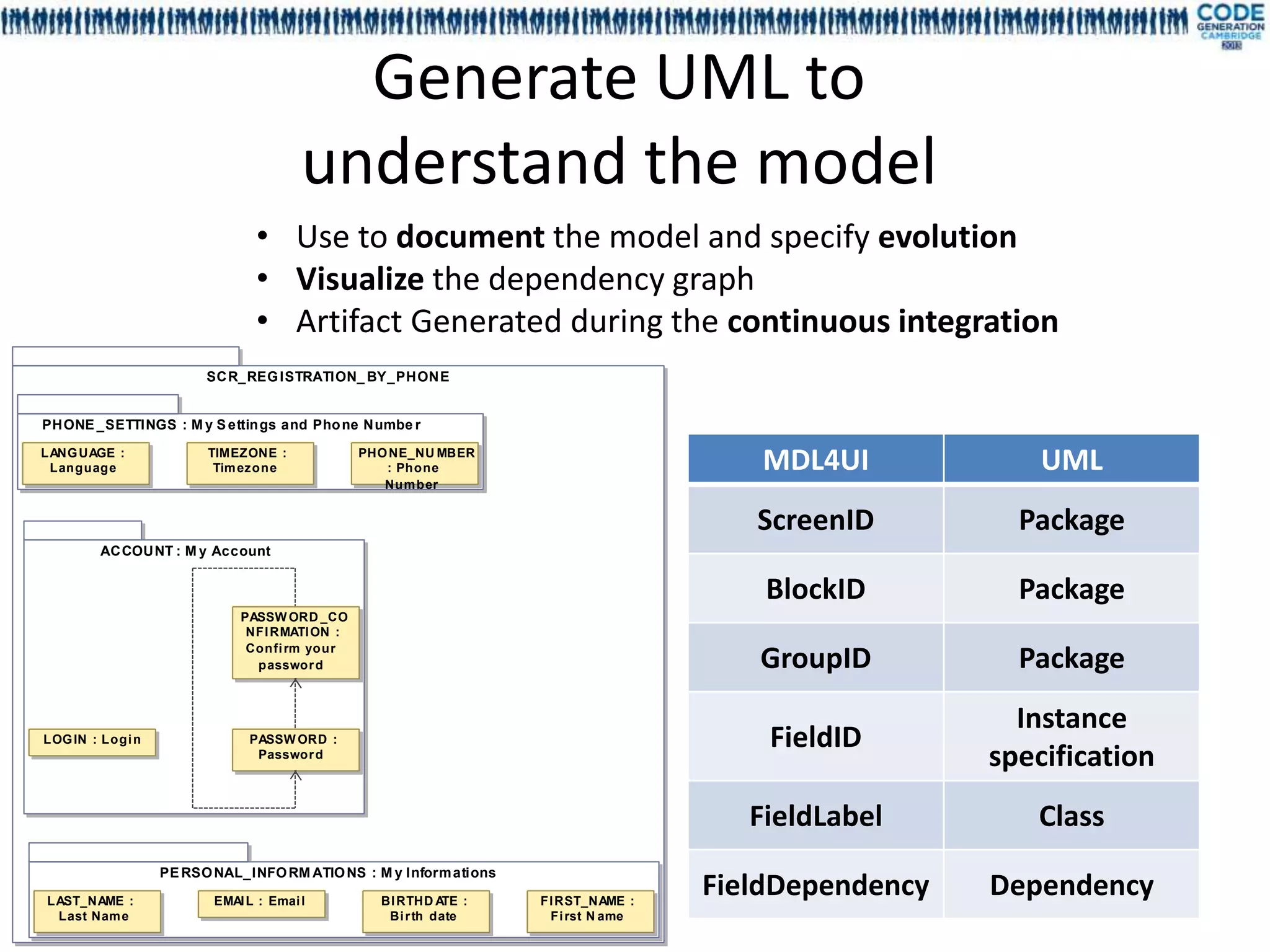
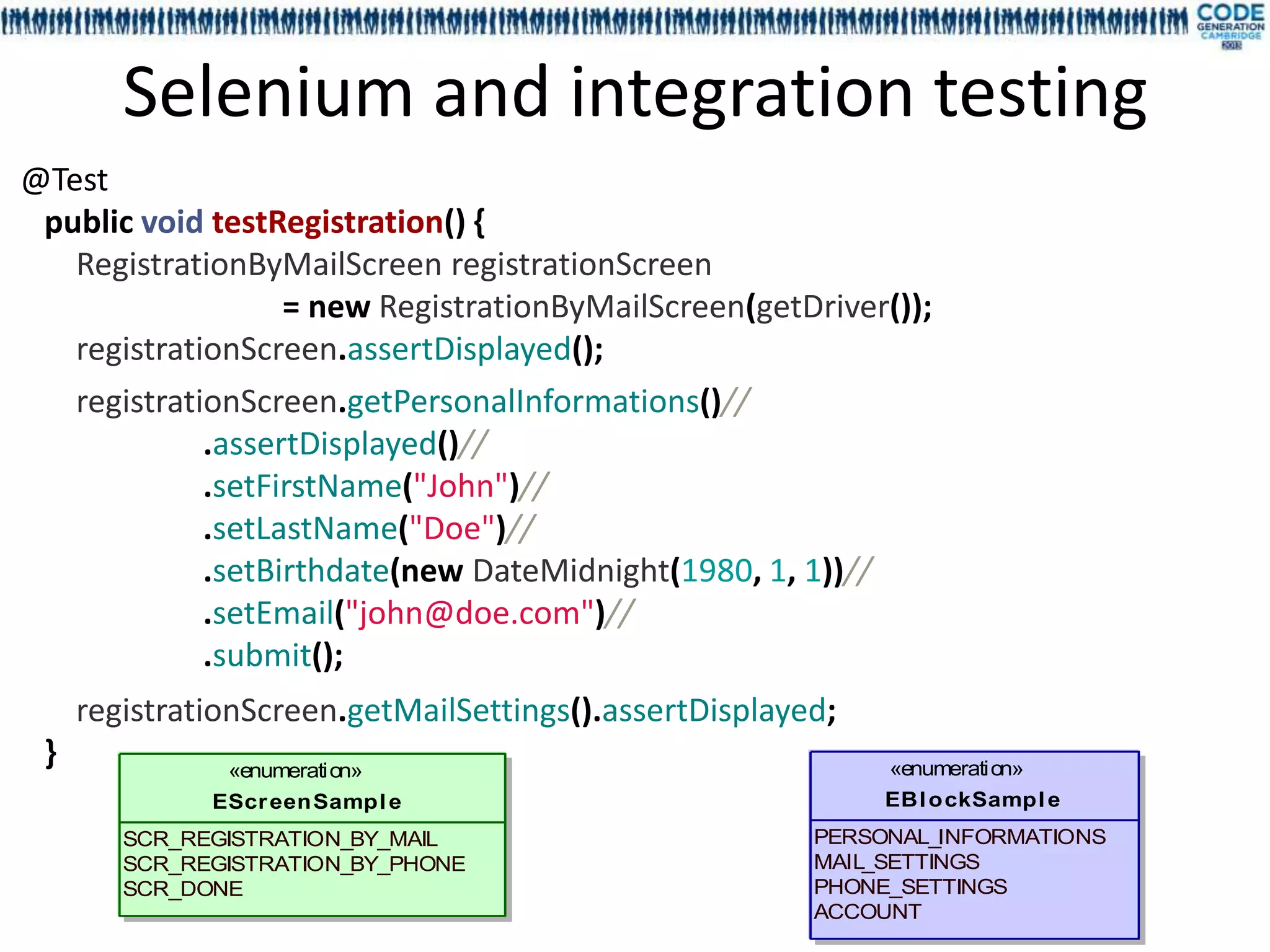
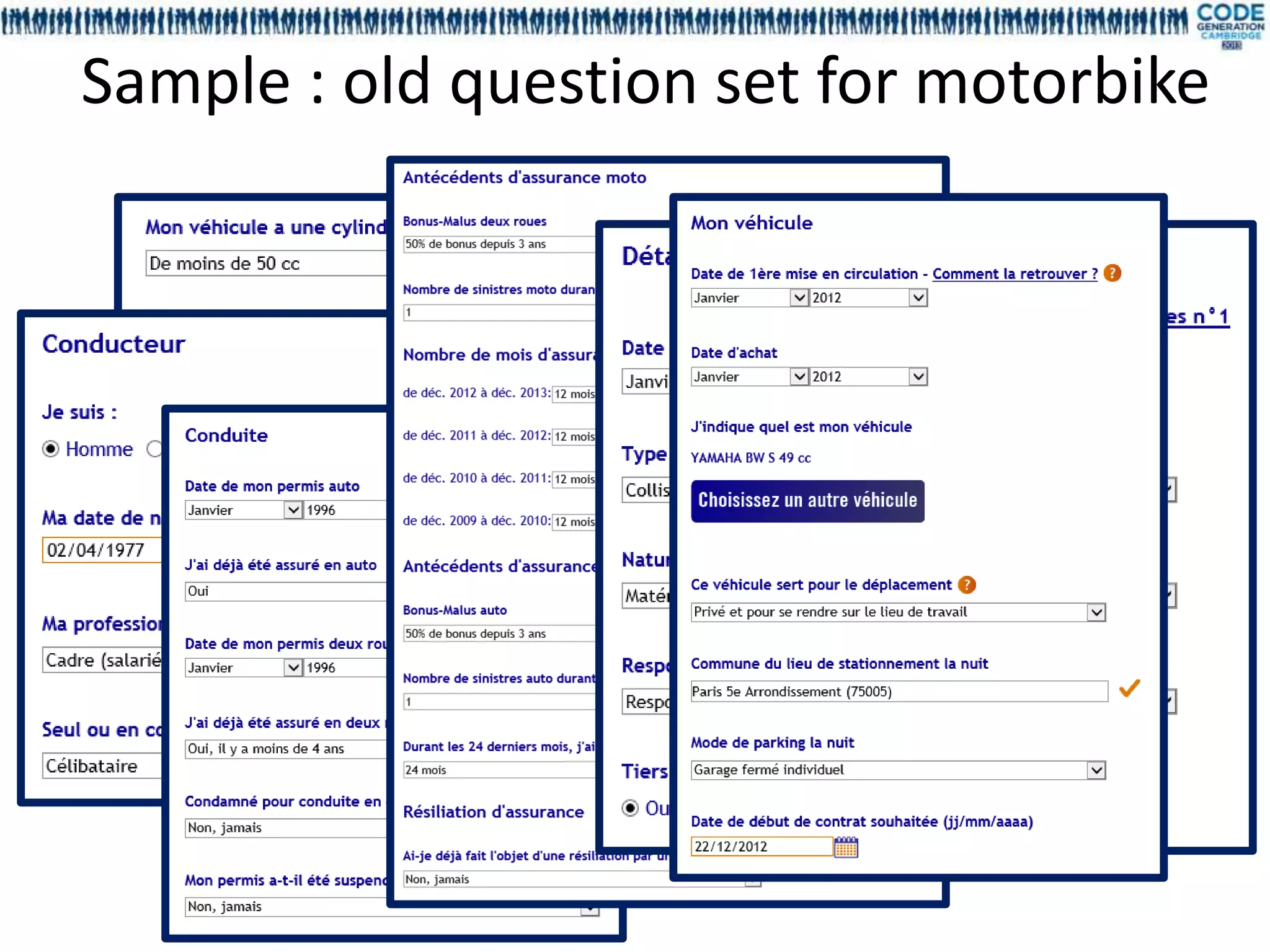
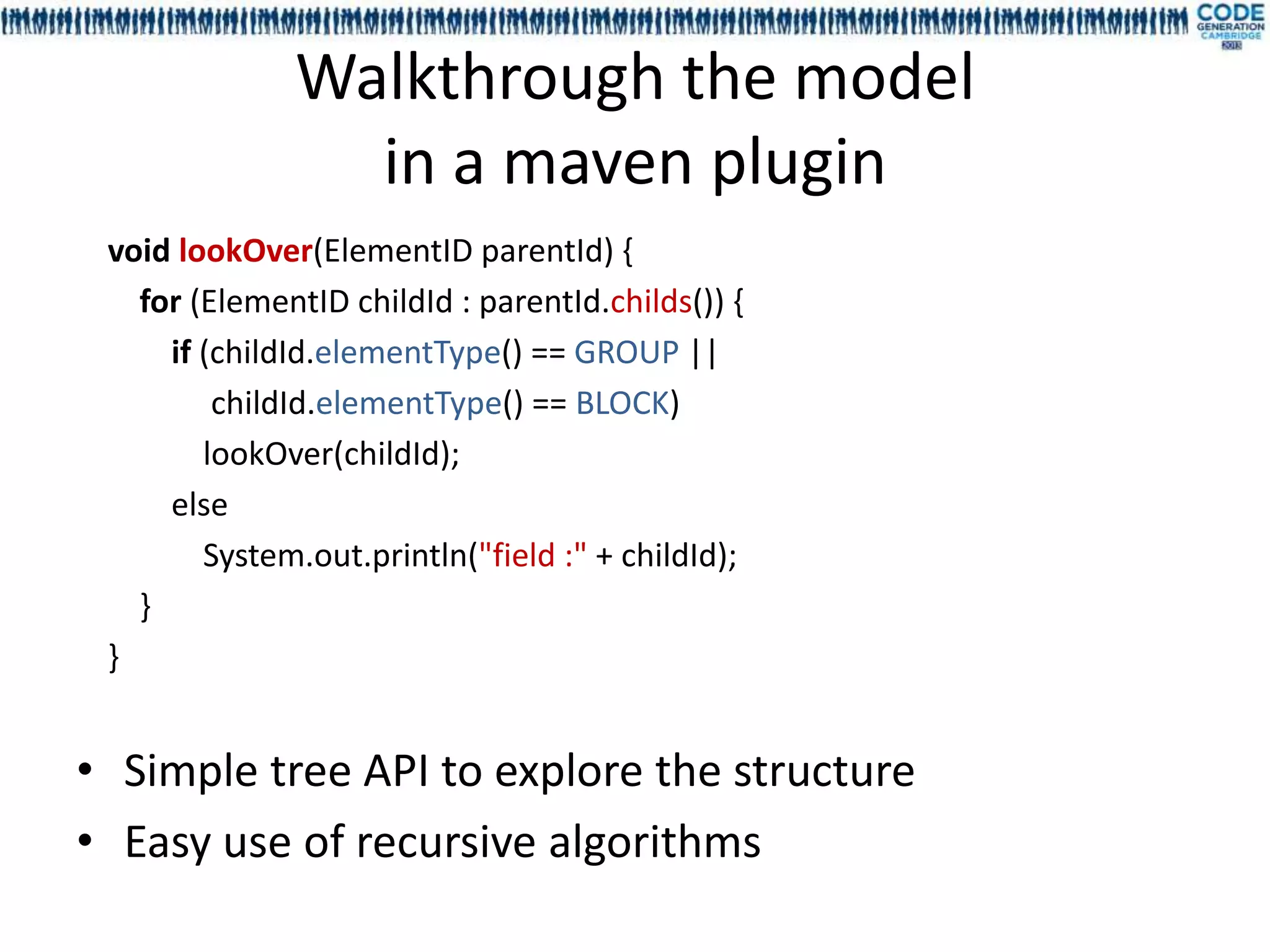
The document discusses a presentation on utilizing annotation processing for effective UI modeling, particularly in the context of insurance aggregator forms with complex business rules. It