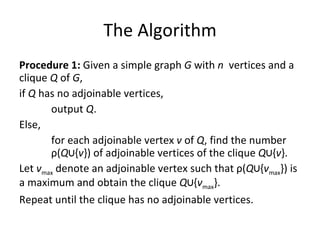
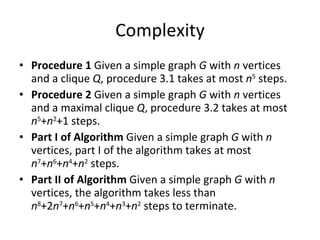
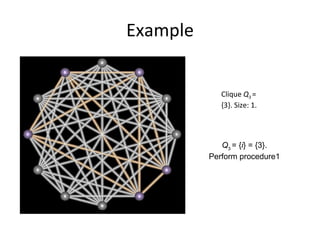
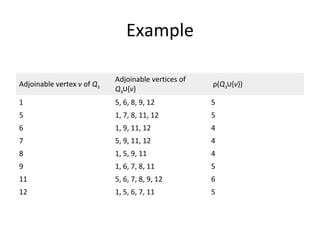
The document describes an algorithm for finding the maximum clique in a graph. The algorithm works in two procedures:
1. Starting with a single vertex, it iteratively adds vertices to the clique that are connected to many existing clique vertices.
2. It finds maximal cliques, then attempts to further expand these by adding and removing vertices based on their connections.
The algorithm runs in less than O(n8) time on a graph with n vertices. An example demonstrates running the algorithm on a sample graph to find a maximum clique.