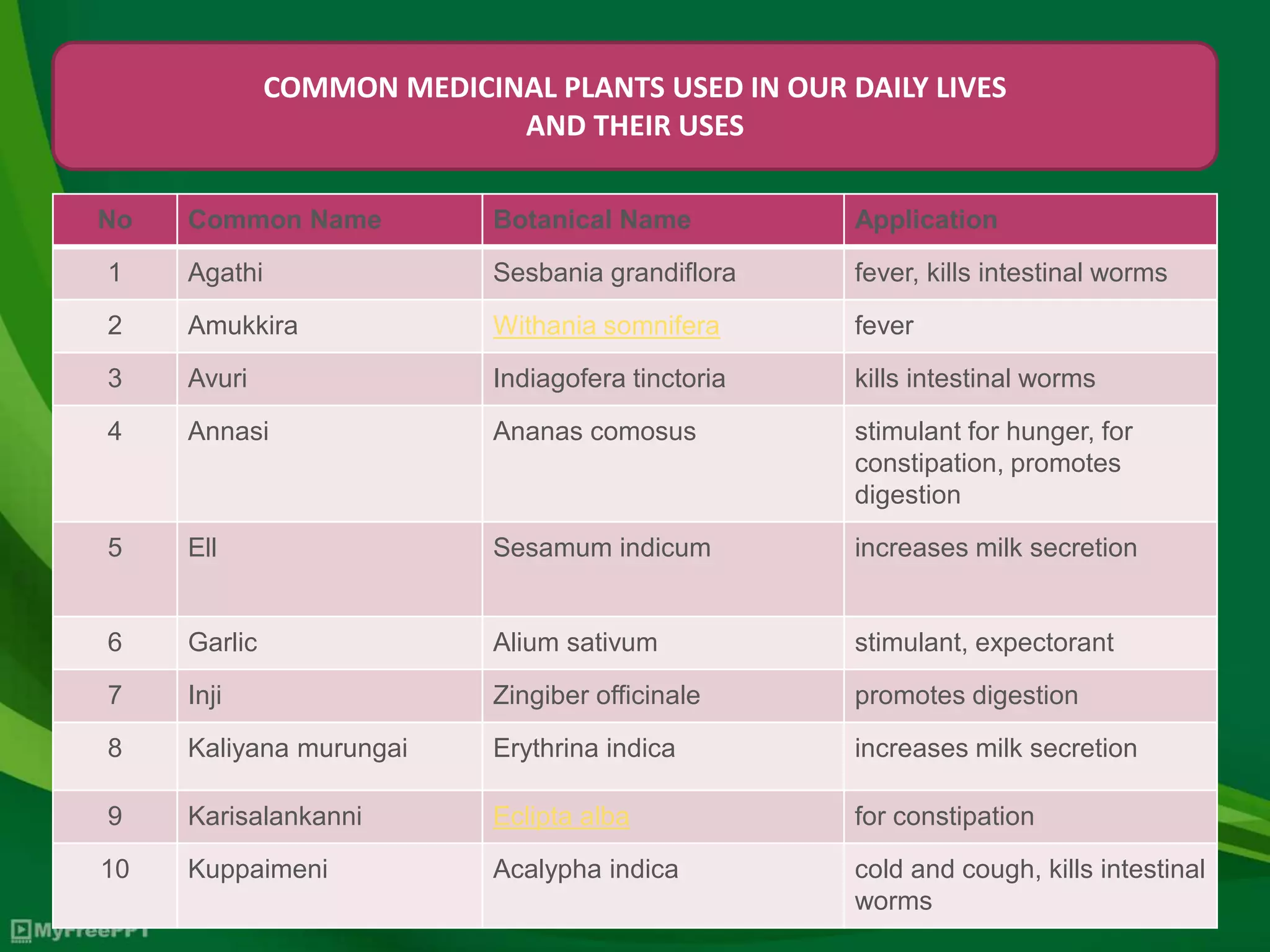
The document discusses medicinal plants, emphasizing their therapeutic properties, characteristics, and importance in traditional Indian medicine. It highlights the various uses of common medicinal plants and advocates for the cultivation and sustainable management of these plants to enhance their availability and benefits. The text calls for a return to natural remedies as a safer alternative to synthetic drugs.