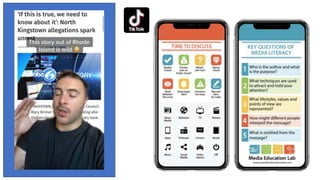
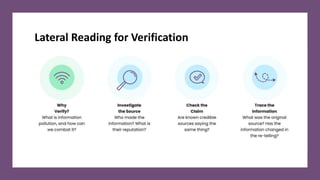
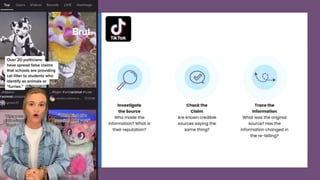
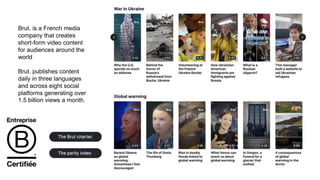
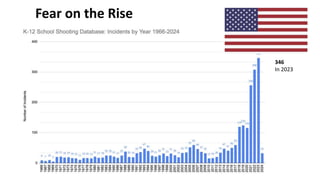
The document discusses the role of media literacy in fostering creativity and critical thinking in an AI-driven world, addressing various media-related challenges such as digital addiction, propaganda, and the influence of digital platforms. It outlines strategies to enhance media literacy and civic resilience, emphasizing the need for quality journalism and innovative news formats. The document also highlights pedagogical approaches for teaching media literacy in schools and the importance of dialogue, discussion, and creative expression in understanding mediated messages.