introduces the mdl4ui framework, which aims to simplify form management, enhance testing, and reduce maintenance efforts through a structured modeling approach. Key features include dependency management, easy integration, and a focus on decoupling UI from underlying logic to improve governance and usability.








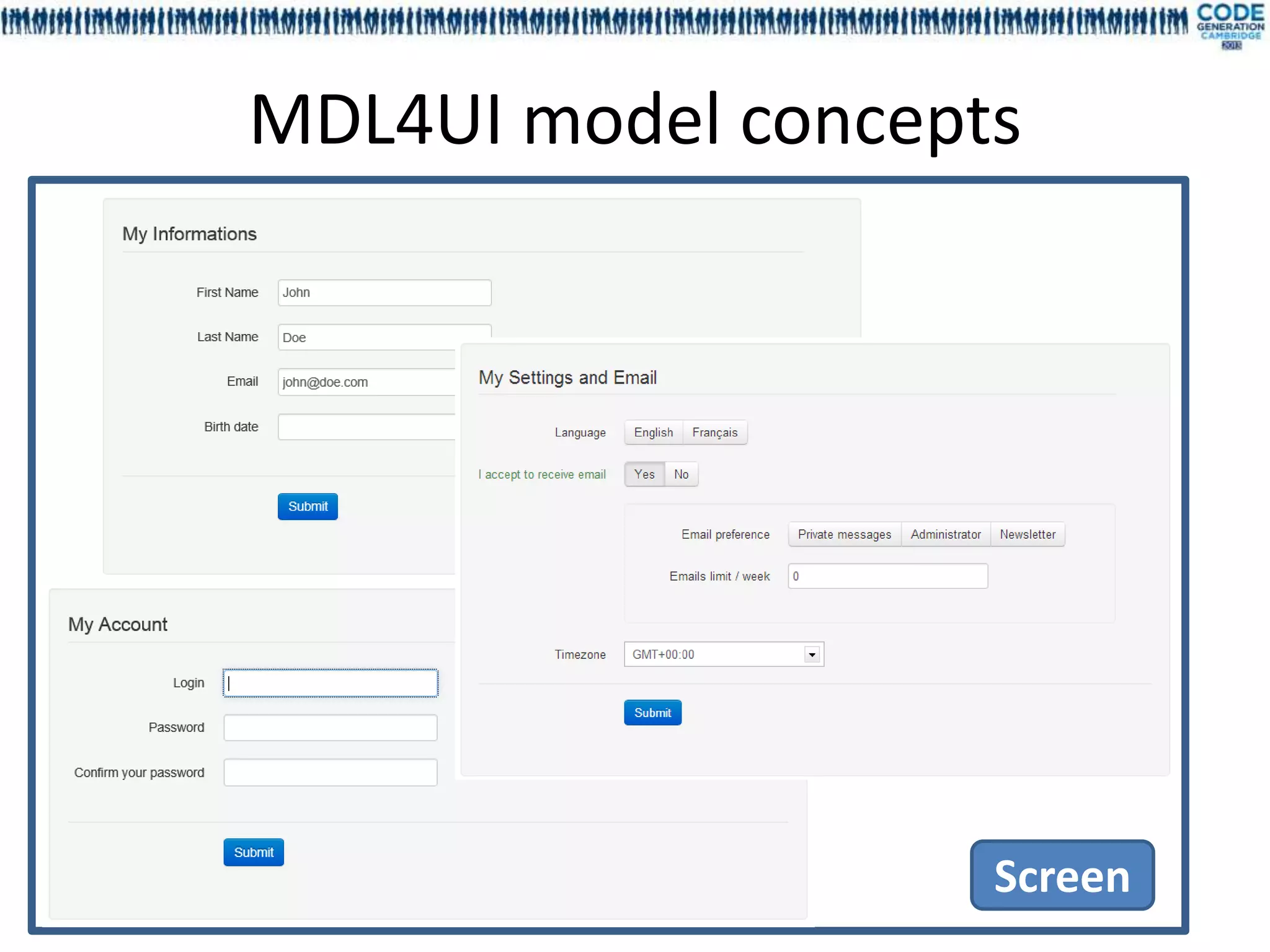
