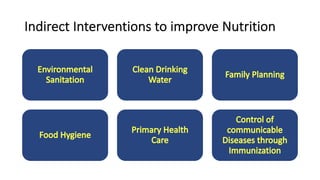
The document discusses preventive medicine in obstetrics, pediatrics, and geriatrics, focusing on maternal and child health (MCH) concepts and objectives such as reducing mortality and promoting physical and psychological development. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of maternal and child health, detailing problems like malnutrition, infections, and uncontrolled reproduction, while outlining direct and indirect interventions to improve health outcomes. The author highlights the importance of social factors in reproductive health and the role of preventive pediatrics in community health care services.