This document discusses the use of blogs in education. It begins by noting some lessons from history on technology in education, such as that technology does not fix problems and shows limited benefits. It then provides rationales for using technology, such as motivation and preparing students for the future. Key factors for effective technology use are alignment with curriculum, opportunities for collaboration, and support from teachers and schools. The document discusses what blogs are, how they differ from websites, how they are created, and examples of educational blogs. Reasons to create a blog include communication and showcasing student work. Potential drawbacks like assessment and student discomfort are also covered. Planning tips are provided like determining curriculum fit and increasing collaboration. Students will create their own blog









![Examples of Blogs
Blogs can be created for many different
educational purposes. Some of these include:
• communication between home and school (Example: The Blog Dogs)
• encouraging students to comment and think about assignments (Example:
Mr. Remien’s Digital World)
• a location for additional resources on particular topics (Example: The
Connected Classroom)
• a teacher portfolio of work, projects, resume, and/or examples of student
work (Examples: Jody J. Wright and Keri Drish [former MEDA5400 student])
• an archive of great ideas, reviews of books, or websites that would be
helpful for projects (Example: Nerdy Book Club)
• serving as a teacher webpage for a classroom (Example: Runde’s Room)
• sharing ideas and professional development for educators (Example:
Teaching Blog Addict)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meda5400blogging-120128122907-phpapp01/85/Meda5400-Teaching-with-Technology-Blogging-10-320.jpg)



![Drawbacks to Blogs
It is felt by some educators that the biggest difficulty with
using blogging technology is figuring out where blogging fits
into classroom curriculum objectives.
Blogging may require some long-range thoughts about the
integration of this type of technology in the classroom.
The informal nature can sometimes hinder teachers who
want to have a formal system for assessment. However blog
responses by students can be evaluated.
Please see the rubrics available at Rubistar
[http://rubistar.4teachers.org/index.php?ts=1284310576]
Students may also not feel immediately comfortable in the
blogging environment and need help with how they can
express themselves.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meda5400blogging-120128122907-phpapp01/85/Meda5400-Teaching-with-Technology-Blogging-14-320.jpg)

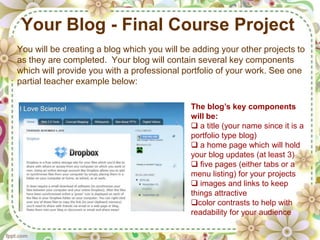
![Task - Creating a Blog
Task Rationale: This task provides for creating a professional portfolio online to
which this class’s technology projects, research paper, and personal blog postings
will be added.
Task Guidelines:
1. Review this PPT and create your personal blog on Blogger using your
ETSU email address. [http://www.blogger.com] You can create more than
one blog using the same address.
2. Read the article: HOT Blogging: Framework for Blogging to Promote Higher
Order Thinking, L. Zawilinski (attached in D2L)
3. Review the rubric for this project to see what components are contained in
this task. (This task will not be scored until the END of our course, after
you have added all the components which we will be creating together.)
4. Read and follow the directions for completing your blog (attached in D2L).
5. Begin creating your blog (does NOT need to be completed) by the due
date on your calendar for this week. PLAY with your blog and experiment.
6. Questions? Ask them in the discussion section of D2L.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meda5400blogging-120128122907-phpapp01/85/Meda5400-Teaching-with-Technology-Blogging-17-320.jpg)