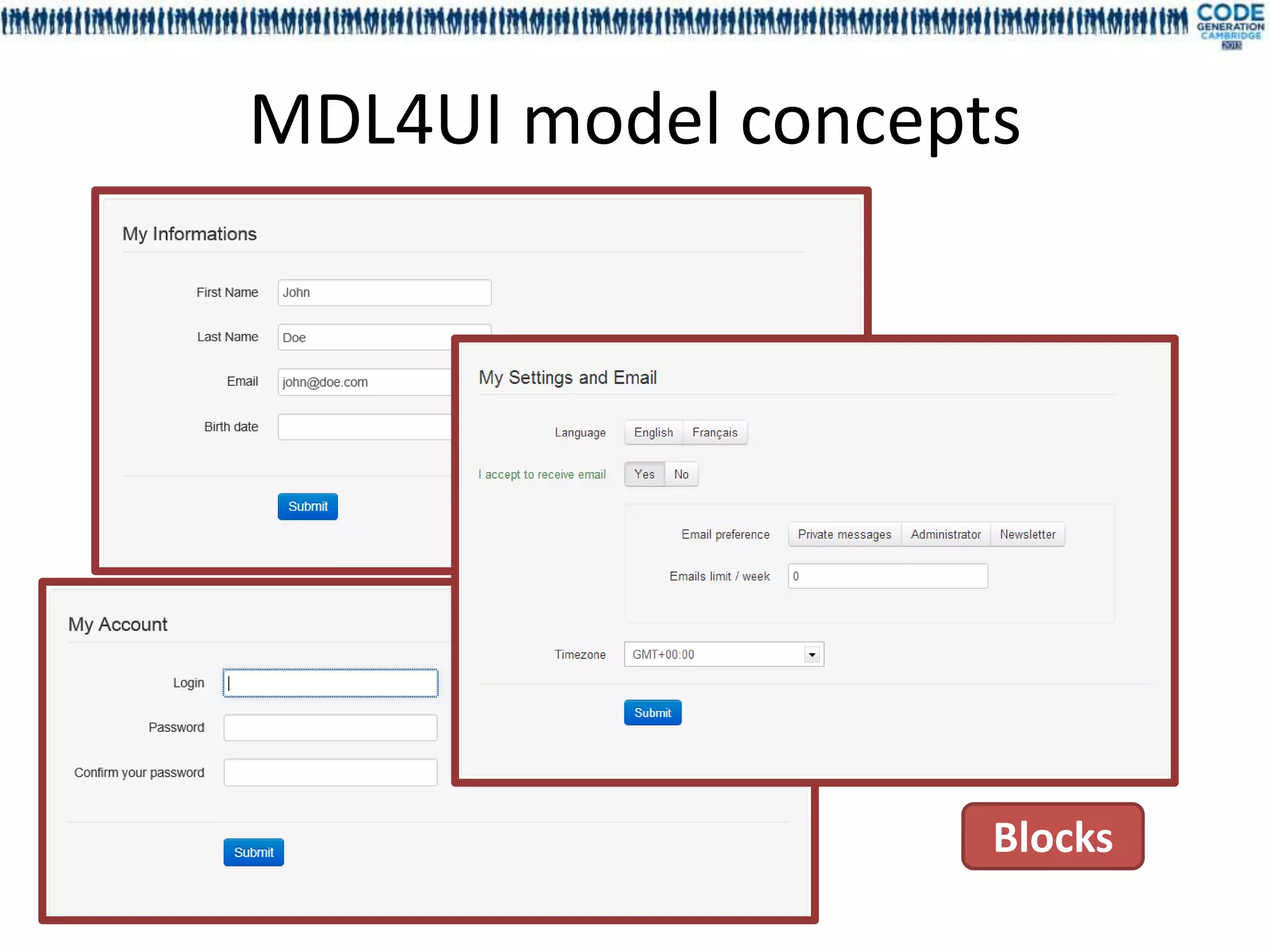
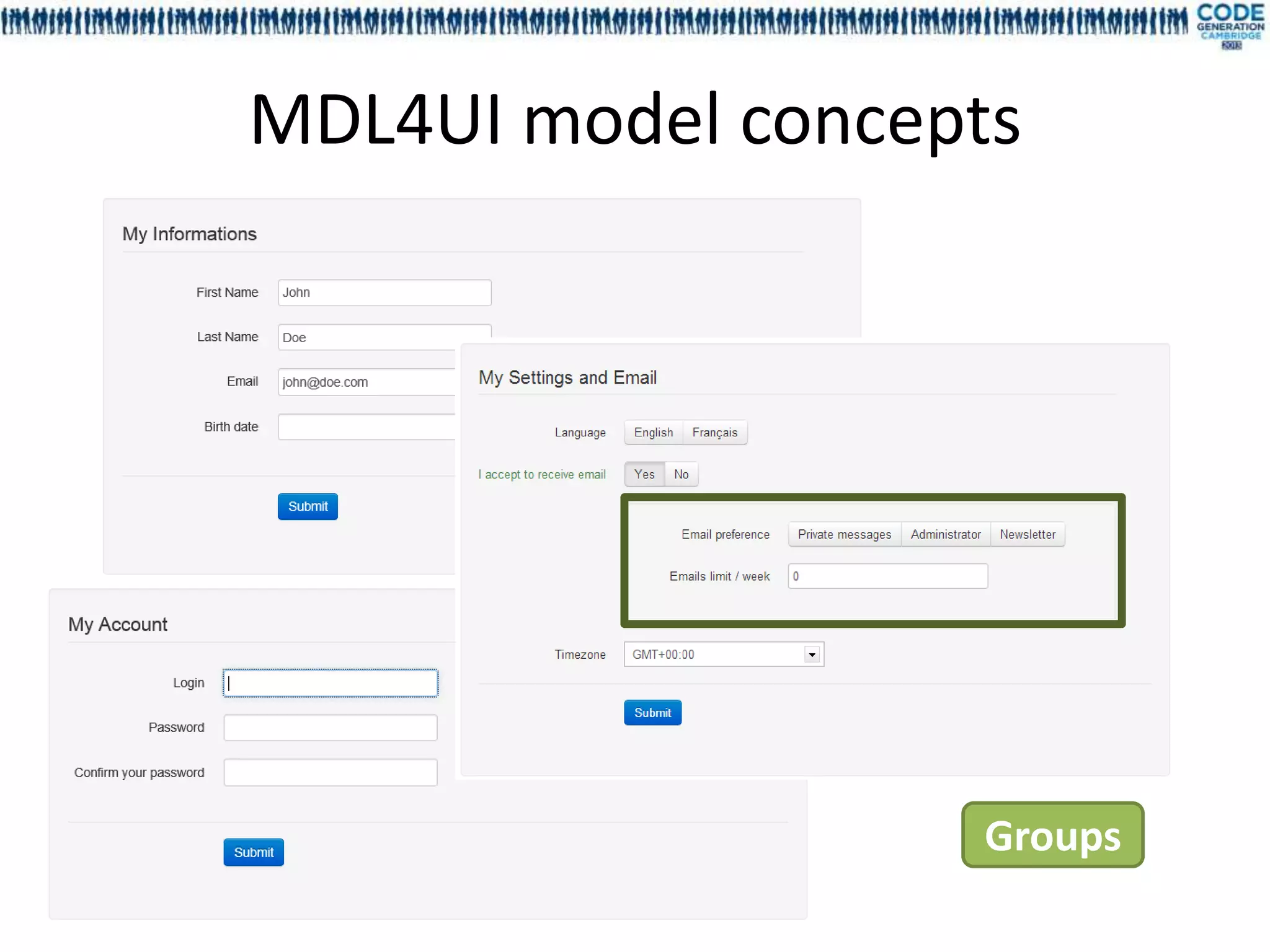
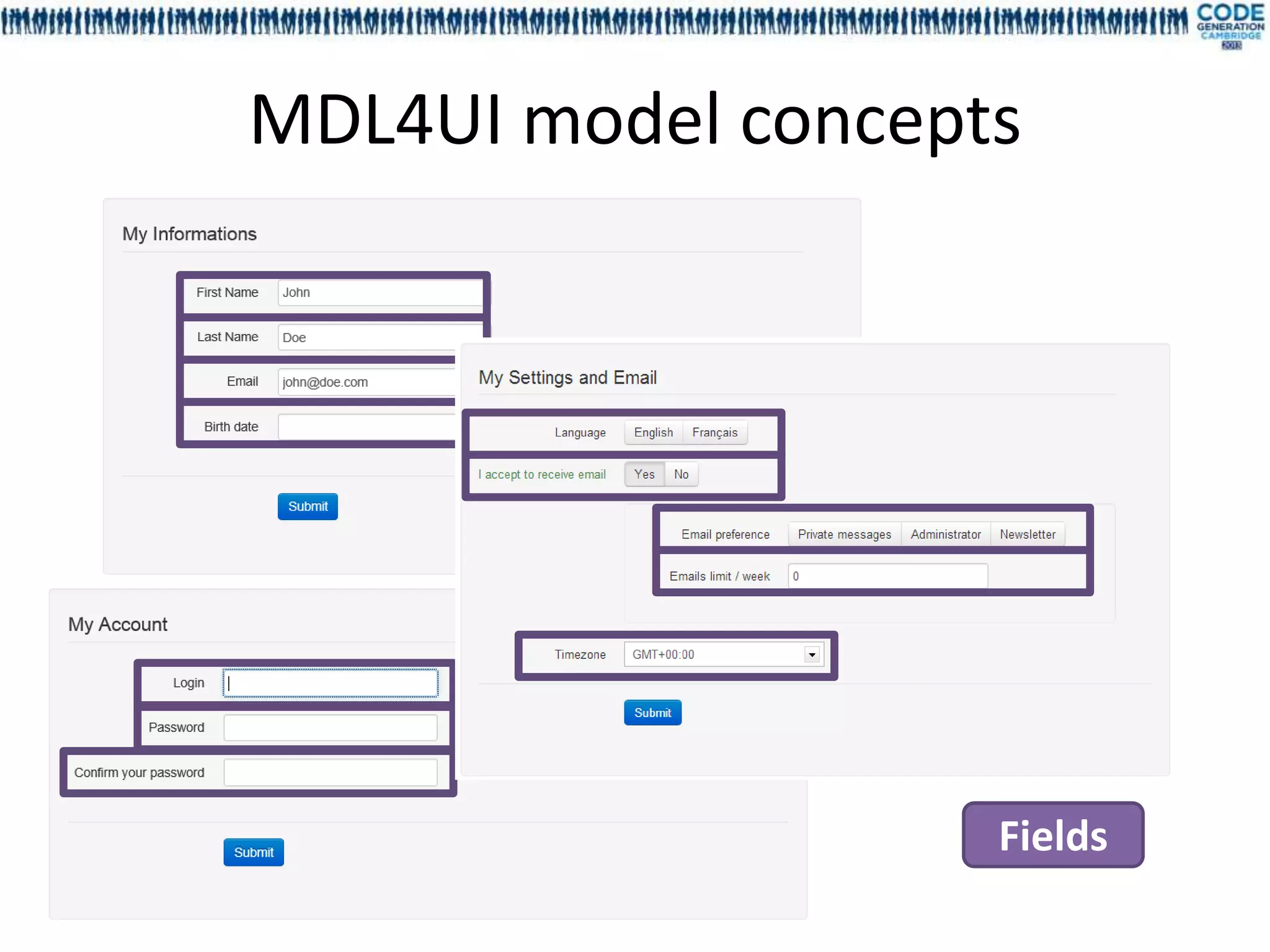
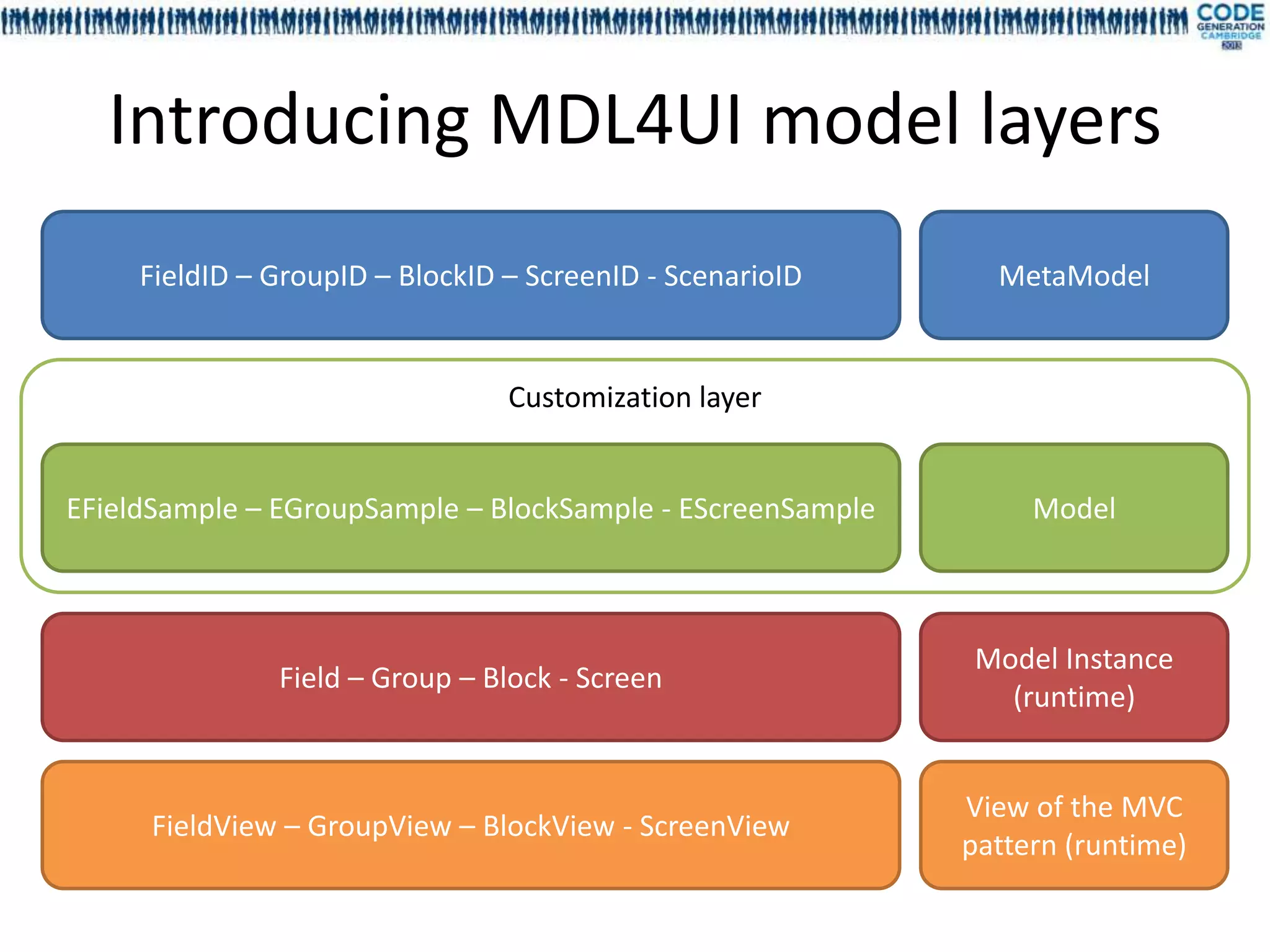
![FieldID – GroupID – BlockID – ScreenID - ScenarioID MetaModel
UI Elem ent
elementTy pe() : ElementTy [1]
pe We define a UI MetaModel, and
childs() : UIElement [0..*] all concept for other layers.
