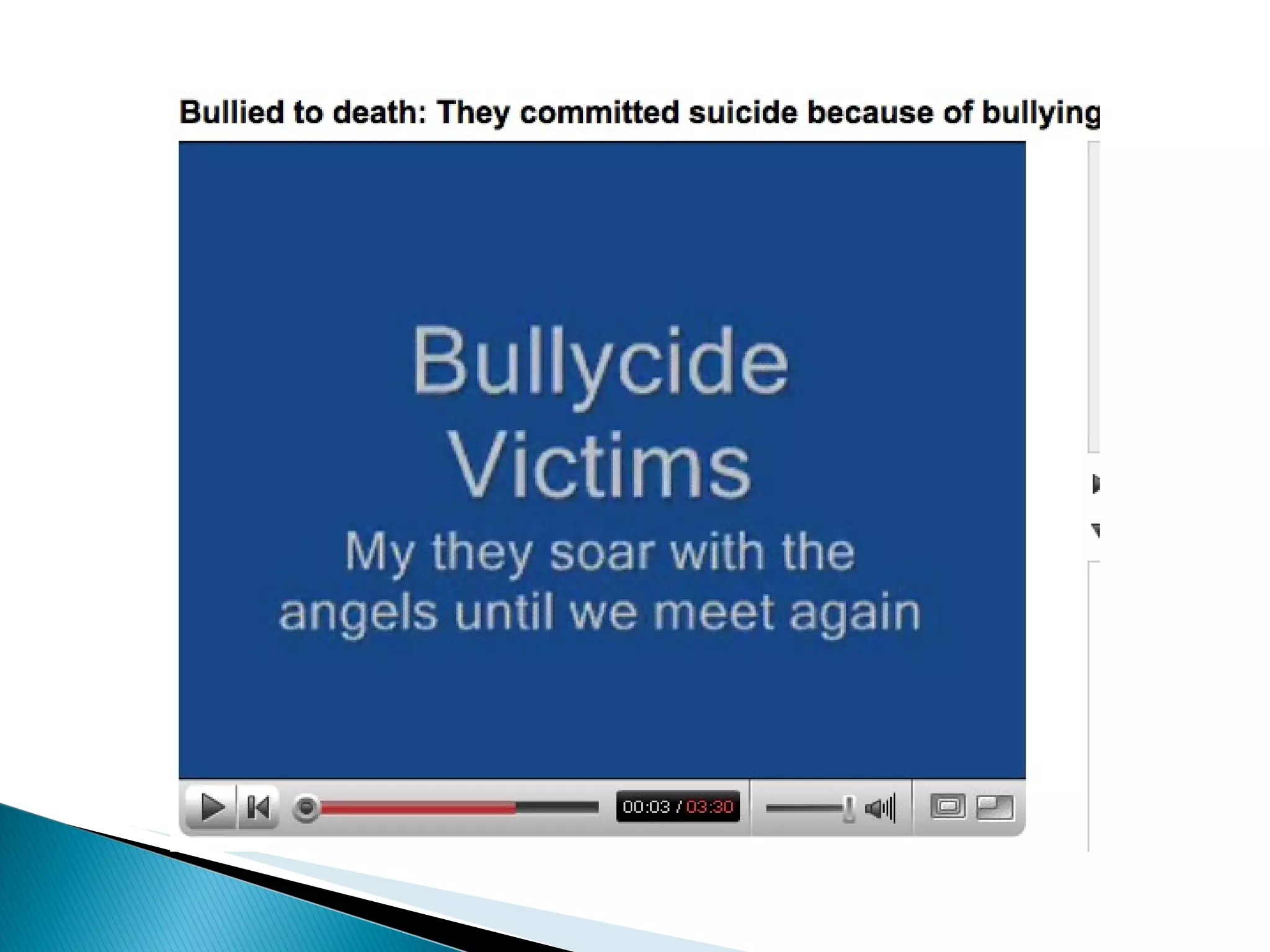
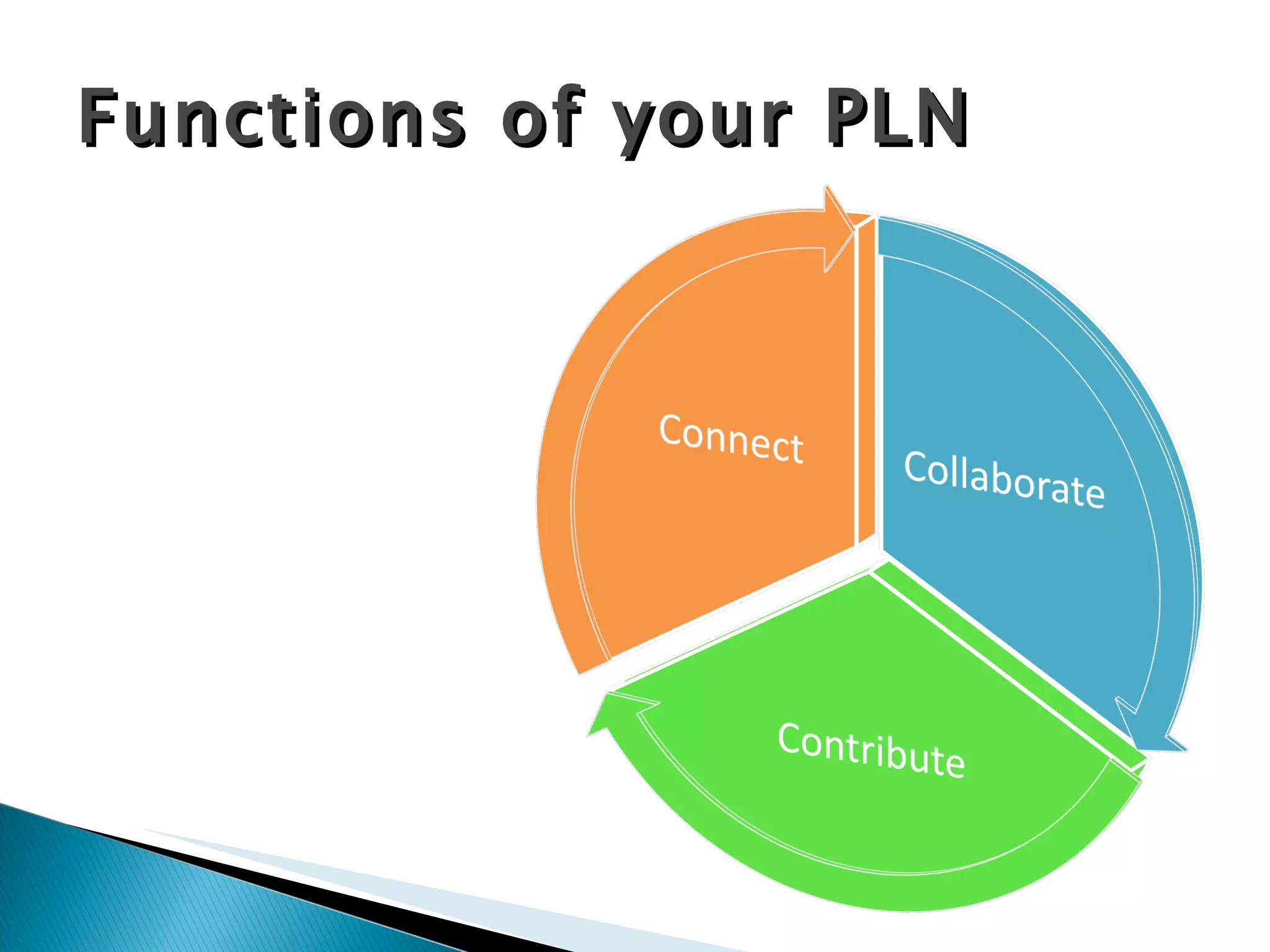
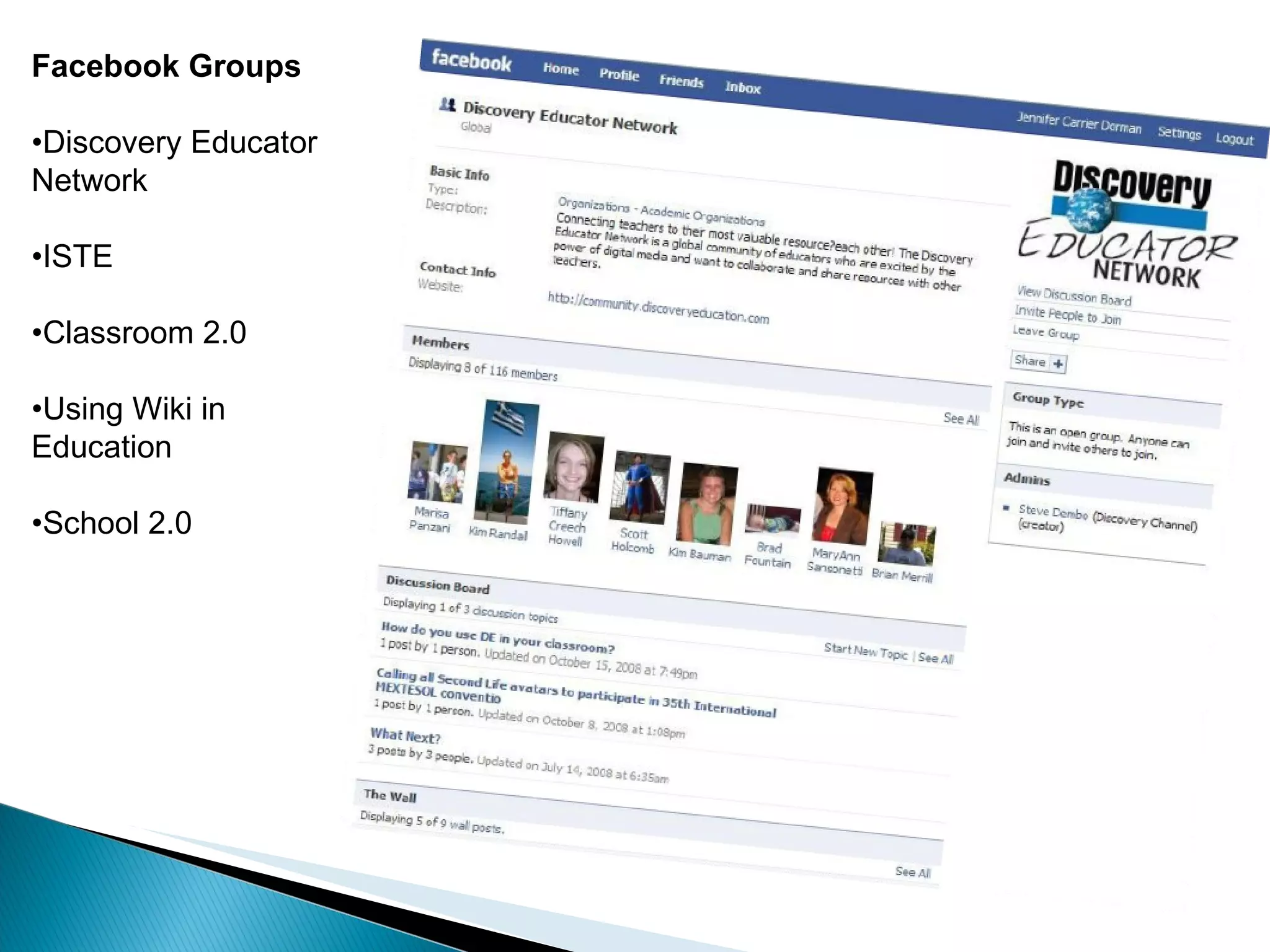
Students will analyze negative internet experiences and collaborate to develop methods to address them. They will also evaluate personal learning networks to establish an ongoing education network. The document provides definitions of cyberbullying and an overview of technologies used for cyberbullying. It then discusses personal learning networks and lists various online tools and platforms that can be used to establish a personal learning network.