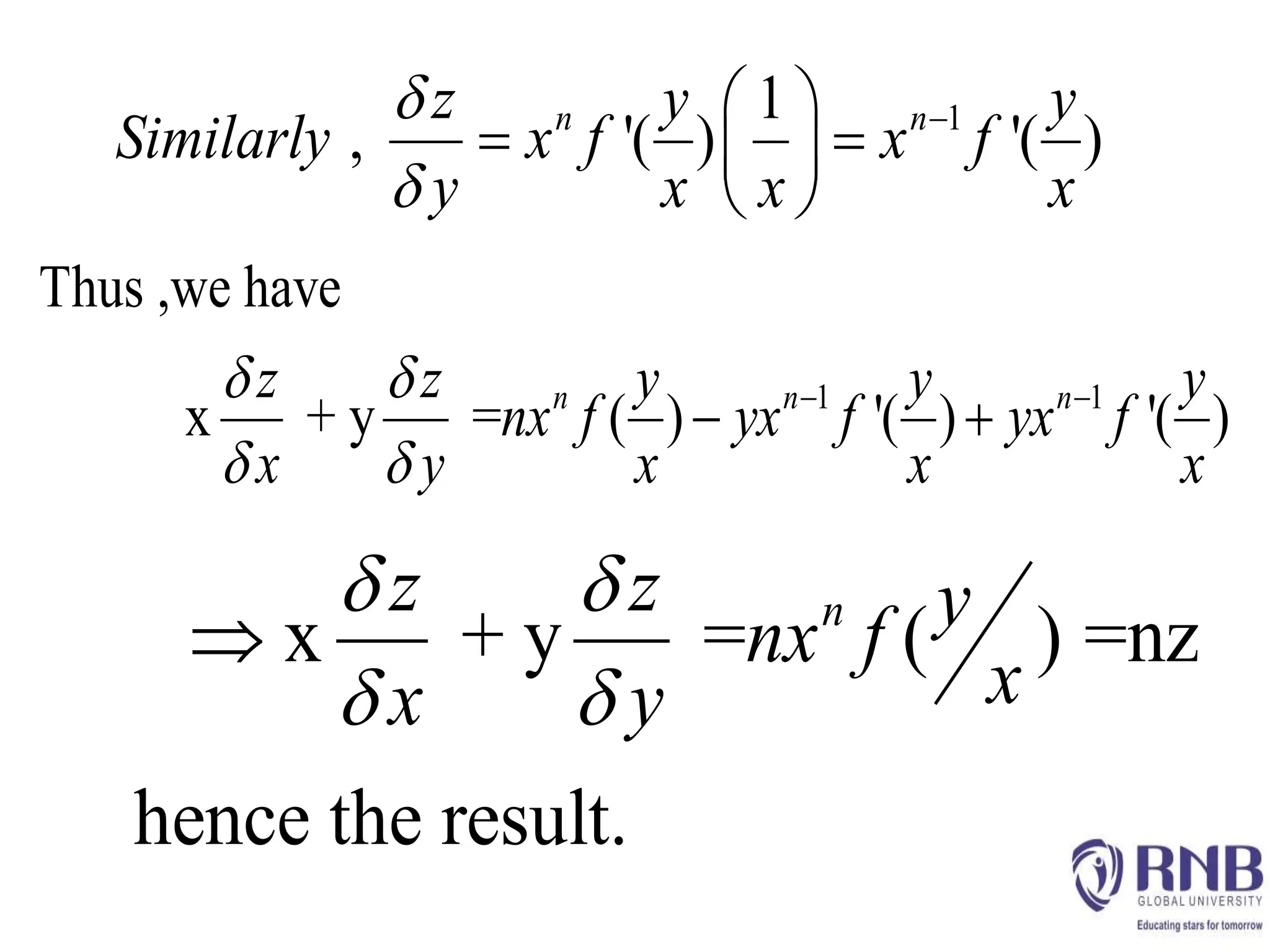1) Partial differentiation allows a function of two variables to be differentiated with respect to one variable while keeping the other constant. This produces partial derivatives that show the rate of change.