Scr eenID
nextBlock( blockID : BlockID [1] ) : Block [1]
ID
El ementID
Bl ockID
Fi eldI D
type() : FieldTy [1]
pe
Gr oupI D
Scenar ioI D
screens() : ScreenID [0..*]
nextScreen( screenID : ScreenID [1] ) : ScreenID [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdl4uicg2013-130409050811-phpapp02/75/Rock-solid-UI-modeling-using-annotation-processing-CodeGeneration-2013-18-2048.jpg)
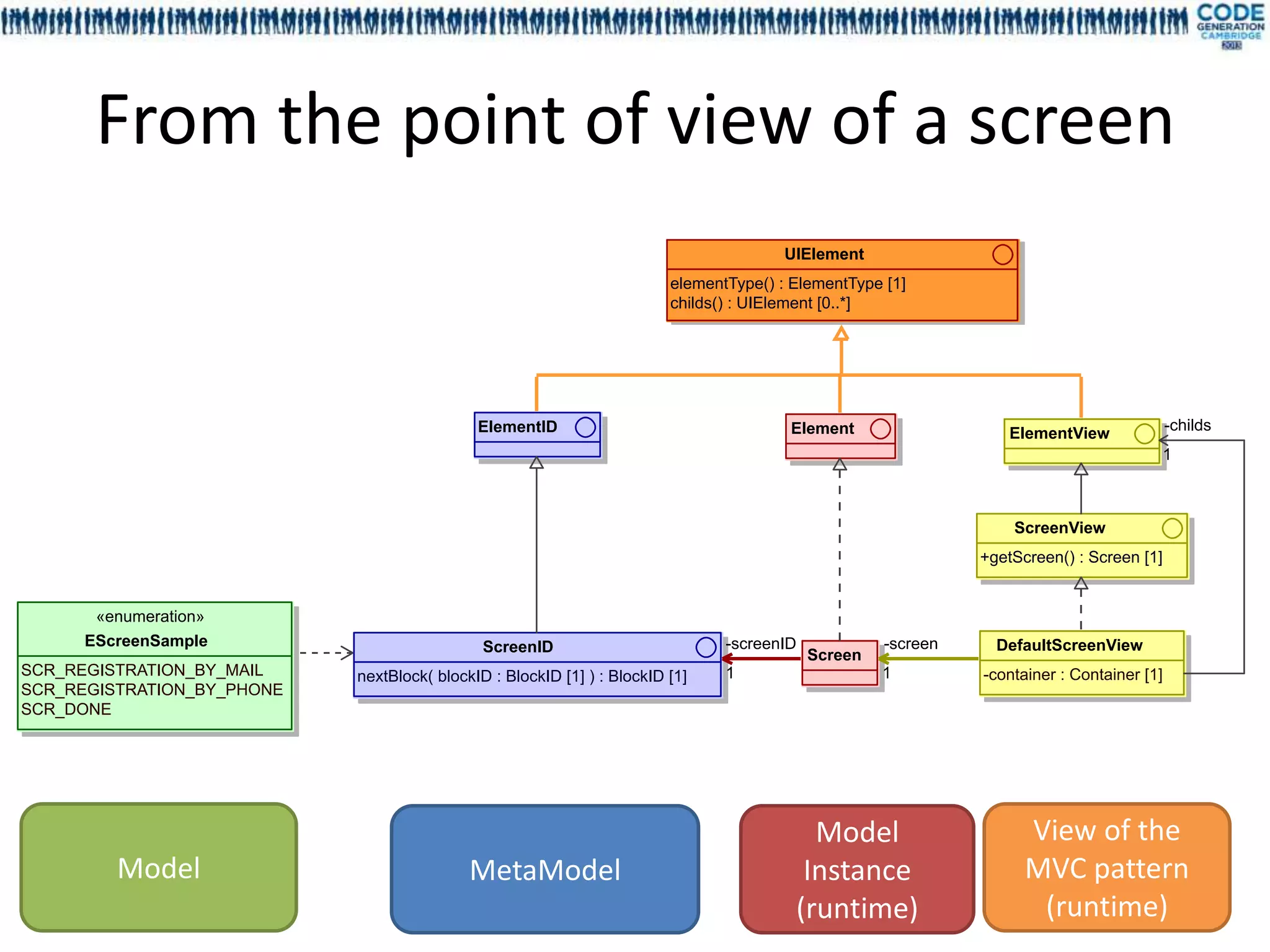
![Customization layer
EFieldSample – EGroupSample – BlockSample - EScreenSample Model
UI Elem ent Scenar ioI D
elementTy pe() : ElementTy [1]
pe screens() : ScreenID [0..*]
childs() : UIElement [0..*] nextScreen( screenID : ScreenID [1] ) : ScreenID [1]
Fi eldI D El ementID
Scr eenID
type() : FieldTy [1]
pe
nextBlock( blockID : BlockID [1] ) : Block [1]
ID
«enumeration» «enumeration»
«enumeration»
EScr eenSampl e EScenar ioS am pl e
EFi eldSam ple Bl ockID
Gr oupI D SCR_REGISTRATION_BY_MAIL
FIRST_NAME SCENARIO_MAIL
SCR_REGISTRATION_BY_PHONE SCENARIO_PHONE
LAST_NAME SCR_DONE
EMAIL
BIRTHDATE
LANGUAGE
TIMEZONE
PHONE_NUMBER «enumeration»
EMAIL_ACCEPTED
«enumeration» EBl ockSampl e We define our UI model (screens,
EMAILS_PREFERENCES
MAX_WEEKLY_EMAILS EGr oupS am pl e PERSONAL_INFORMATIONS fields, etc.), only using
LOGIN
PASSWORD
EMAIL_GROUP MAIL_SETTINGS
PHONE_SETTINGS
enumerations.
PASSWORD_CONFIRMATION ACCOUNT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdl4uicg2013-130409050811-phpapp02/75/Rock-solid-UI-modeling-using-annotation-processing-CodeGeneration-2013-19-2048.jpg)
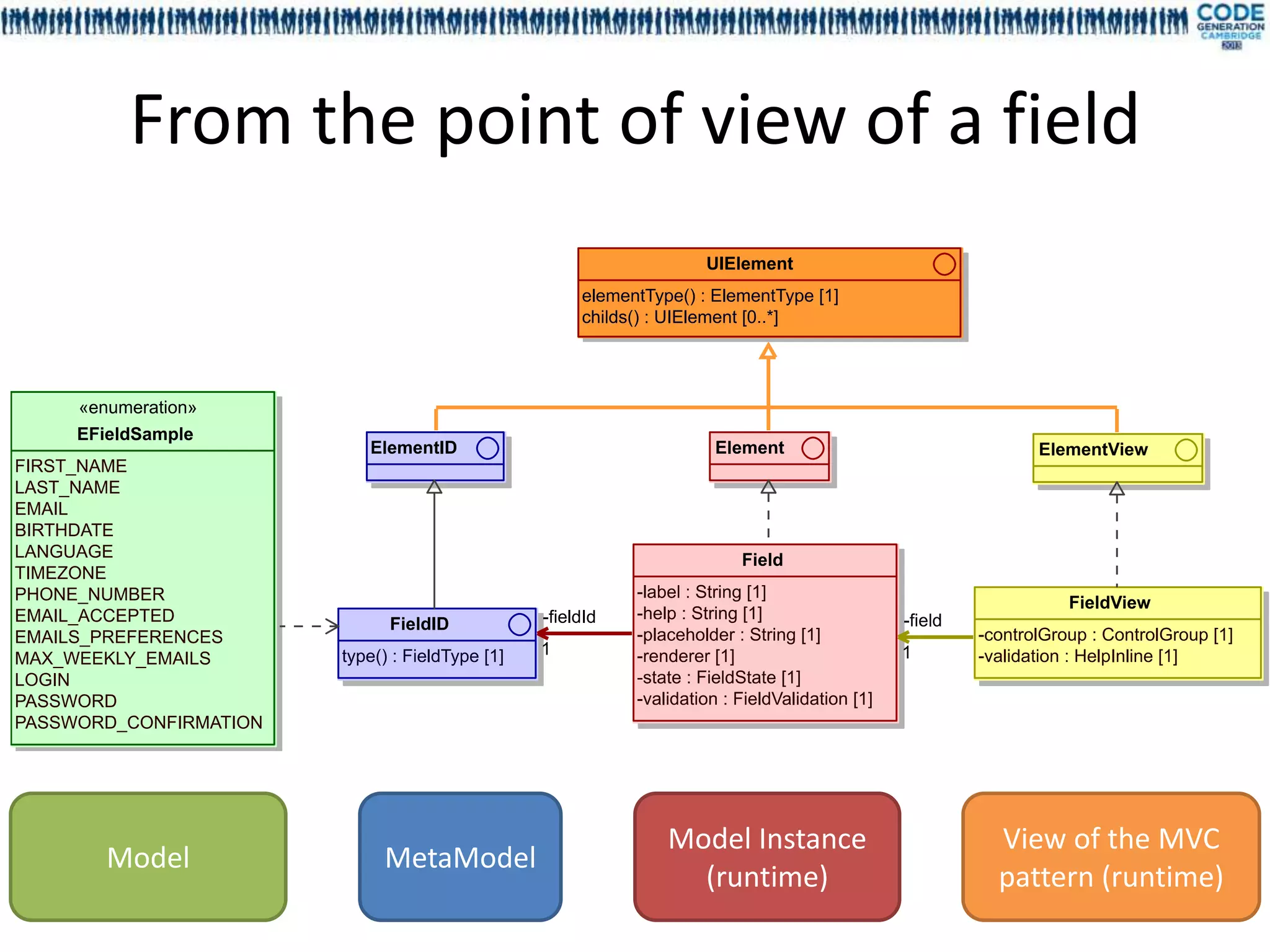
![Model Instance
Field – Group – Block - Screen
(runtime)
UI El em en t
We instantiate our UI model,
elementTy pe() : ElementTy [1]
pe with i18n resources injected.
childs() : UIElement [0..*]
-items El emen t
0..*
Gr o u p
-fields
F i eld
-label : String [1] 0..*
Bl o ck -blocks -help : String [1]
Scr een -placeholder : String [1]
-label : String [1] 0..* -renderer [1]
-state : FieldState [1]
-validation : FieldValidation [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdl4uicg2013-130409050811-phpapp02/75/Rock-solid-UI-modeling-using-annotation-processing-CodeGeneration-2013-20-2048.jpg)
![View of the MVC
FieldView – GroupView – BlockView - ScreenView
pattern (runtime)
UI Elem ent We instantiate all HTML widgets
elementType() : ElementType [1] from a UI model instance, using
childs() : UIElement [0..*] GWT and twitter bootstrap
frameworks.
