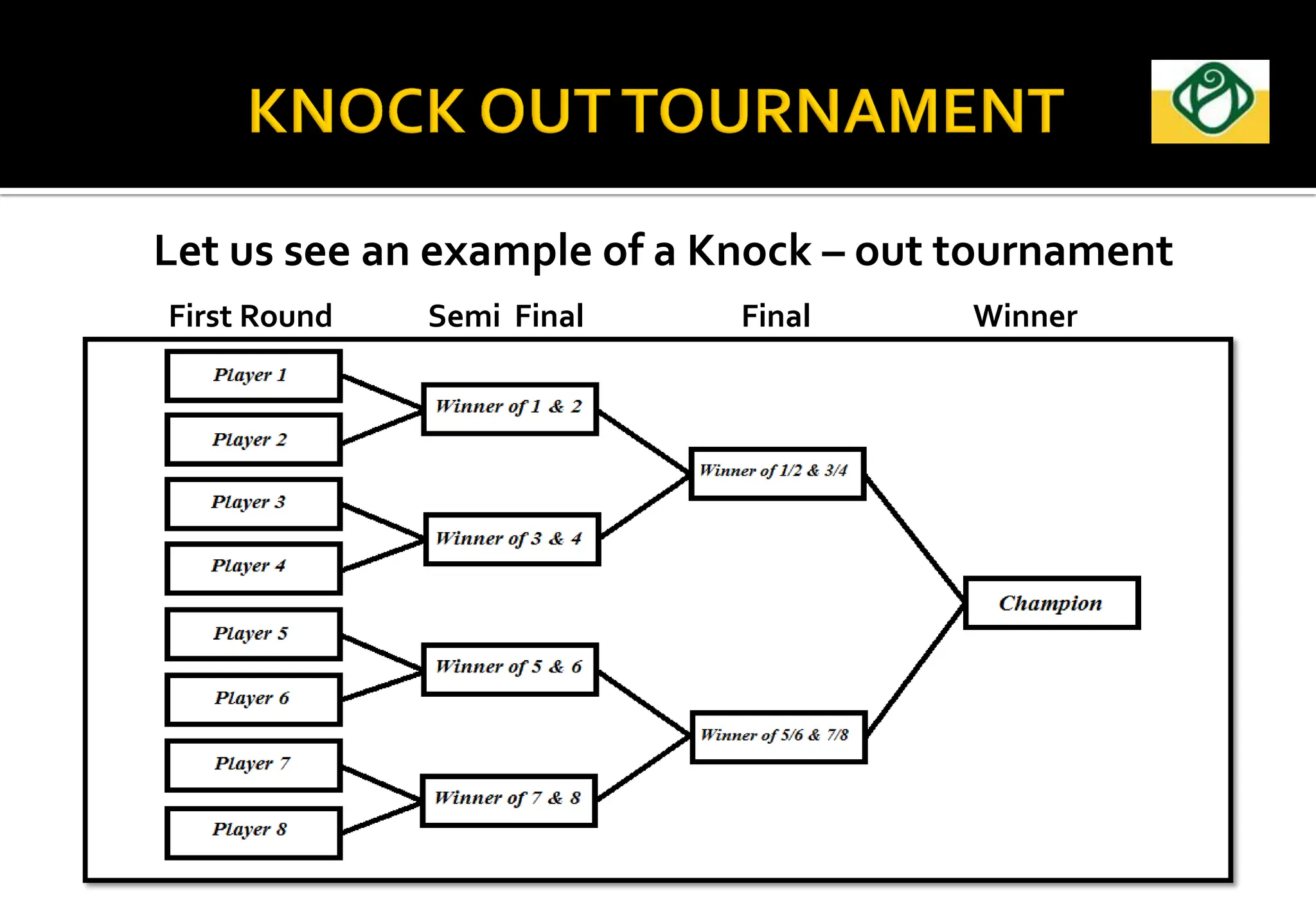
