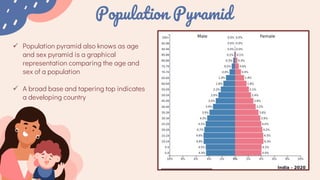
This document summarizes key aspects of demography and family welfare programs in India. It discusses that demography is the study of human populations, focusing on population size, composition, and distribution. India has a large population of over 139 crore people. The family welfare program aims to control population growth and reduce mortality rates through family planning initiatives like contraception and sterilization. The Reproductive and Child Health program and National Health Mission work to improve maternal, newborn, and child health indicators in India.