The document discusses several key concepts related to distribution and retailing, including:
1) Product classes have different placement needs - convenience products are best in convenient small stores while shopping products work well in malls and superstores.
2) Placement must consider the product life cycle as locations that work in growth stages may not in later stages.
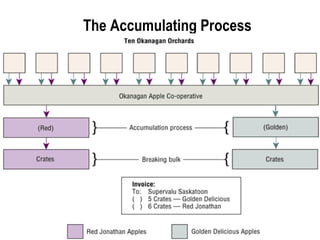
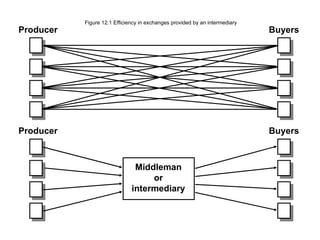
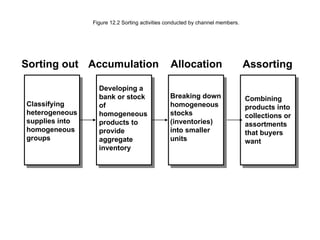
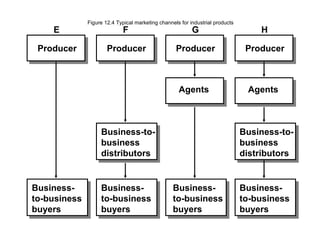
3) Distribution intermediaries help overcome discrepancies in quantity and assortment between what producers make and what consumers want through accumulation, breaking bulk, sorting, and assorting.
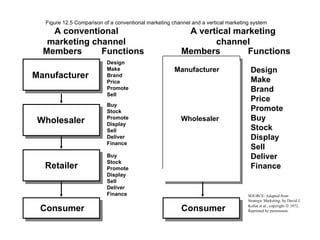
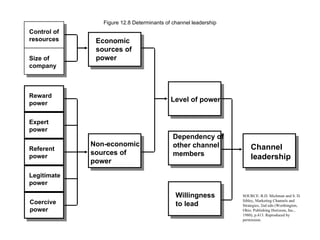
4) Channels create time, place and ownership utility by delivering products at the right time, place and with appropriate legal ownership.