-childs
-childs
El ementView 1
-childs
0..*
0..*
Bl ockView
Fi eldVi ew Scr eenView Gr oupVi ew -form : WellForm [1]
-controlGroup : ControlGroup [1] -modify : Button [1]
+getScreen() : Screen [1] -row : Row [1] -submit : Button [1]
-validation : HelpInline [1]
-fieldset : Fieldset [1]
-actions : FormActions [1]
DefaultScr eenV iew
-container : Container [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdl4uicg2013-130409050811-phpapp02/75/Rock-solid-UI-modeling-using-annotation-processing-CodeGeneration-2013-21-2048.jpg)
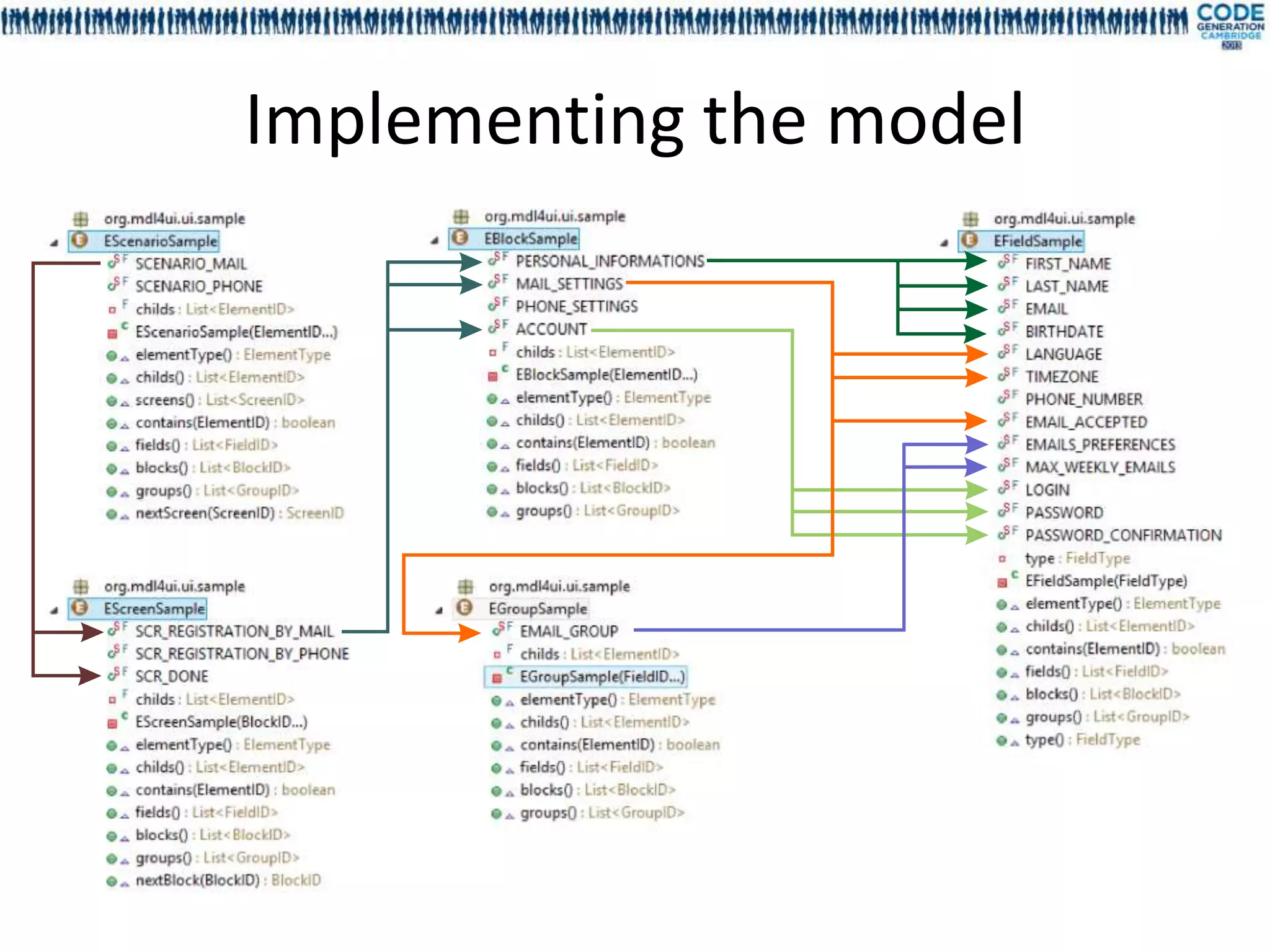
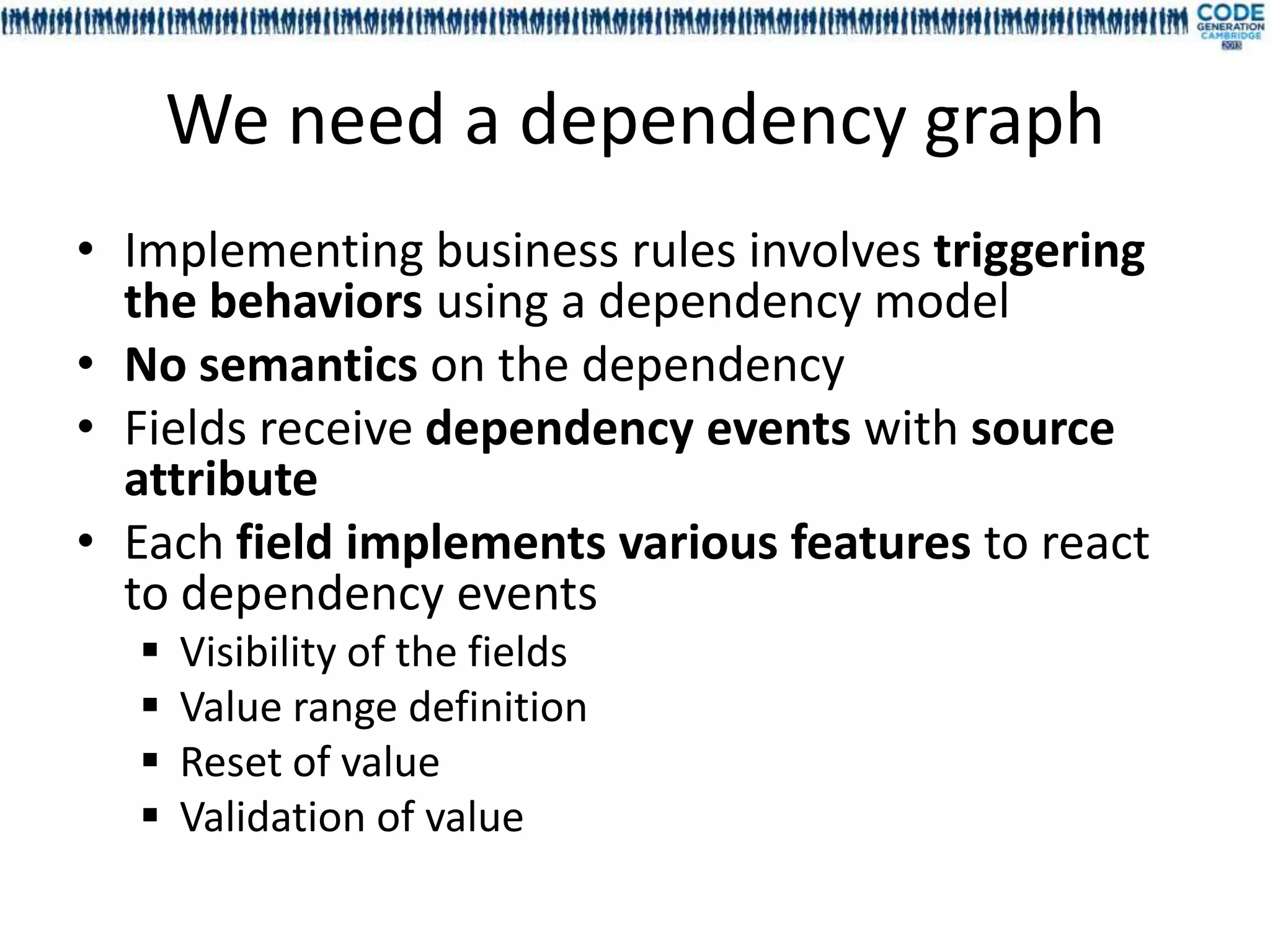
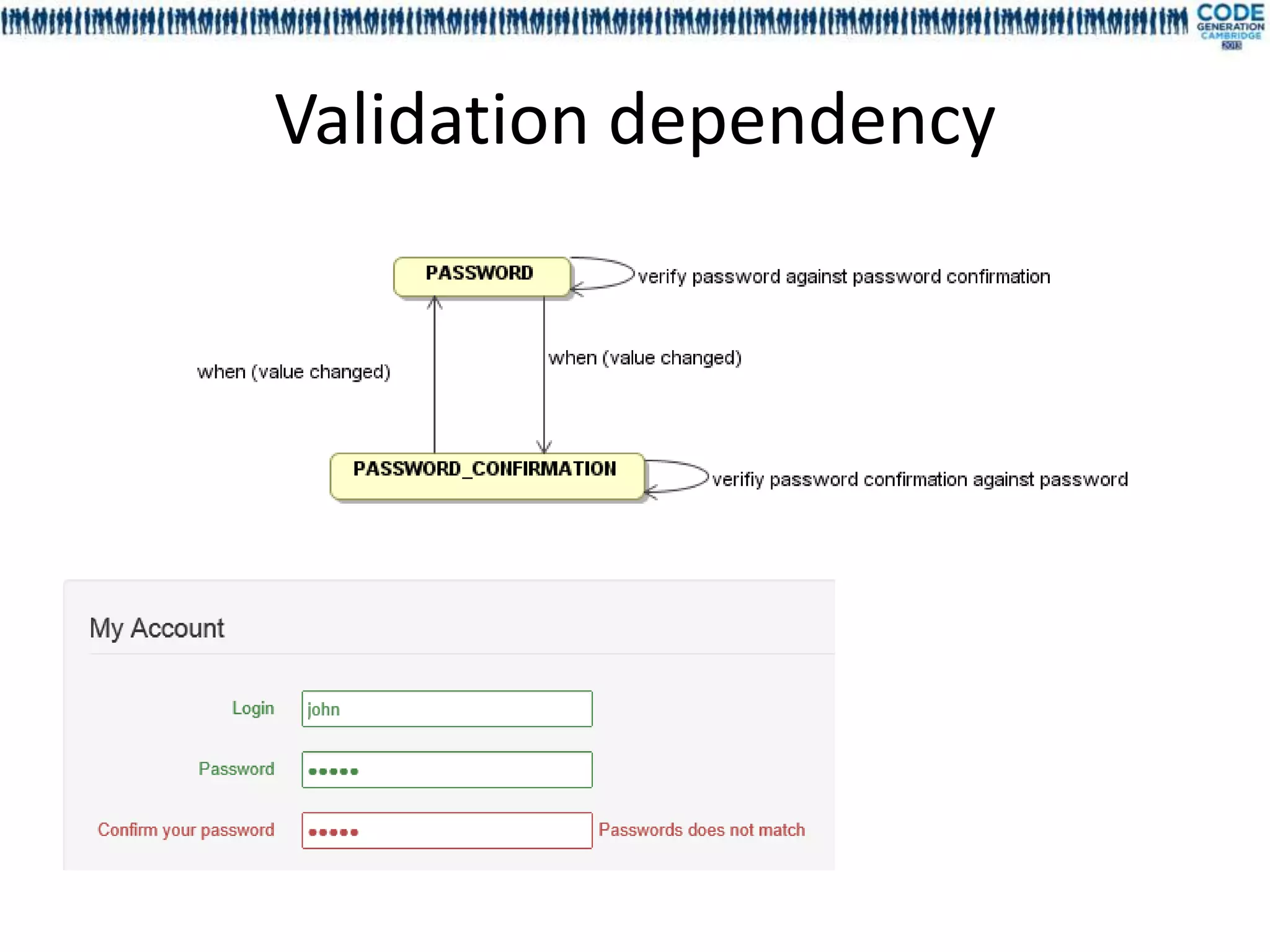
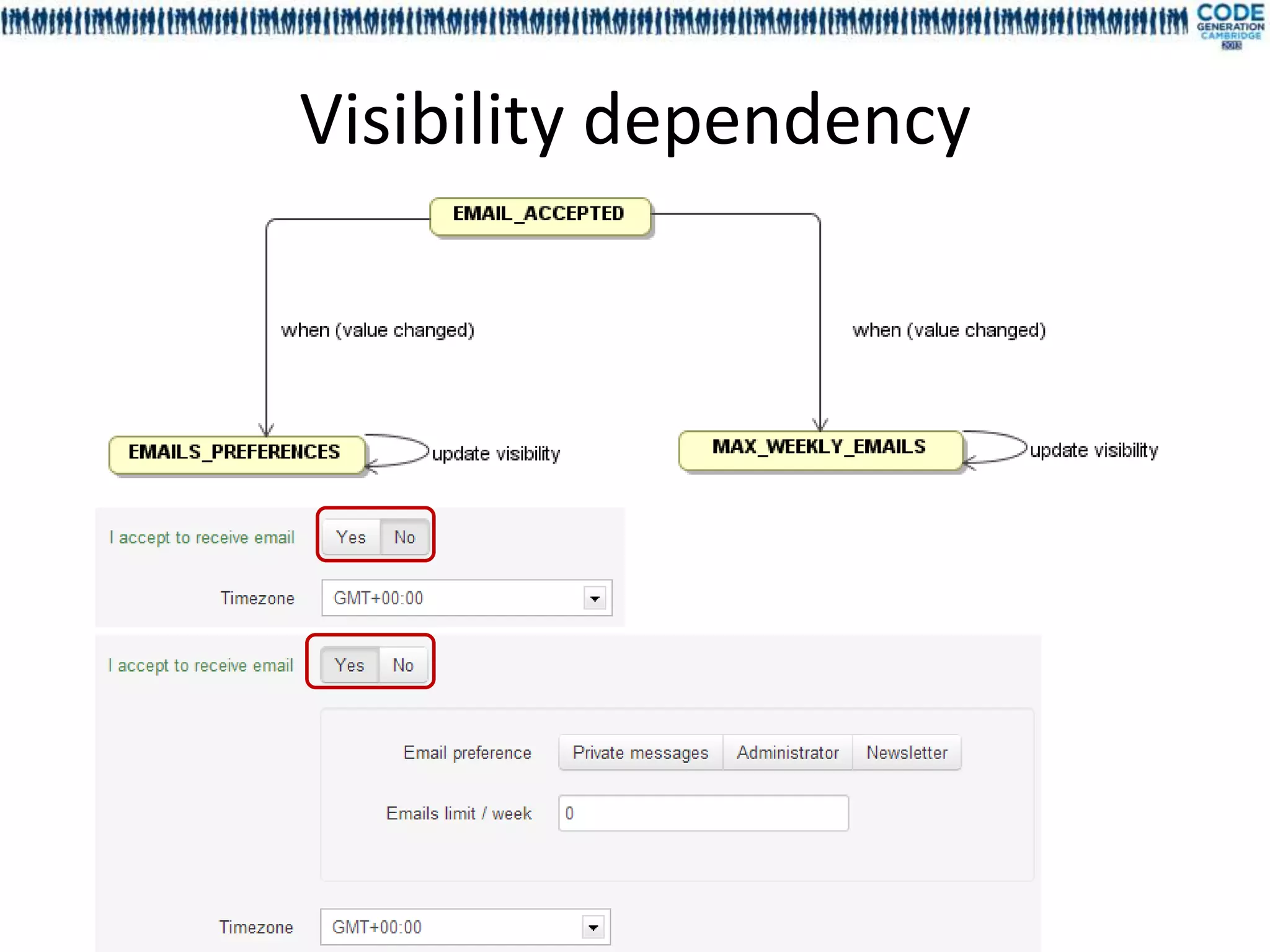
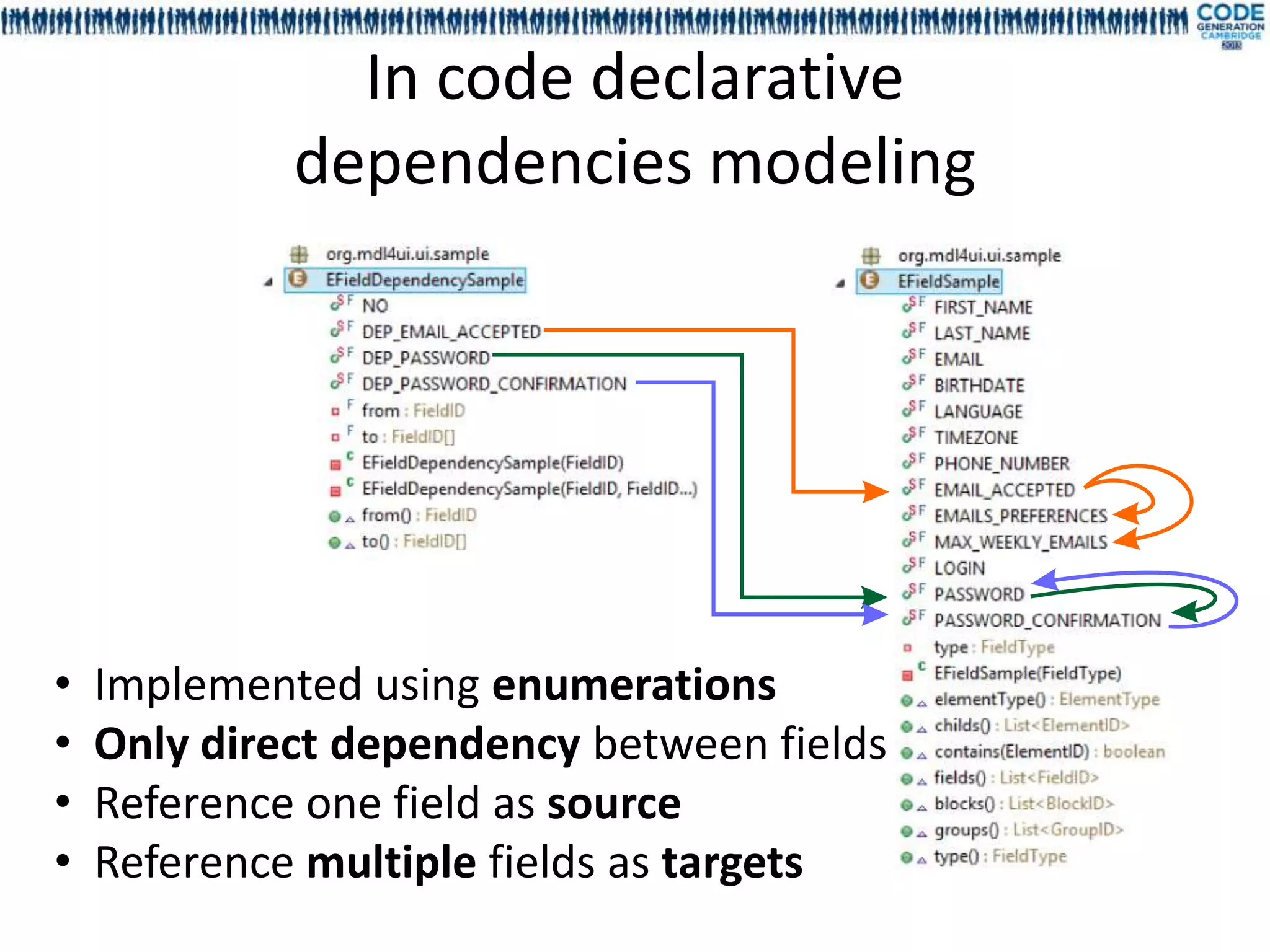
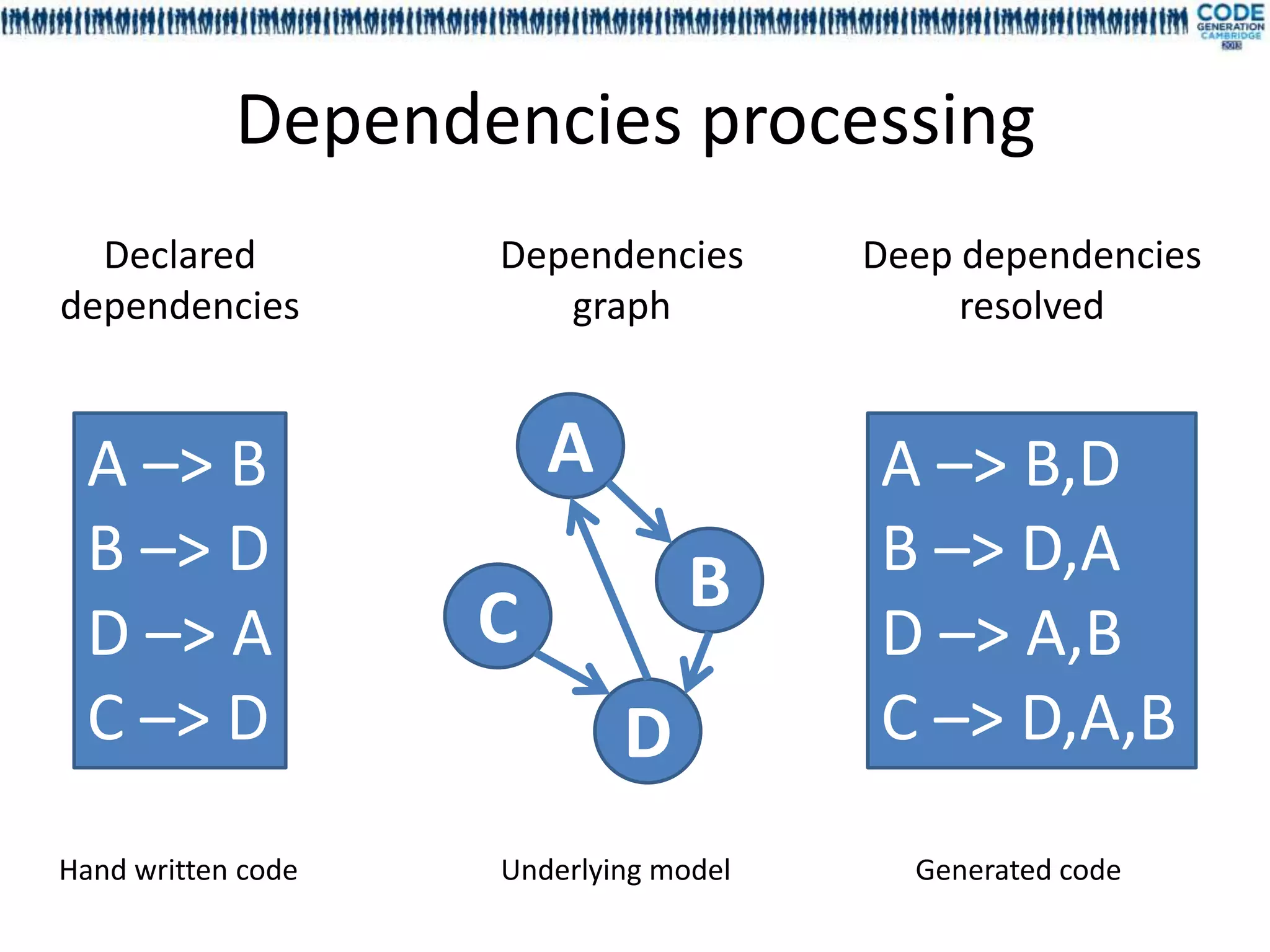
![Deep dependency, dependency cycle,
graph validation
• Cycle declaration between fields is allowed
• Deep dependencies are statically resolved
For each field the deep dependencies are
generated during the compilation
Model declared in EFieldDependency[Sample]
Deep dependency are generated in
EFieldDeepDependency[Sample]
Dependency order is not guaranteed
