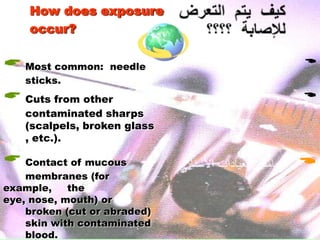
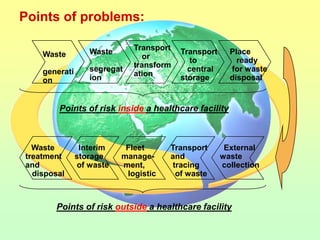
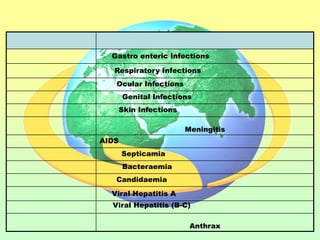
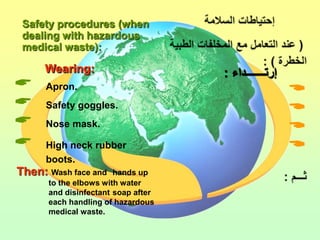
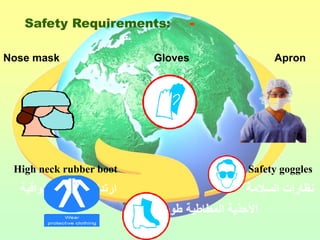
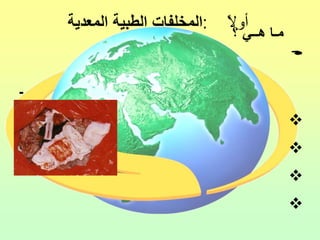
The document discusses the handling and classification of hazardous medical waste within healthcare facilities. It outlines the risks posed by improper medical waste management to doctors, nurses, patients, and the environment. Various types of hazardous medical waste are defined, including infected, sharp, pharmaceutical, chemical and radioactive waste. Guidelines are provided for the safe segregation, storage, treatment and disposal of different categories of medical waste to minimize health and environmental risks.