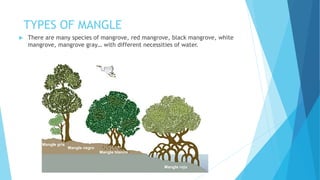
Mangroves are salt-tolerant trees that grow in the intertidal zone near freshwater outlets in tropical and subtropical coastlines. They provide habitat for numerous species and protect coastlines from strong winds, waves, and tidal waves. Mangroves play an important role in absorbing carbon from the atmosphere and providing nutrients to other marine habitats. There are many species of mangrove trees with different water needs, including red, black, white, and grey mangroves. Mangroves support a diverse wildlife including marine, mangrove, and terrestrial species and are facing threats from coastal development, climate change, and illegal logging.