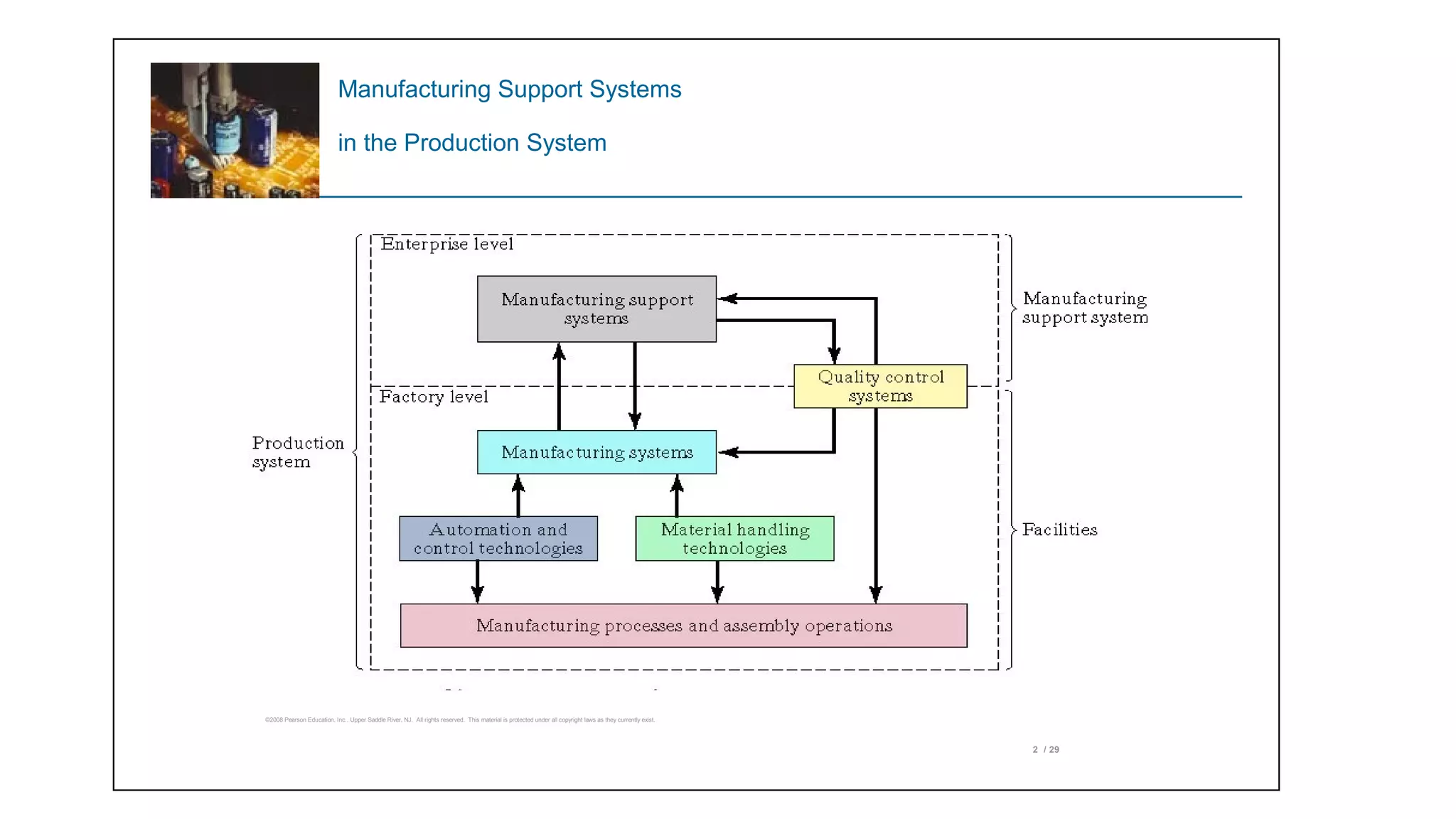
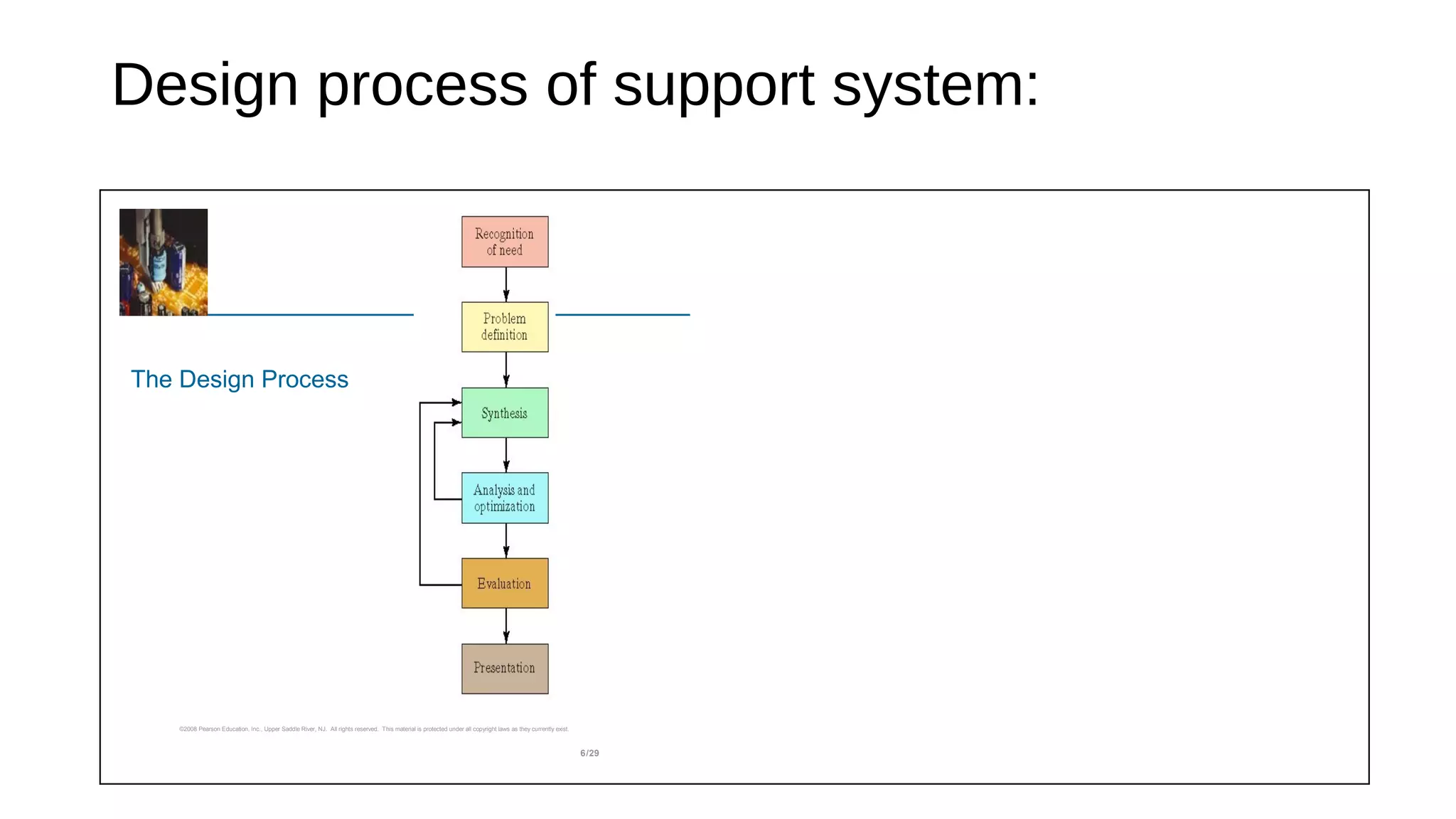
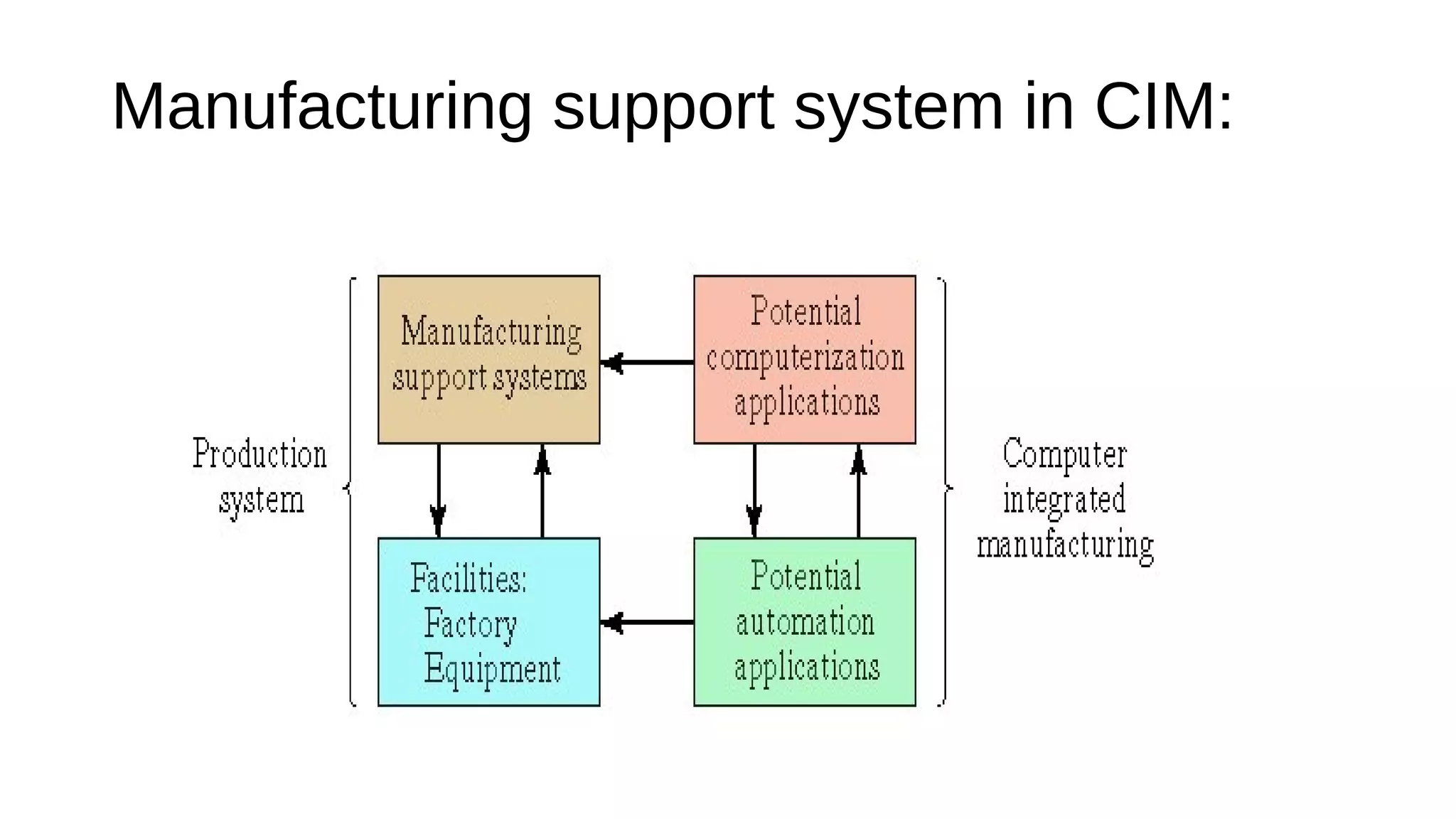
The document discusses manufacturing support systems, which are procedures used to manage production and address technical issues in manufacturing. It outlines the design process of support systems and their functions, including business operations, product design, manufacturing planning, and control. The benefits of these systems include increased productivity, reduced labor costs, improved product quality, and enhanced manufacturing efficiency.