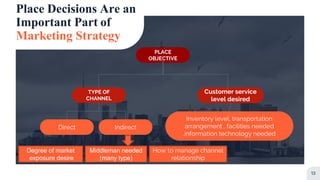
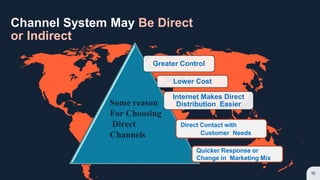
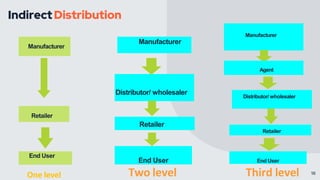
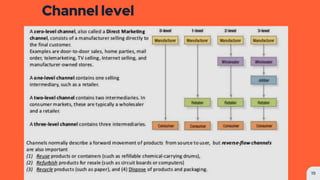
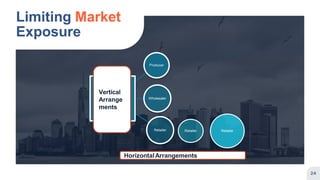
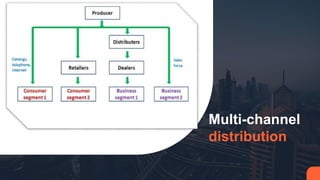
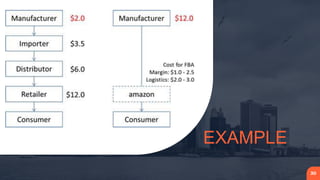
Place refers to how a product is distributed to reach target customers. Key considerations for place include establishing warehouses and distribution centers, managing inventory levels, and selecting channels of distribution. Distribution decisions involve selecting locations, determining market coverage, choosing channel members, and setting logistics and service levels. The objective is to make products available to customers at the right place and time in the required quantities at minimum cost while satisfying customers. Marketing channels refer to the pathways through which products reach consumers. Distribution can be direct from producer to consumer or indirect through intermediaries like wholesalers or retailers. Producers must decide on the appropriate channel structure and relationships.