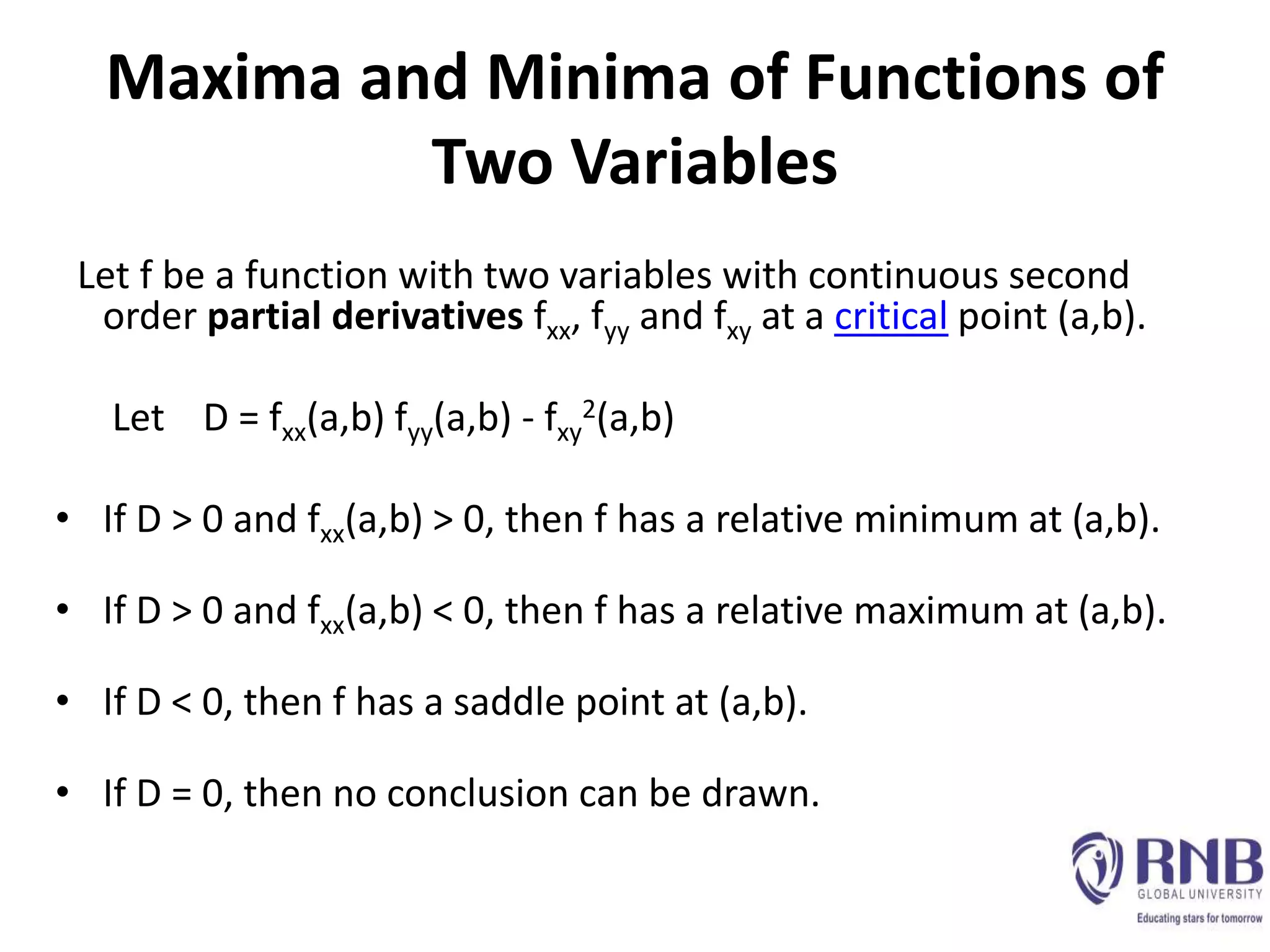
2) Second-order partial derivatives take the partial derivative of a first-order partial derivative, producing four possible second-order partial derivatives.
