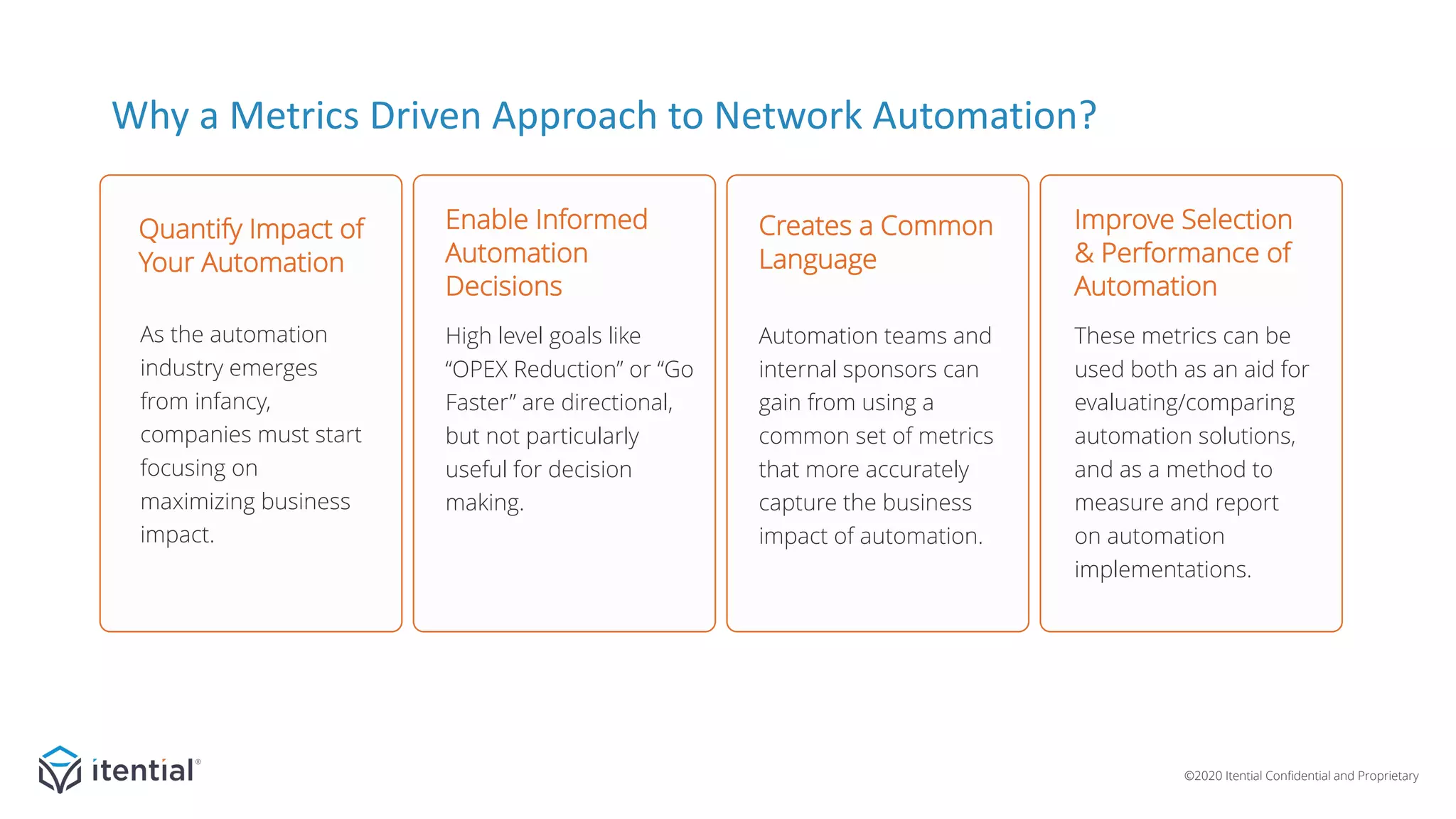
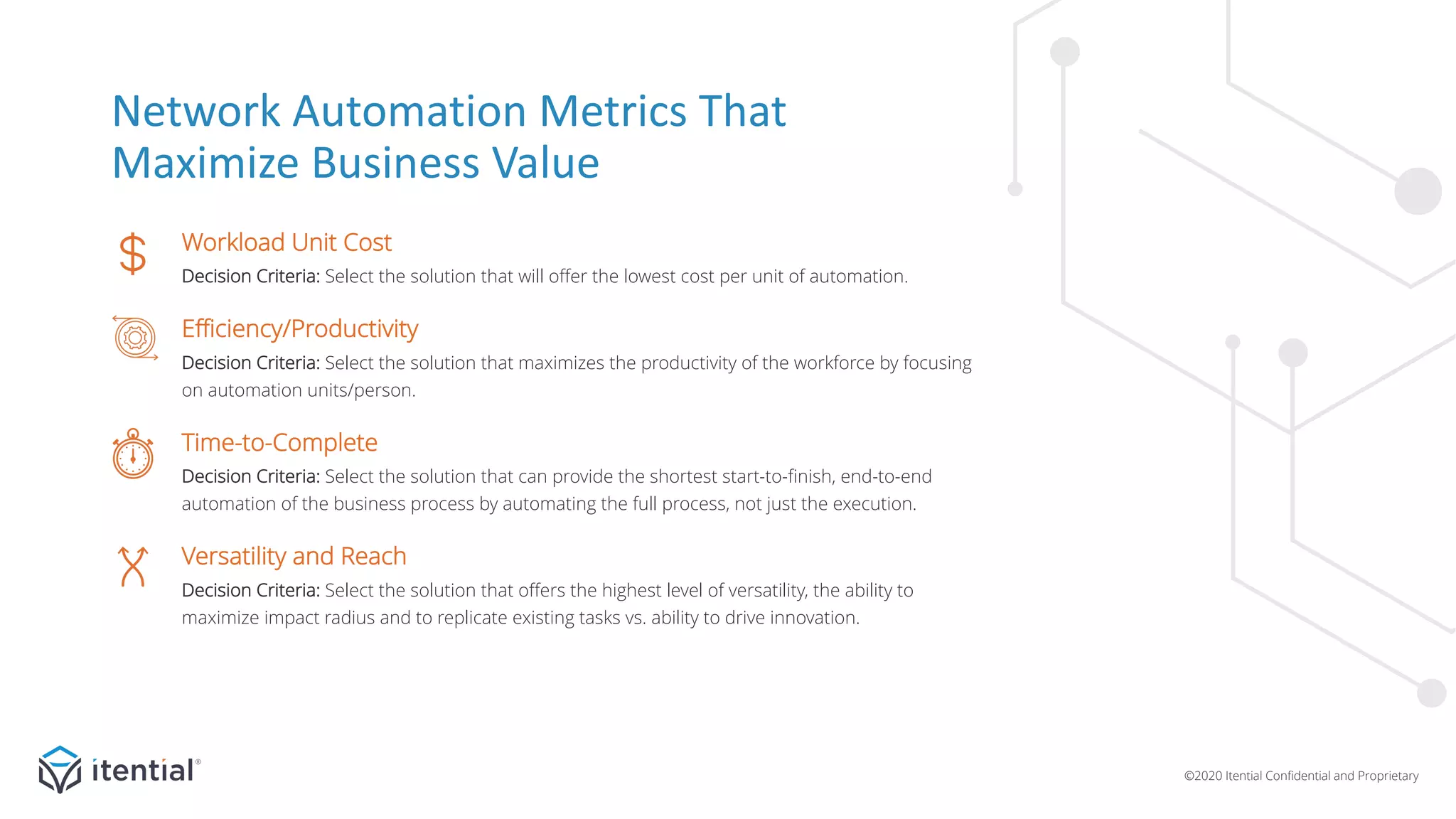
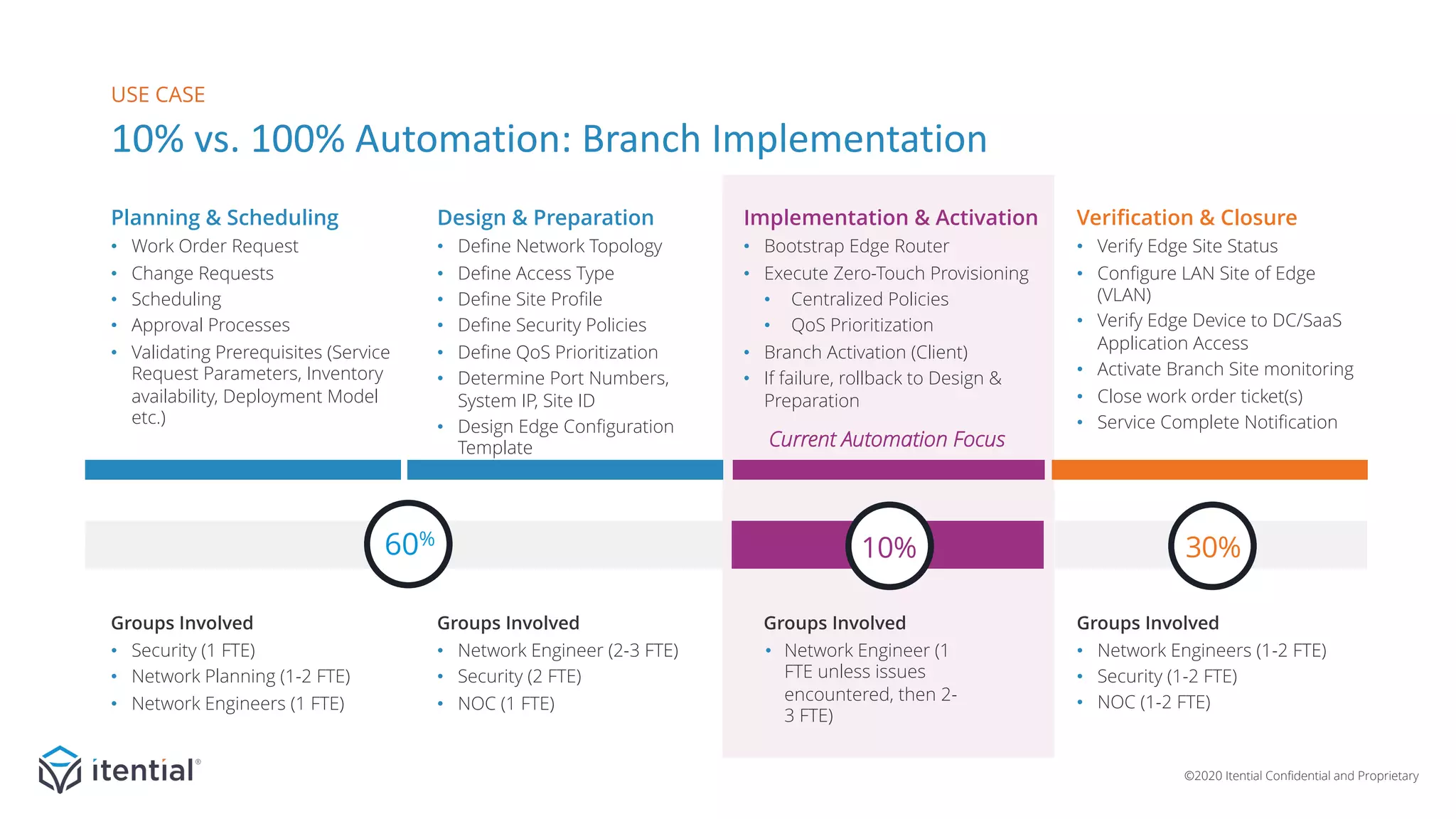
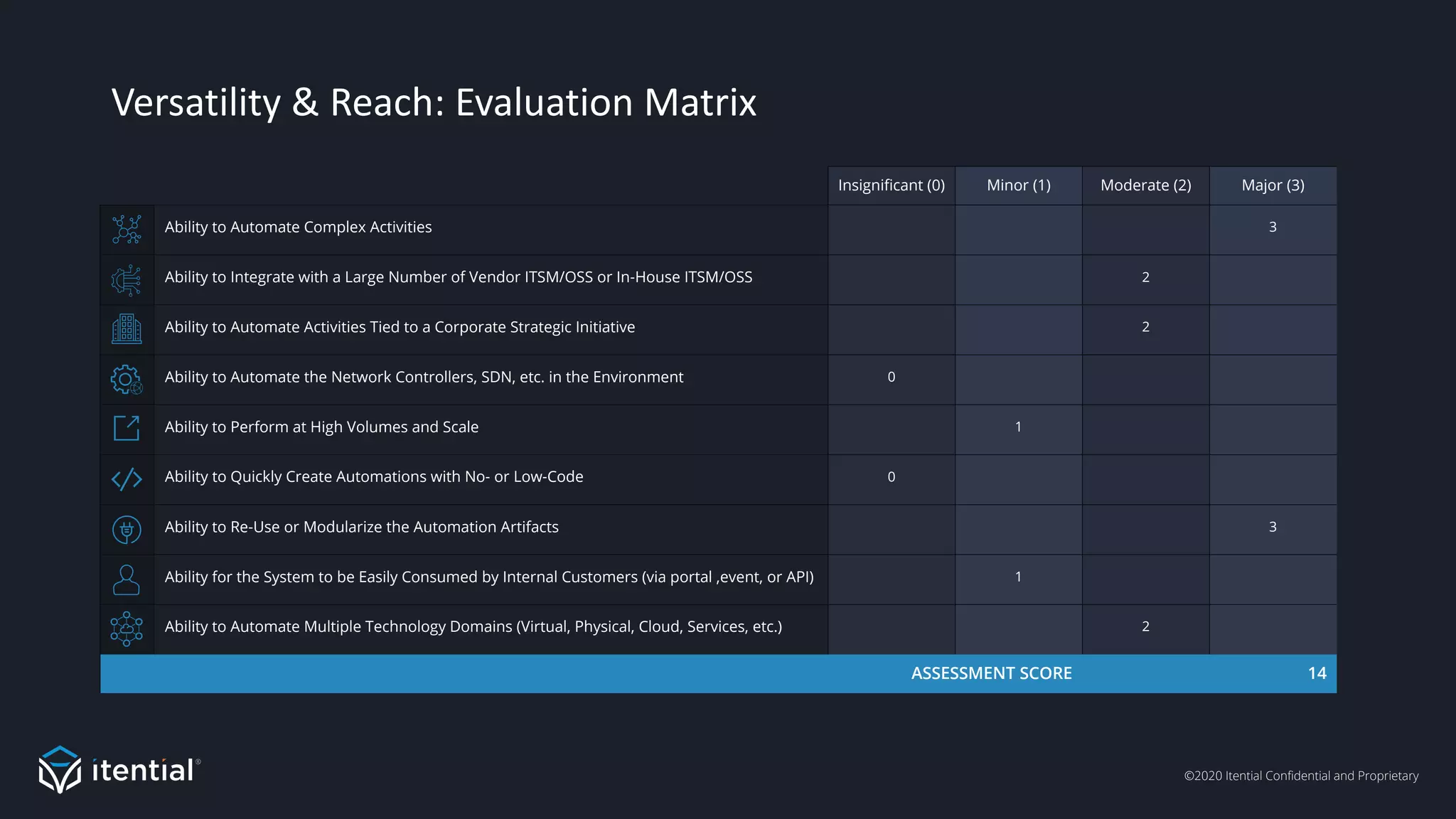