• No runtime infinite loop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdl4uicg2013-130409050811-phpapp02/75/Rock-solid-UI-modeling-using-annotation-processing-CodeGeneration-2013-32-2048.jpg)
![Simple dependency API
public interface FieldDependencyFactory {
FieldID[] get(FieldID fieldId);
}
• Implementation is generated by our maven plugin
• Graph is built from the FieldDependency declaration
• Deep dependencies are statically resolved for each field
Look at the implementation EFieldDeepDependency[Sample]
• No runtime computation of the dependencies
• Safe and efficient](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdl4uicg2013-130409050811-phpapp02/75/Rock-solid-UI-modeling-using-annotation-processing-CodeGeneration-2013-33-2048.jpg)


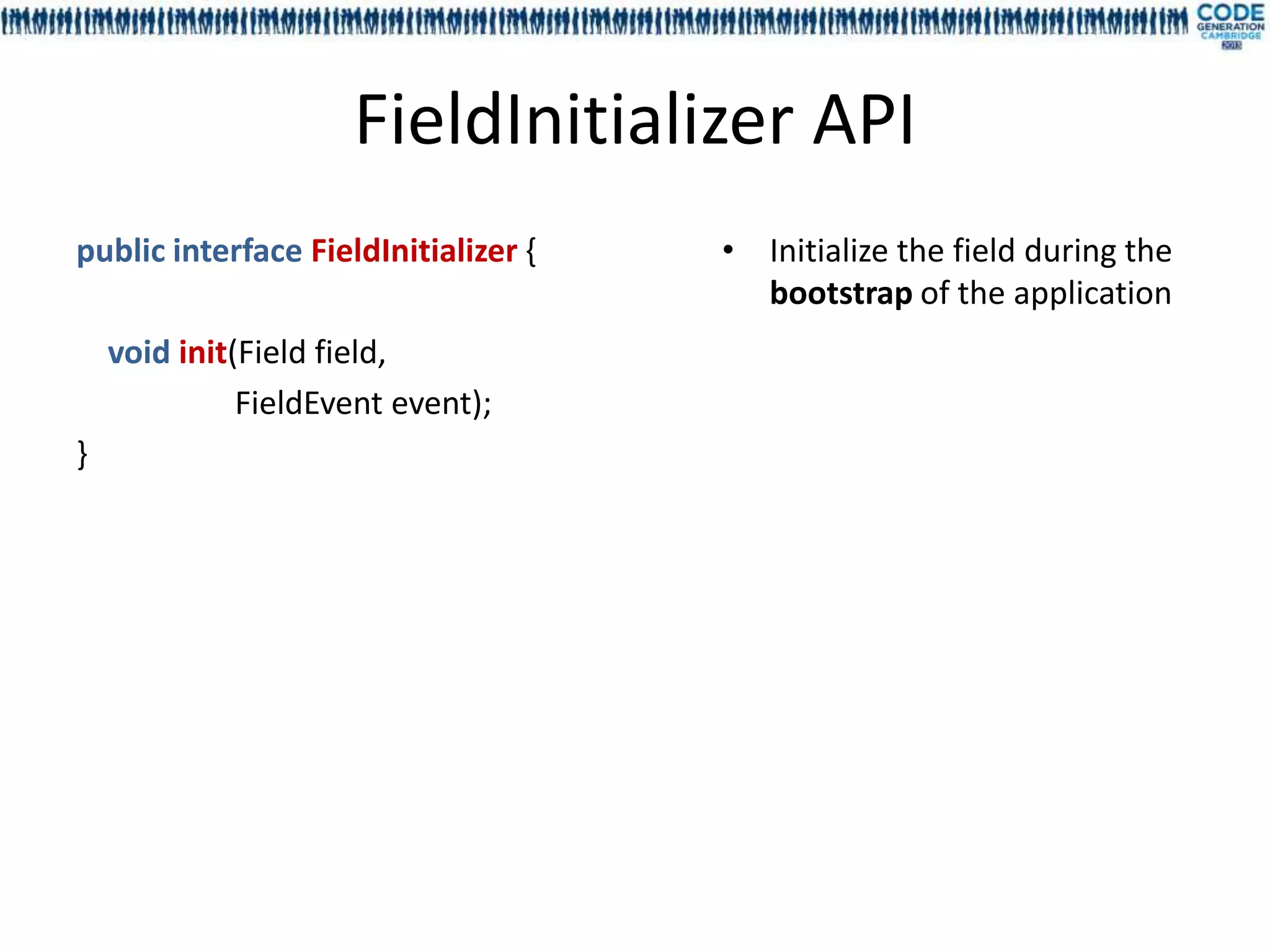

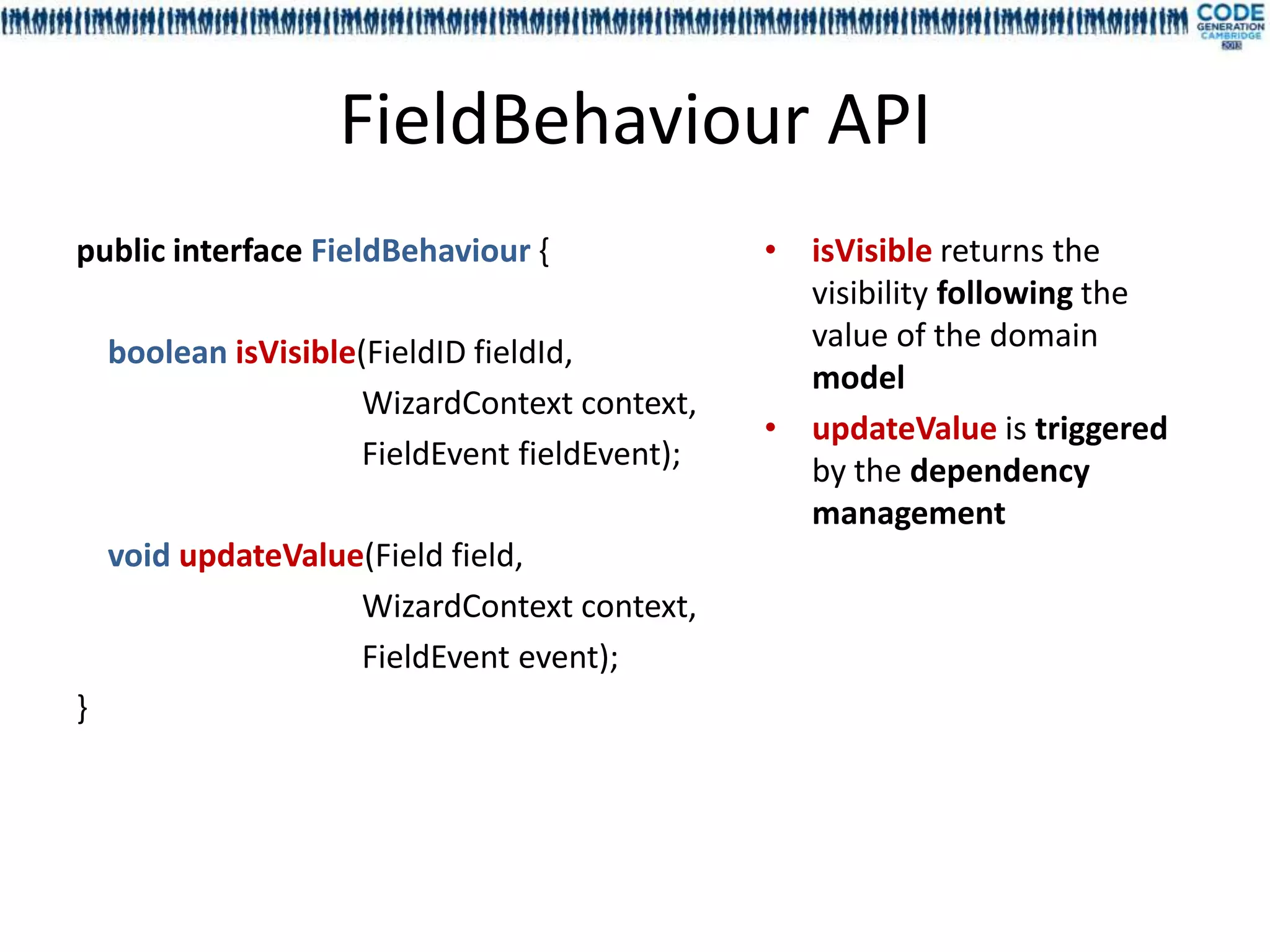

![Injecting the field features with
annotations and meta annotation
Meta annotation Custom annotation Injected resource
@InjectInit @InjectSampleInit Any class implementing
Reference one or more EFieldSample FieldInitializer
@InjectEditor @InjectSampleEditor Any class implementing
Reference one or more EFieldSample FieldEditor