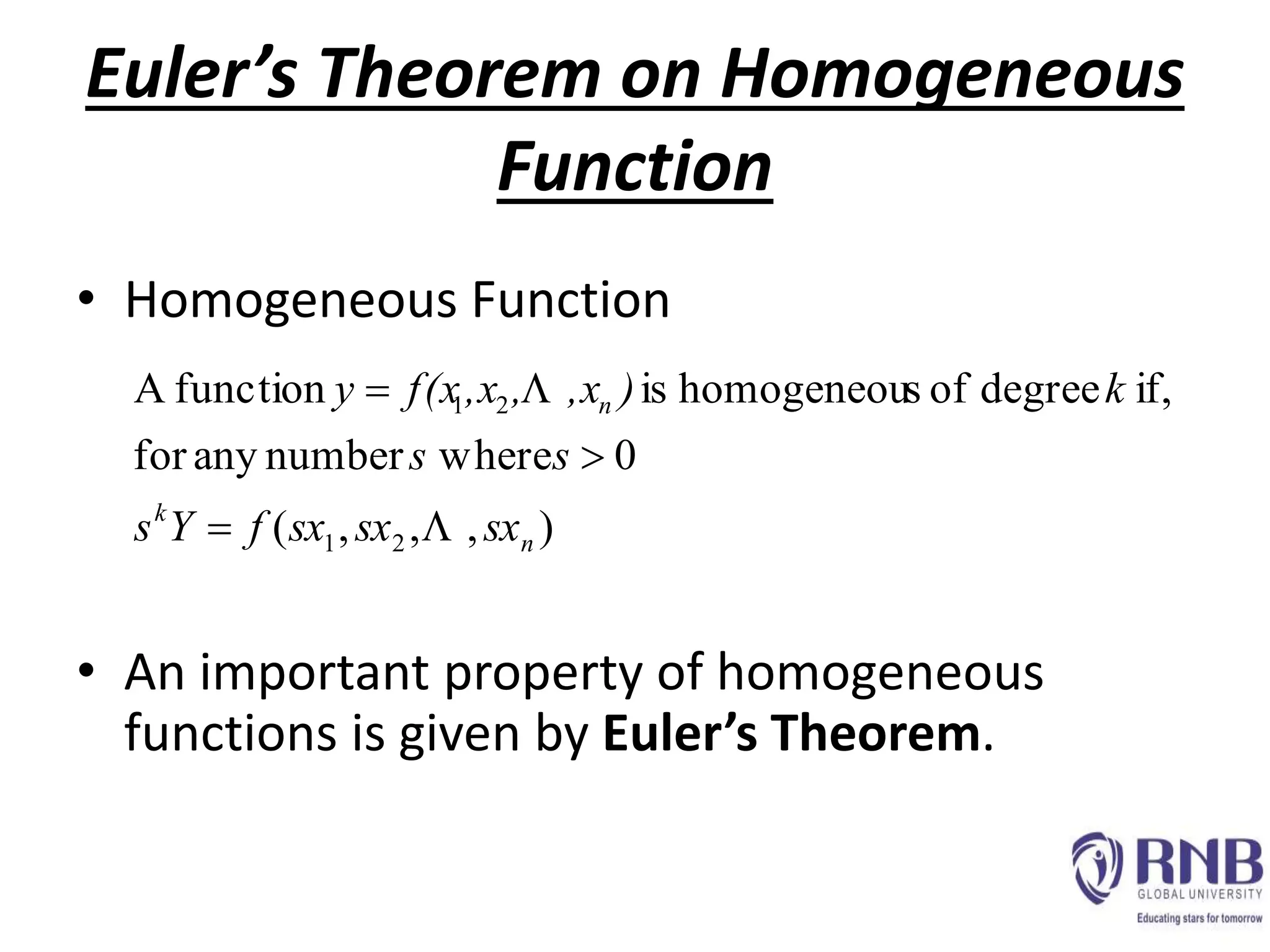
3) Euler's theorem states that if a function is homogeneous of degree n, the sum of its variables multiplied by the function value will equal n times the function value. This can be used to prove properties of homogeneous functions.