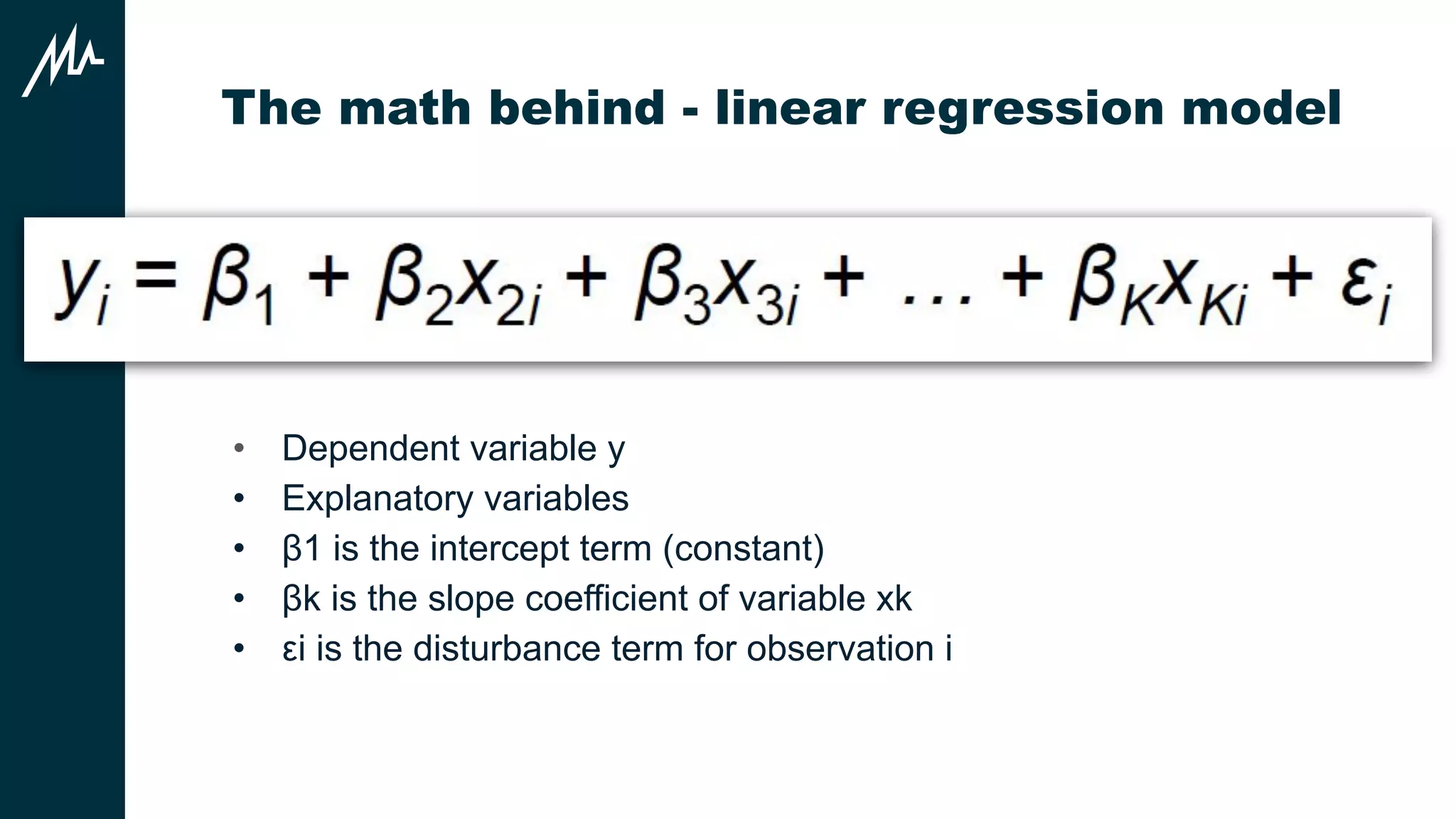
The document discusses marketing mix modeling (MMM) as a statistical analysis technique to understand the impact of various marketing activities on sales. It outlines the challenges and steps in creating MMM, including data collection and model evaluation, while highlighting the tools and methodologies used. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of accurate data and the future development of MMM for better marketing effectiveness.