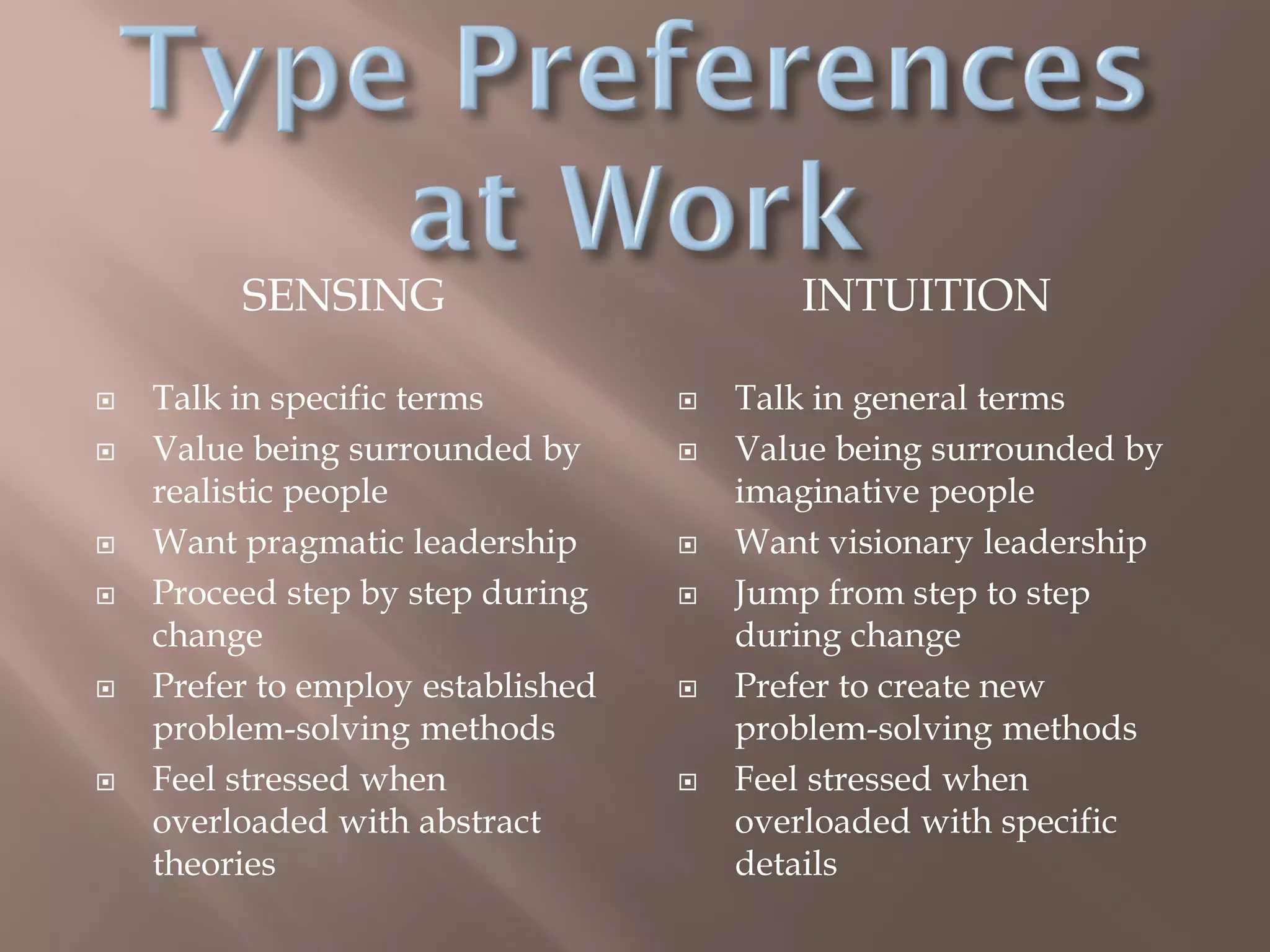
This document provides an overview of a presentation given to library staff on using Myers-Briggs Type Indicators to improve teamwork and communication. The presentation discusses learning individual type preferences to take in information and make decisions, developing stronger team dynamics, and practicing constructive ways of working together such as giving everyone a chance to speak and keeping discussions confidential. It also outlines the four dichotomies that comprise Myers-Briggs types and how they influence energy, information, decision-making, and approach to life. The goal is to help staff appreciate individual differences and find better ways of problem solving as a team.