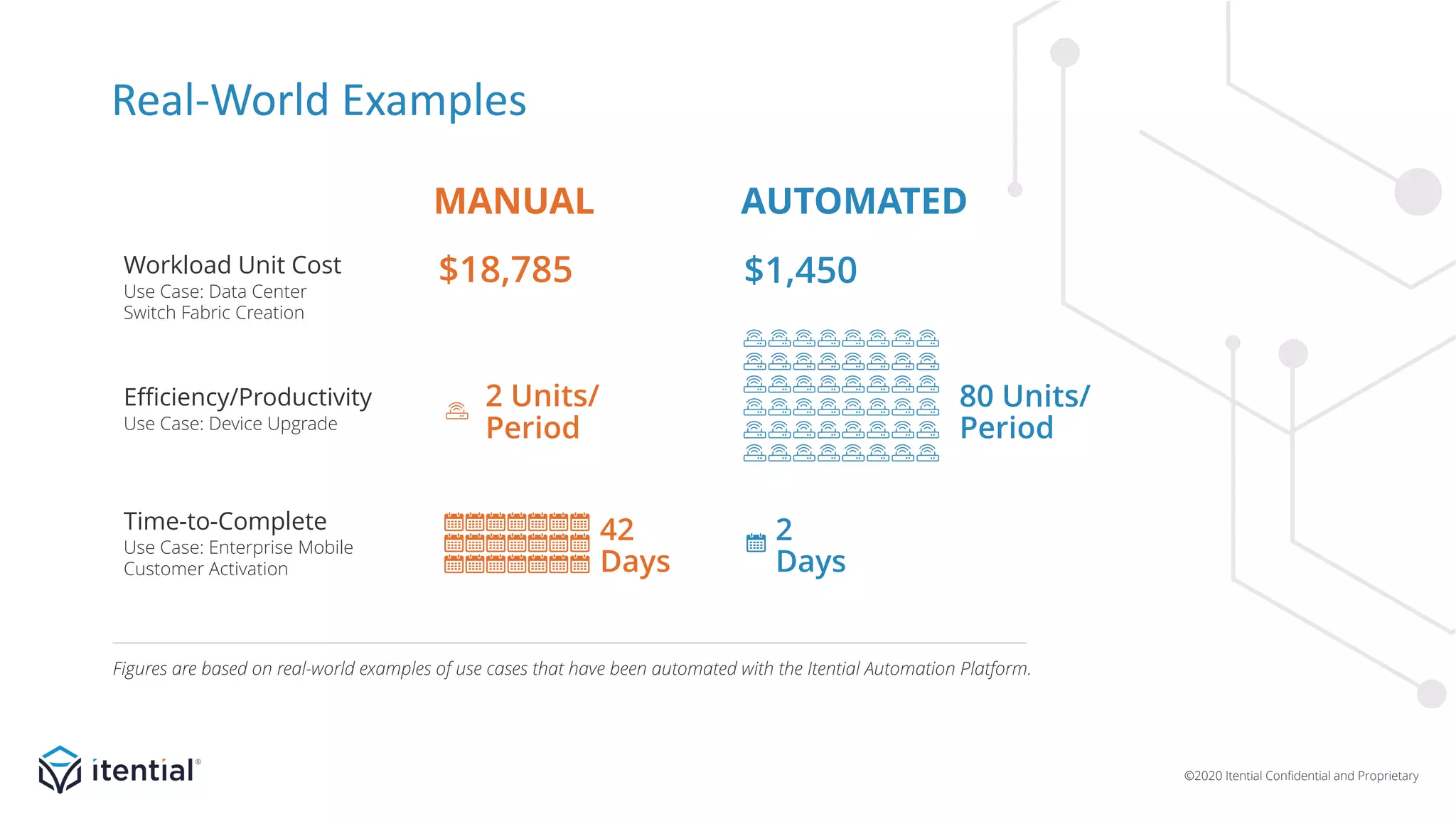
The document discusses the importance of a metrics-driven approach to network automation for maximizing business impact and transforming operations. It highlights four key metrics—workload unit cost, time-to-complete, productivity/efficiency, and versatility/reach—that help organizations evaluate and improve their automation strategies. By leveraging these metrics, businesses can make informed decisions, measure performance, and ultimately achieve cost reductions and enhanced productivity through automation.