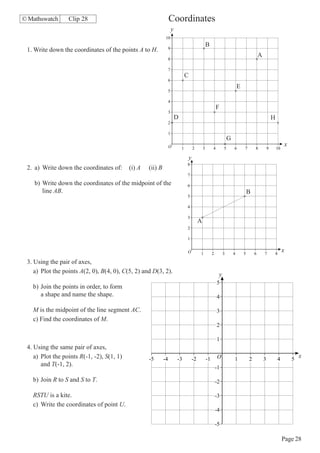
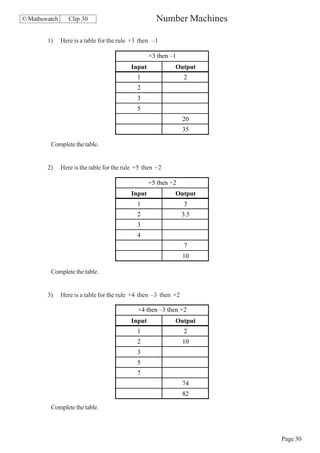
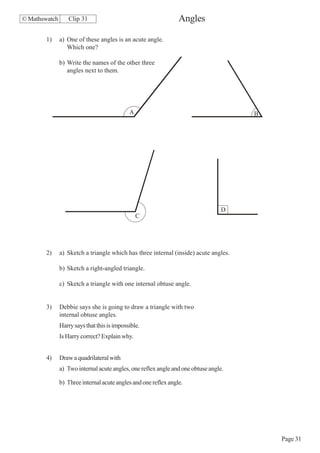
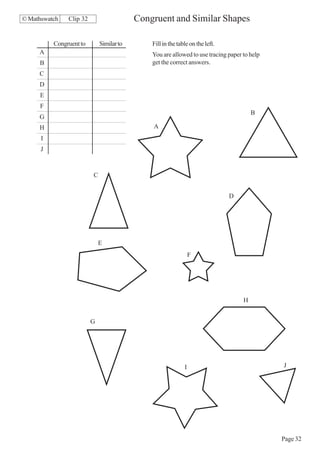
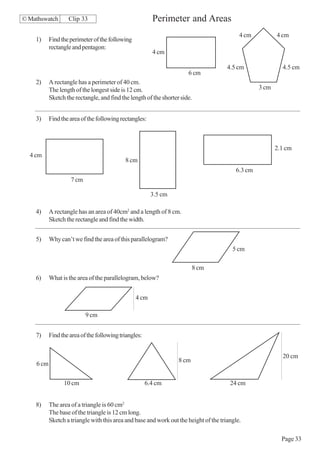
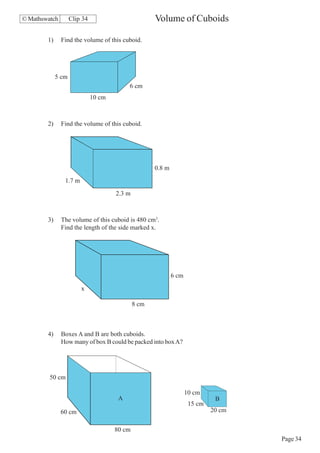
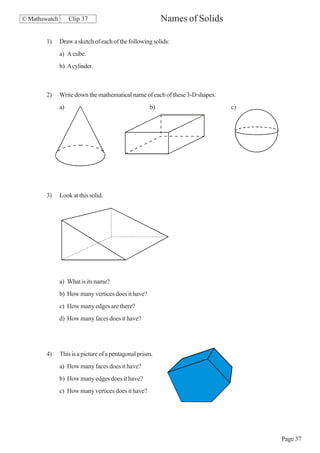
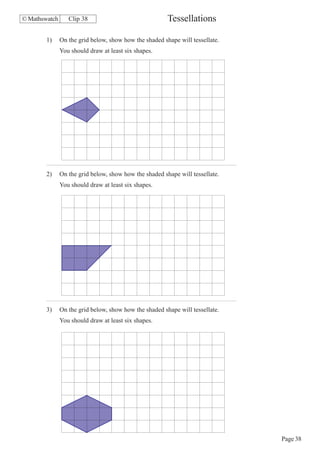
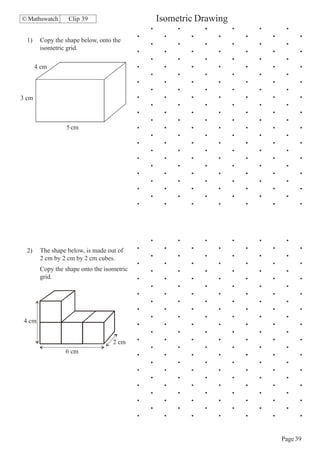
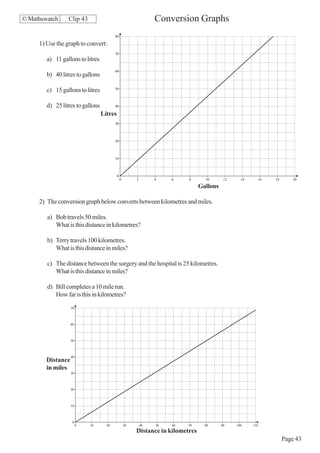
This document contains a series of math problems and exercises related to place value, ordering numbers, rounding, reading scales, operations with decimals and fractions, percentages, and more. The problems are arranged into 13 clips or sections covering different math topics. Some of the key areas covered include:
- Writing numbers in figures and words
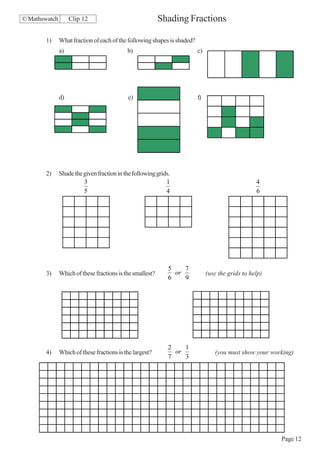
- Ordering and comparing decimals, fractions, percentages
- Rounding numbers to various places
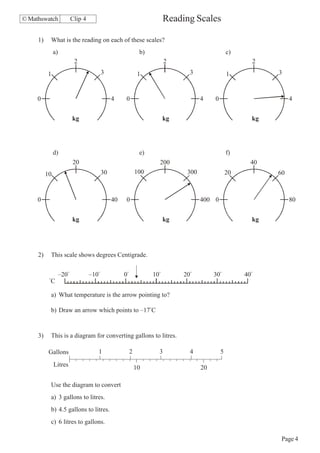
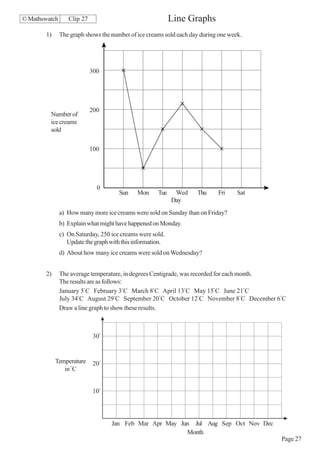
- Reading information from scales and diagrams
- Performing calculations with positive and negative numbers
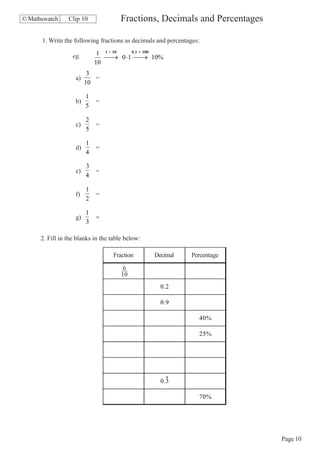
- Converting between fractions, decimals, and percentages
- Working with square and cube numbers
- Solving word problems involving money, time, and rates
The document provides a comprehensive set of math skills