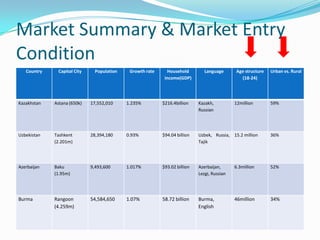
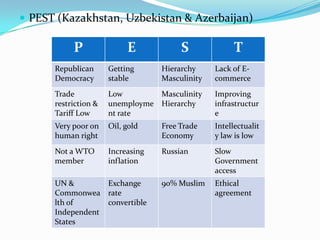
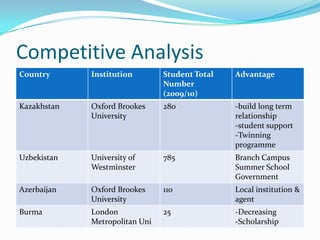
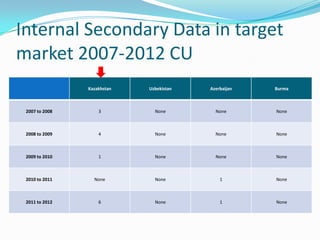
This document provides a research plan for analyzing the demand for UK transnational education (TNE) activities in potential markets such as Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Azerbaijan, and Burma. The plan includes conducting secondary research on market conditions and primary research through surveys. A literature review covers definitions of TNE, issues, and strategies. Market analyses use PEST and SWOT frameworks. The research aims to identify opportunities for Coventry University, recommend the best country and partner to start with, and provide benefits of TNE for the university.






















![Reference
McBurnie.G., Ziguras,C(2007) Transnational
Education Issues and trends in offshore higher
education.1st edn.New York: Routledge
University World News (2012) Higher education
trends, challenges and recommendation [online]
available from
http://www.universityworldnews.com/article.php?stor
y=20120609110849181
UNESCO/Council of Europe (2000) Code of Good
Practice in the provision of transnational
education:Bucharest:UNESCO-CEPES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-131206164206-phpapp02/85/Transnational-Marketing-Strategy-for-New-East-Asia-Market-2012-35-320.jpg)