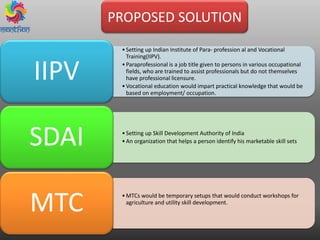
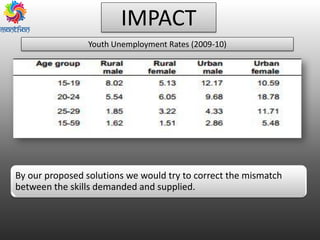
The document discusses the significant issue of youth unemployment in India, highlighting that over 80% of Indians lack marketable skills, leading to difficulty in job acquisition. It proposes the establishment of the Indian Institute of Para-Professional and Vocational Training (IIPV) and the Skill Development Authority of India (SDAI) to provide vocational training and assist in skill identification for better employment opportunities. Additional elements include mobile training camps and certification courses to bridge the gap between skills demanded by employers and those supplied by the workforce.