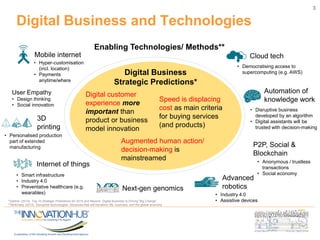
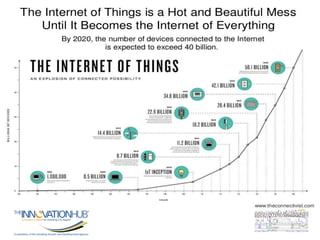
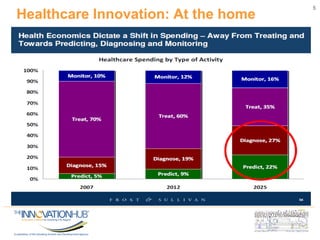
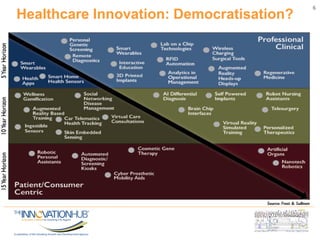
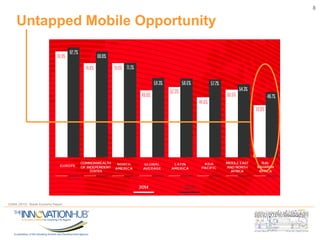
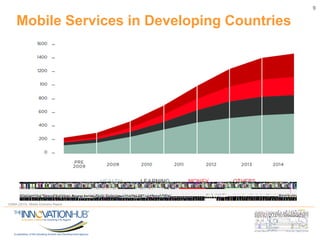
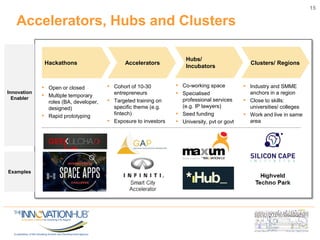
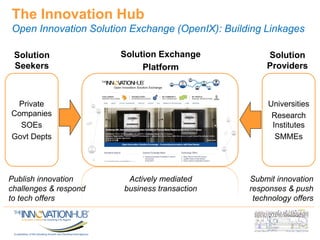
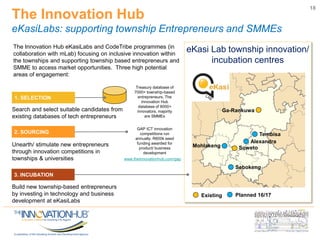
This document discusses the role of information and communications technology (ICT) in supporting small, medium and micro-sized enterprises (SMMEs) in the digital economy. It outlines key ICT trends like the democratization of technology and innovation at the edge. It also discusses how digital technologies are disrupting businesses and describes enabling technologies. Further, it explores opportunities for SMMEs in areas like mobile services, smart infrastructure, and m-health. Finally, it presents initiatives to connect entrepreneurs with developers and funding through hackathons, accelerators, hubs and clusters to help SMMEs develop digital solutions.