@InjectBehaviour @InjectSampleBehaviour Any class implementing
Reference one or more EFieldSample FieldBehaviour
@InjectLabel @InjectSampleLabel Any interface method without
Reference one or more EField, EGroup, parameter returning a String
EBlock and EScreen[Sample]
@InjectHelp @InjectSampleHelp Any interface method without
Reference one or more EField, EGroup, parameter returning a String
EBlock and EScreen[Sample]
@InjectPlaceHolder @InjectSamplePlaceHolder Any interface method without
Reference one or more EField, EGroup, parameter returning a String
EBlock and EScreen[Sample]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdl4uicg2013-130409050811-phpapp02/75/Rock-solid-UI-modeling-using-annotation-processing-CodeGeneration-2013-44-2048.jpg)
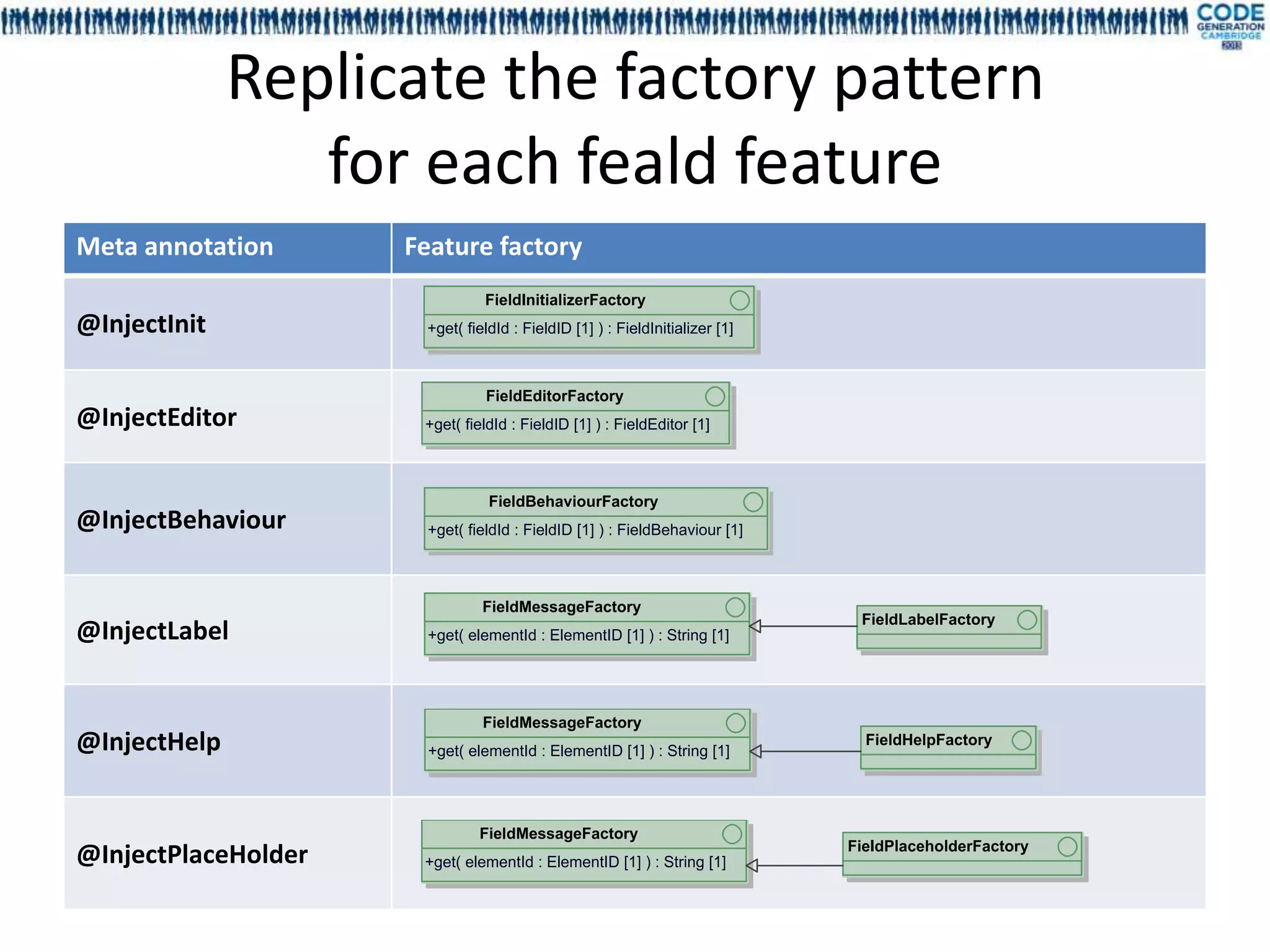
![Generated pattern to glue things
together
Code generation is triggered
Fi eldB eh avi our Factor y
+get( fieldId : FieldID [1] ) : FieldBehaviour [1] by @InjectBehaviour
APT processor is executed
during the compilation of
Mdl4ui-field project
«Generated» «Generated»
Gw tFi eldB ehavi our Facto ry MockFi eldB ehaviour Factory We perform some validations,
.. . .. .
