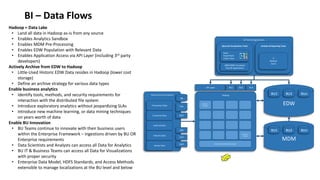
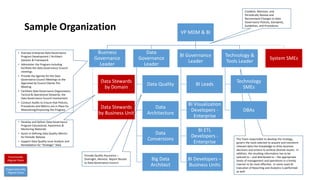
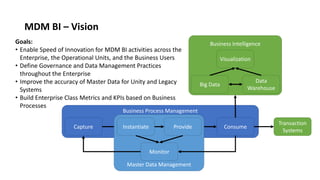
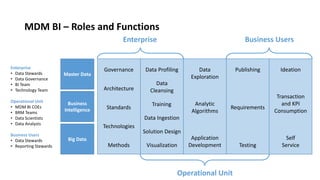
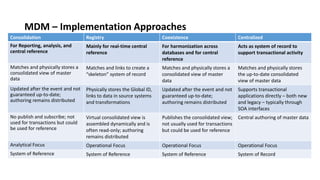
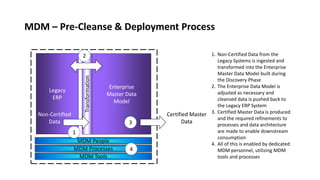
The document outlines a comprehensive strategy for Master Data Management (MDM) and Business Intelligence (BI), emphasizing the importance of governance, data management practices, and the roles of various stakeholders. It presents a structured approach to improving data accuracy, facilitating innovation, and establishing clear accountability within data governance processes. Additionally, it details a 180-day plan for implementing effective data governance, technology integration, and the alignment of business processes to enhance data utility across the enterprise.





![BI – Ownership Structure
Sandbox (50%)
[user created content]
Shared (30%)
[user created and shared
content]
Production
(20%)
Gather
Data
Visualize
PublishConsume
Ideate
Business
Users
Require-
ments
Profile
Data
DesignDevelop
Test
IT
Sandbox Environment
• Business users author and use BI content with no
constraints or limitations. This is where data
exploration, discovery, and what-if analyses
happen.
• Tools and technologies: Microsoft Office
• IT involvement is strictly limited to infrastructure
and tools support plus monitoring to identify
usage patterns, commonalities, and opportunities
(using BI on BI) for potential production
hardening.
• Content produced here is used in individual tasks
and low-risk applications.
Shared Environment
• Business users share and collaborate on BI content
with their colleagues.
• Tools and technologies: SharePoint BI, Office 365
• IT steps up monitoring and now watches for red
flags (too much data, too many users, too critical
or risky applications) and opportunities (using BI
on BI) for production hardened BI Content.
• Content produced here is shared within
departments and workgroups. Low-risk, low-
criticality decisions can be made based on this
content.
Production Environment
• Business uses and authors BI content within the
limitations and constraints of the enterprise data
model, standards, policies, rules, guidelines, etc.
• Tools and technologies: EDW, Visual Studio,
SharePoint BI, Office 365
• Owned, run, and managed by IT.
IT Benefits
• Backlog Reduction – only heavily-used,
complex, or critical applications come to IT for
production-hardening.
• Requirements already defined; Project Lifecycle
is greatly reduced; Enhancements during
testing cycle minimized.
• Shadow IT is embraced as a competitive
advantage; however, using the strategic
technology stack defined by IT.
Business Benefits
• Business users are empowered to
create BI content on their own
schedule without any constraints
or limitations – at the speed of
business innovation.
• They modify the model and
visualizations through iteration until
the requirements are identified and
met.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdmbistrategyvisionforlargeenterprises-160325000955/85/MDM-BI-Strategy-For-Large-Enterprises-10-320.jpg)