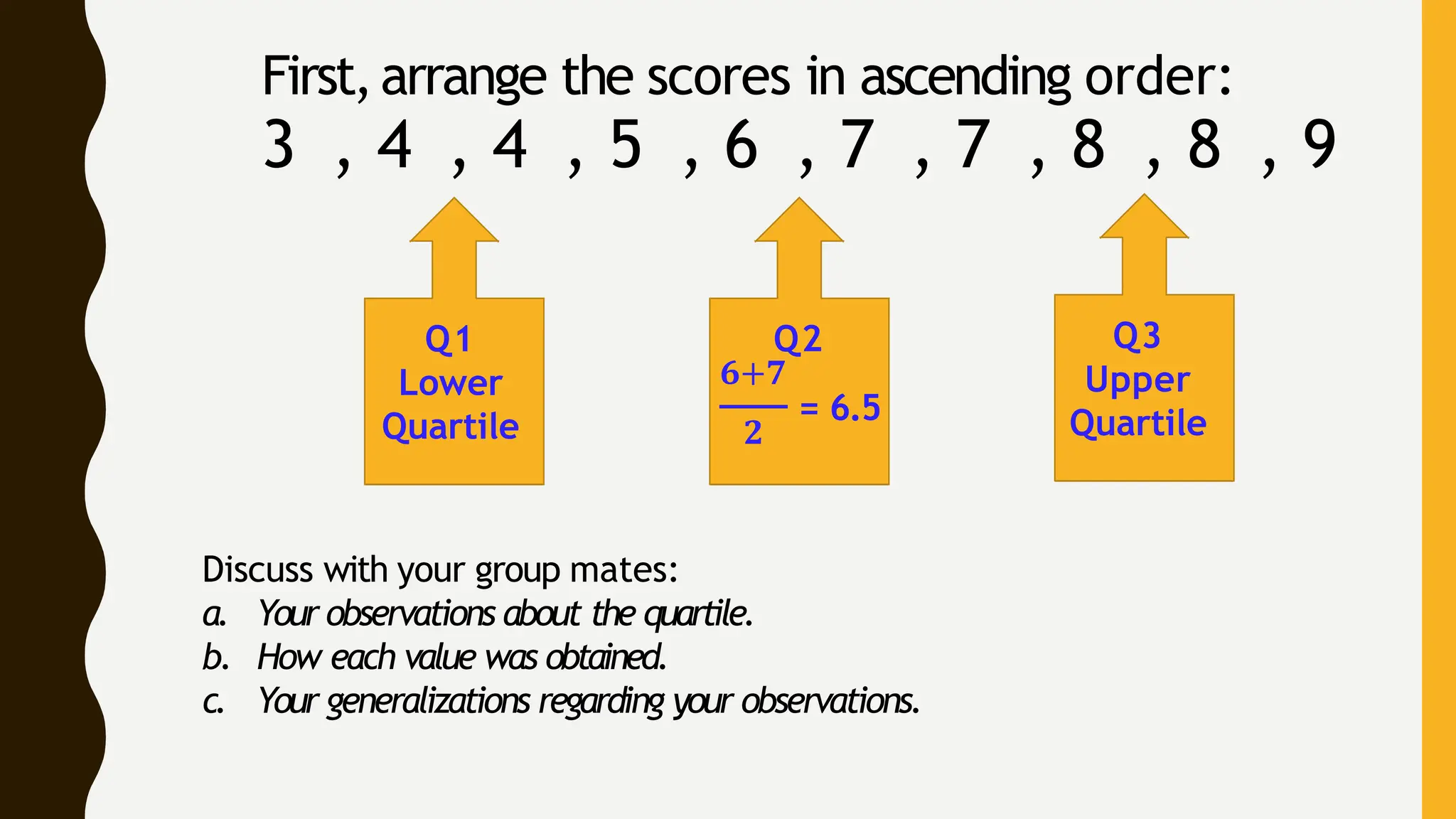
This document defines measures of position such as quartiles, deciles, and percentiles. It explains that these are techniques used to divide ordered data into equal groups in order to describe the position of data values relative to the rest of the data set. Quartiles specifically divide a data set into four equal parts, with the first quartile (Q1) separating the lowest 25% of values, the second quartile (Q2) or median separating the middle 50% of values, and the third quartile (Q3) separating the highest 25% of values. The document provides examples of calculating quartiles for ungrouped data sets.