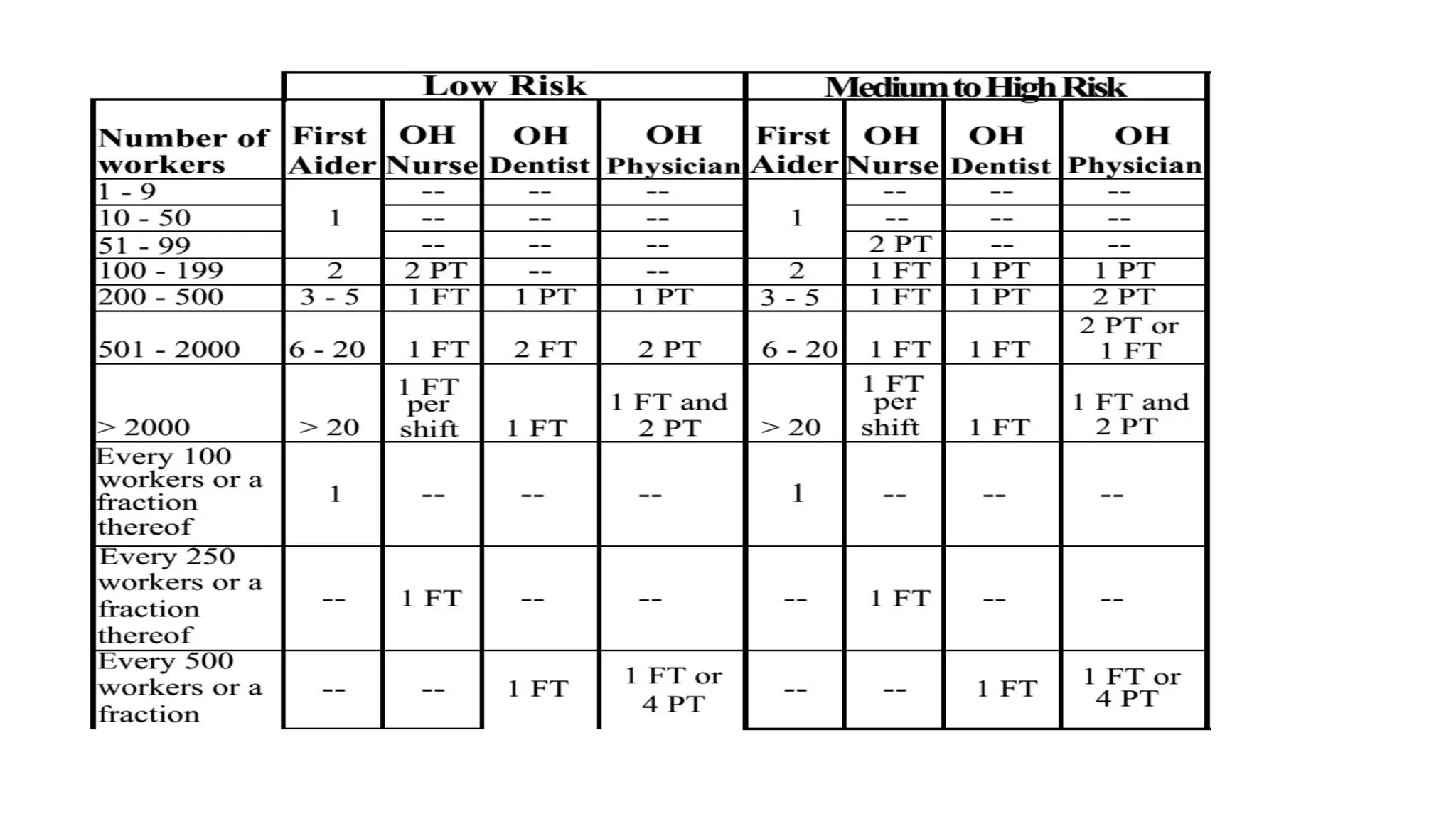
The document outlines the roles and responsibilities related to occupational safety and health (OSH) in the workplace, highlighting the necessity of training, hazard recognition, and compliance with legislation. It presents statistical data on occupational injuries and emphasizes the importance of health programs to prevent work-related diseases. Additionally, it details the legal framework and employer/worker duties under Philippine OSH standards, including rights to safety, reporting, and personal protective equipment.