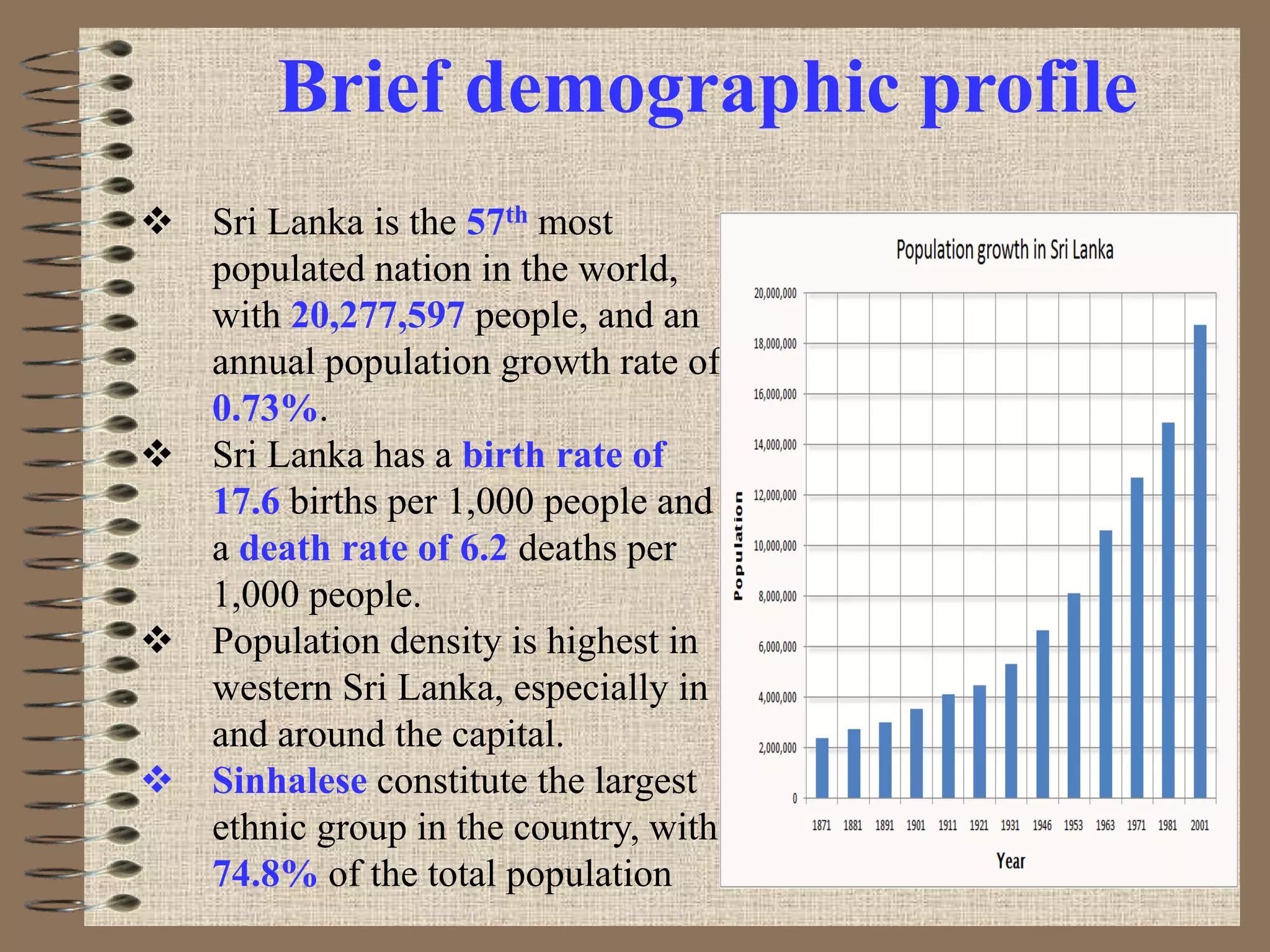
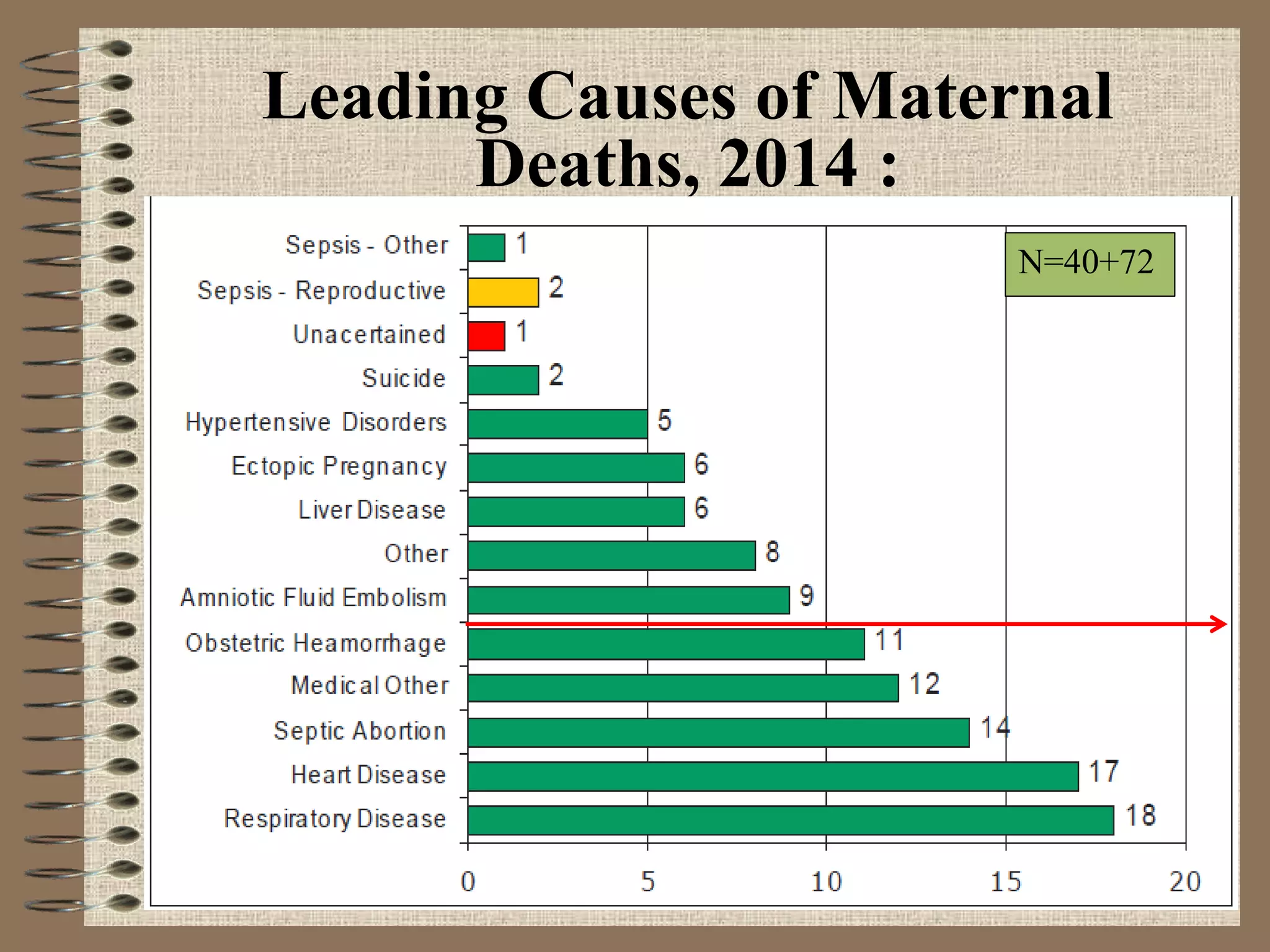
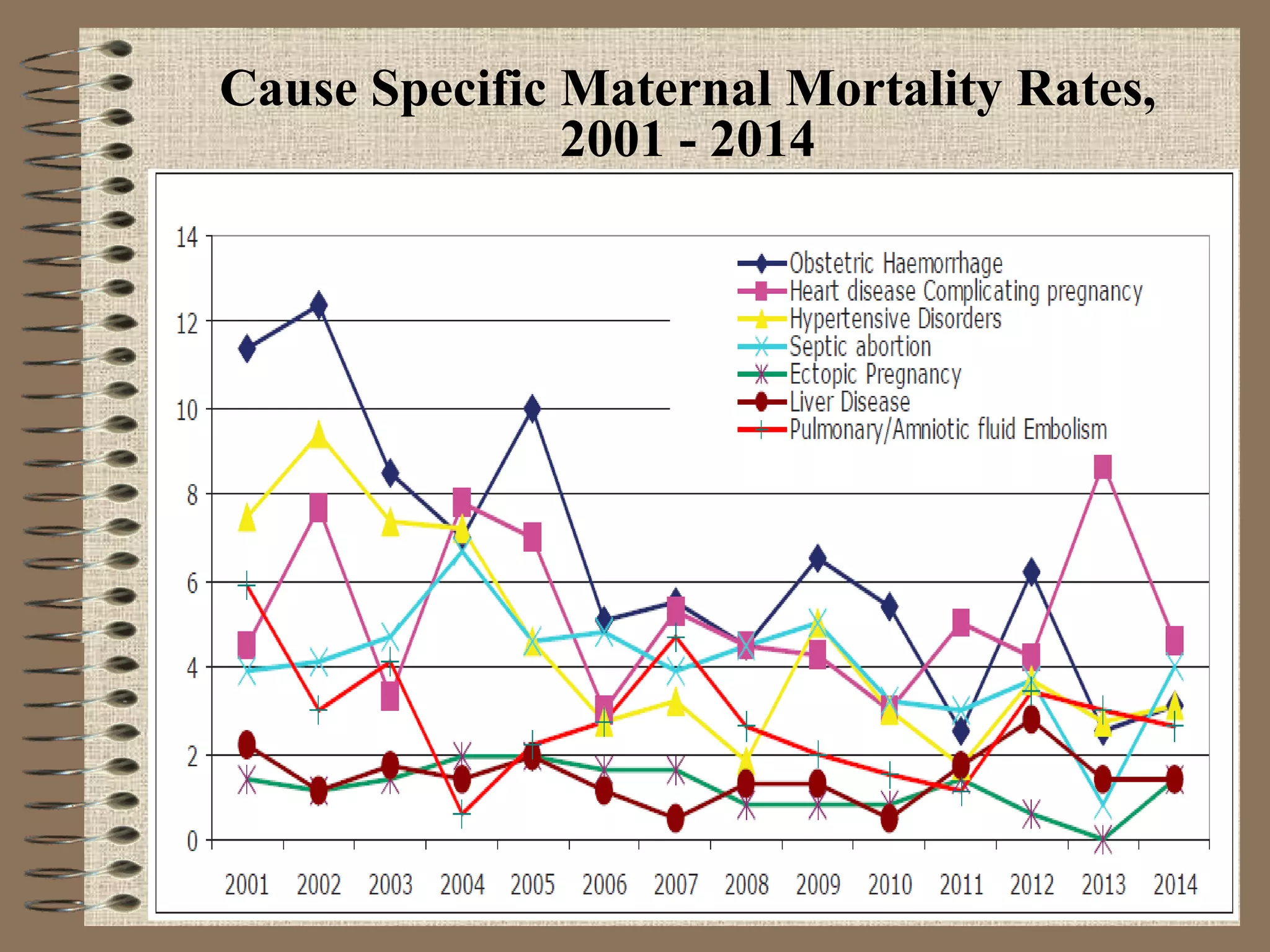
The document outlines Sri Lanka's maternal health program, detailing the country's demographic and health profile, current maternal health situation, and key challenges. It highlights significant indicators such as high literacy rates, life expectancy, and maternal mortality compared to global averages. Furthermore, the program emphasizes the need for continuous improvements in maternal and child health services through political commitment and an organized healthcare delivery system.