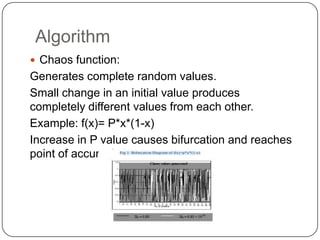
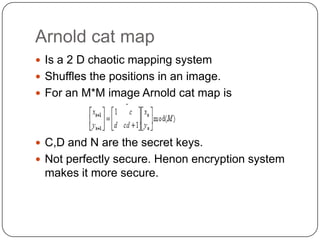
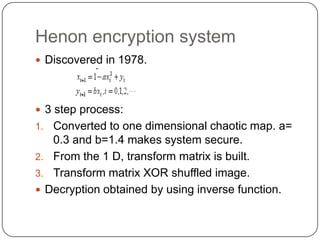
This document discusses and compares three different image encryption techniques: 1) One time padding, which uses the Vernam cipher and has a large random key space to securely transmit images. 2) Image encryption using a chaos system combined with an improved version of the DES algorithm that reduces the number of DES iterations for faster encryption. 3) Image encryption using a Henon chaotic system that first shuffles pixel positions using the Arnold cat map, then encrypts the shuffled image values. The document analyzes the security and performance of each technique.