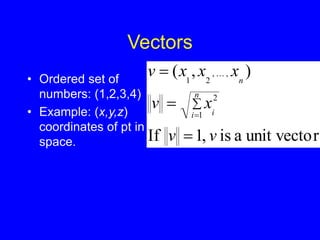
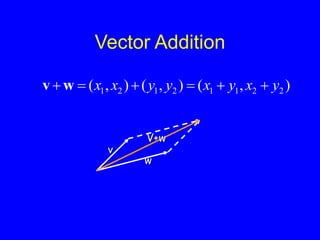
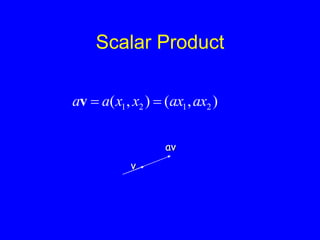
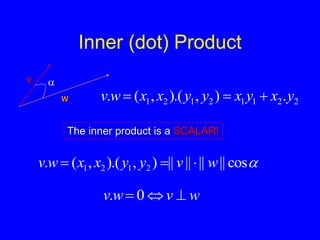
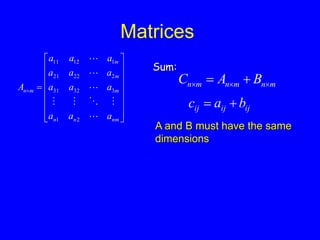
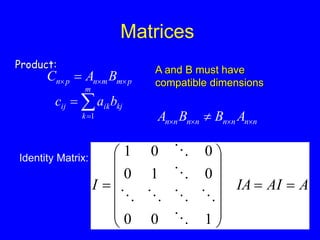
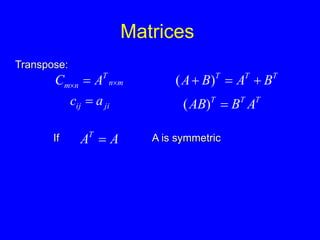
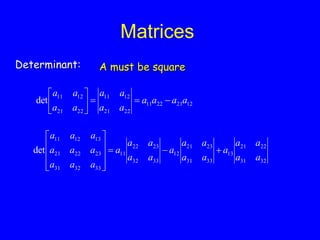
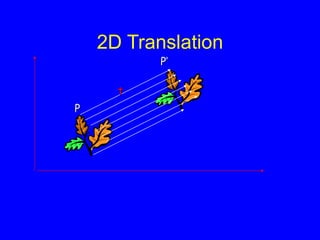
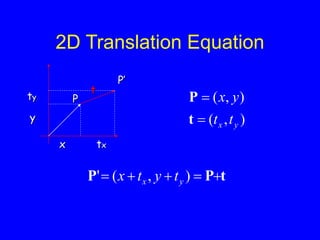
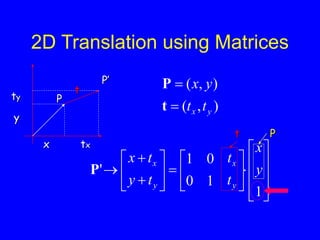
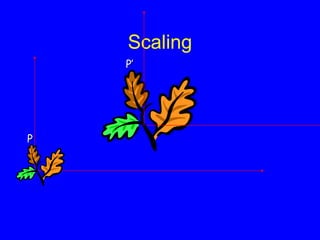
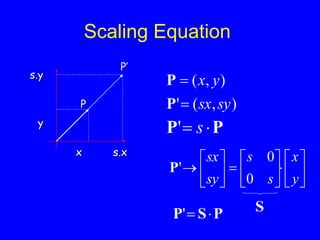
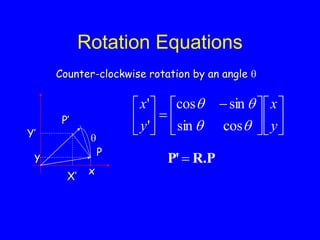
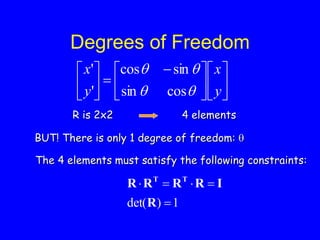
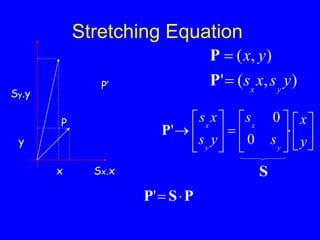
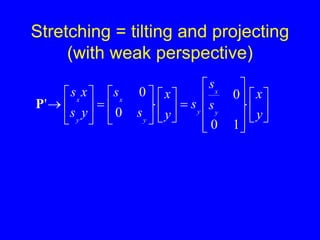
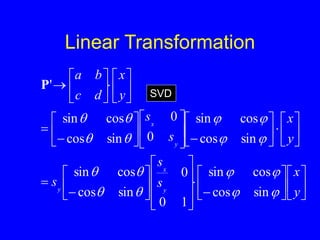
This document provides an introduction to Matlab and a review of linear algebra concepts. It discusses starting Matlab, getting help, vectors, matrices, common operations, and linear transformations including translation, scaling, rotation, and affine transformations. Examples are provided for how to represent and perform these transformations using Matlab code and matrix mathematics. The document concludes by mentioning files, functions, images, and debugging in Matlab.