like detecting duplicated
injections
We use a factory pattern
-behaviours * -behaviours *
Fi eldB eh avi our
+isVisible( fieldId : FieldID [1], context : WizardContex [1], fieldEv : FieldEvent [1] ) : boolean [1]
t ent
+updateValue( field : Field [1], context : WizardContext [1], event : FieldEv [1] ) : void [1]
ent returning the right instance for
each field
An implementation for GWT
DefaultBehaviour
client runtime purpose
A mock implementation GWT
less for unit testing purpose](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdl4uicg2013-130409050811-phpapp02/75/Rock-solid-UI-modeling-using-annotation-processing-CodeGeneration-2013-46-2048.jpg)

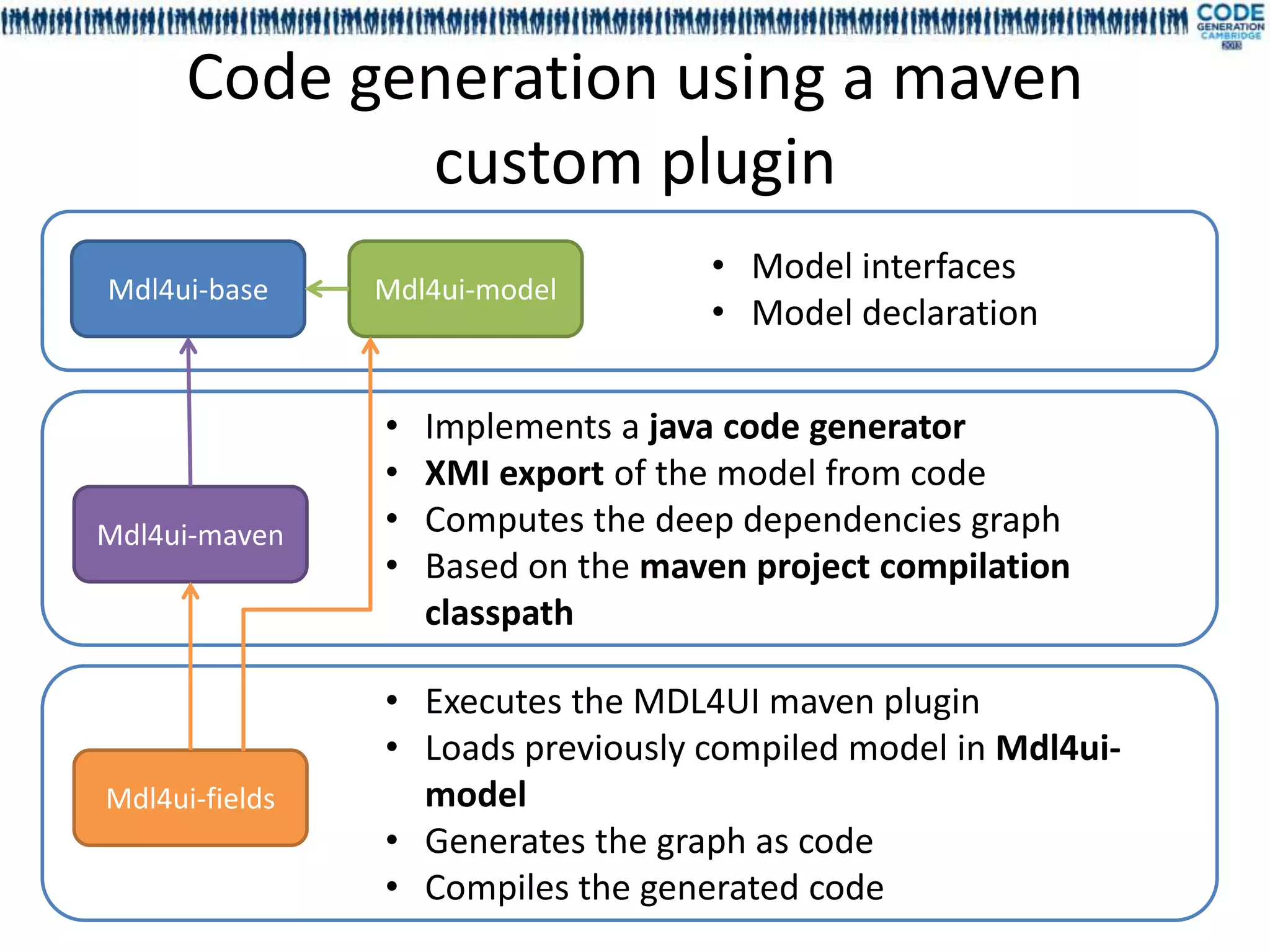
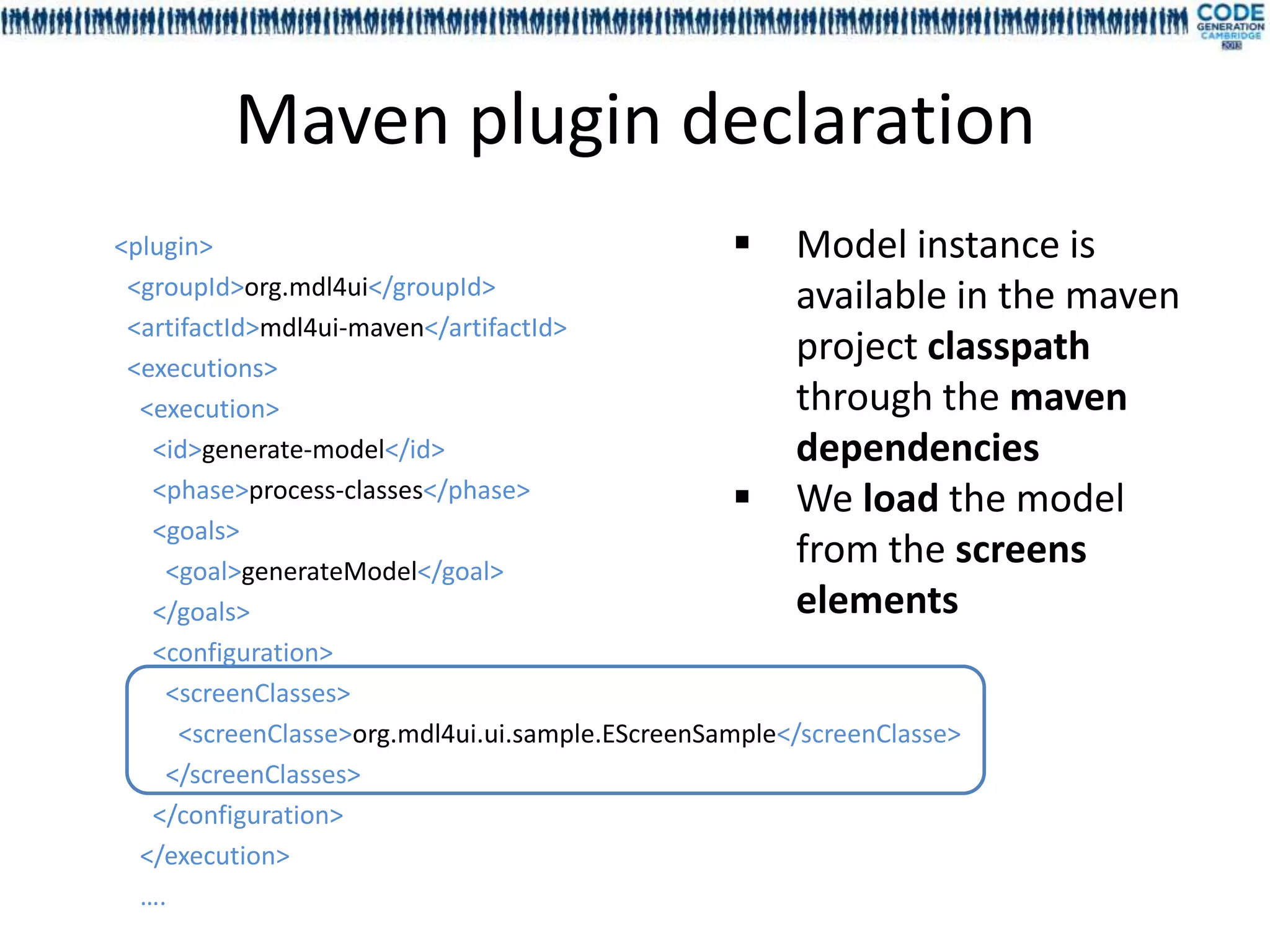
![Content of MDL4UI
• Mdl4ui-I18n : foundation framework for text resource injection, containing APT
processors and annotations
• Mdl4ui-base: foundation framework for the UI model interfaces, containing
APT processors and annotations
• Mdl4ui-model: model instance for our code sample, including fields and
dependencies
• Mdl4ui-maven: maven plugin part of the foundation framework that generate
and check the dependency graph between the fields, export the model in XMI
• Mdl4ui-fields: business rules, validation and field editors (MVC pattern) for
our sample
• Mdl4ui-webapp: the web
[INFO] Reactor Summary:
[INFO]
[INFO] mdl4ui-root ....................................... SUCCESS [0.375s]
application that assembles [INFO]
[INFO]
mdl4ui-i18n ....................................... SUCCESS [1.921s]
mdl4ui-base ....................................... SUCCESS [0.829s]
[INFO] mdl4ui-model ...................................... SUCCESS [2.860s]
the code, compiles various [INFO]
[INFO]
mdl4ui-maven ...................................... SUCCESS [1.641s]
mdl4ui-fields ..................................... SUCCESS [4.751s]
resources with GWT and [INFO]
[INFO]
mdl4ui-webapp ..................................... SUCCESS [39.632s]
------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESS
adds styling [INFO]
[INFO]
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total time: 52.166s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdl4uicg2013-130409050811-phpapp02/75/Rock-solid-UI-modeling-using-annotation-processing-CodeGeneration-2013-49-2048.jpg)