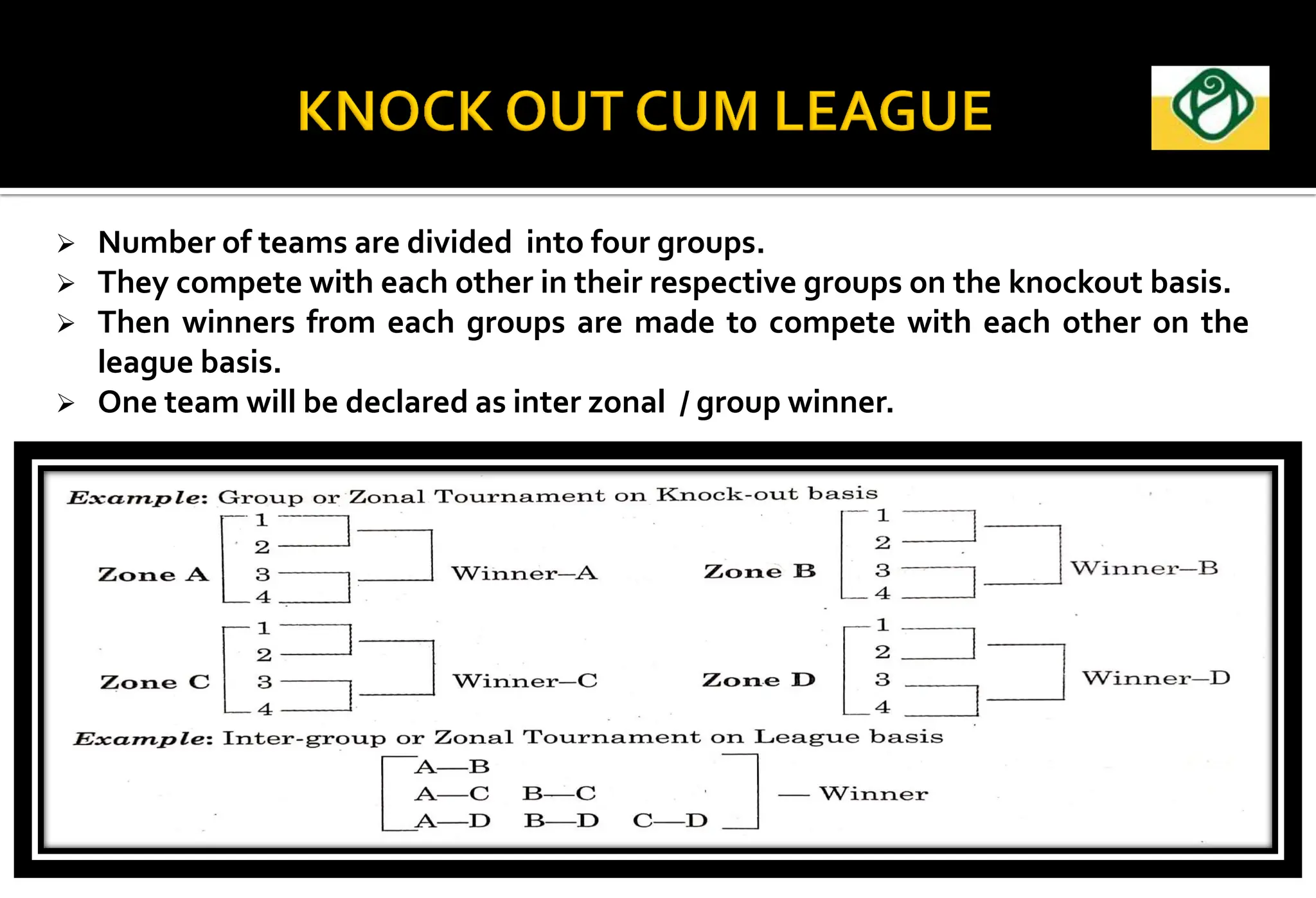
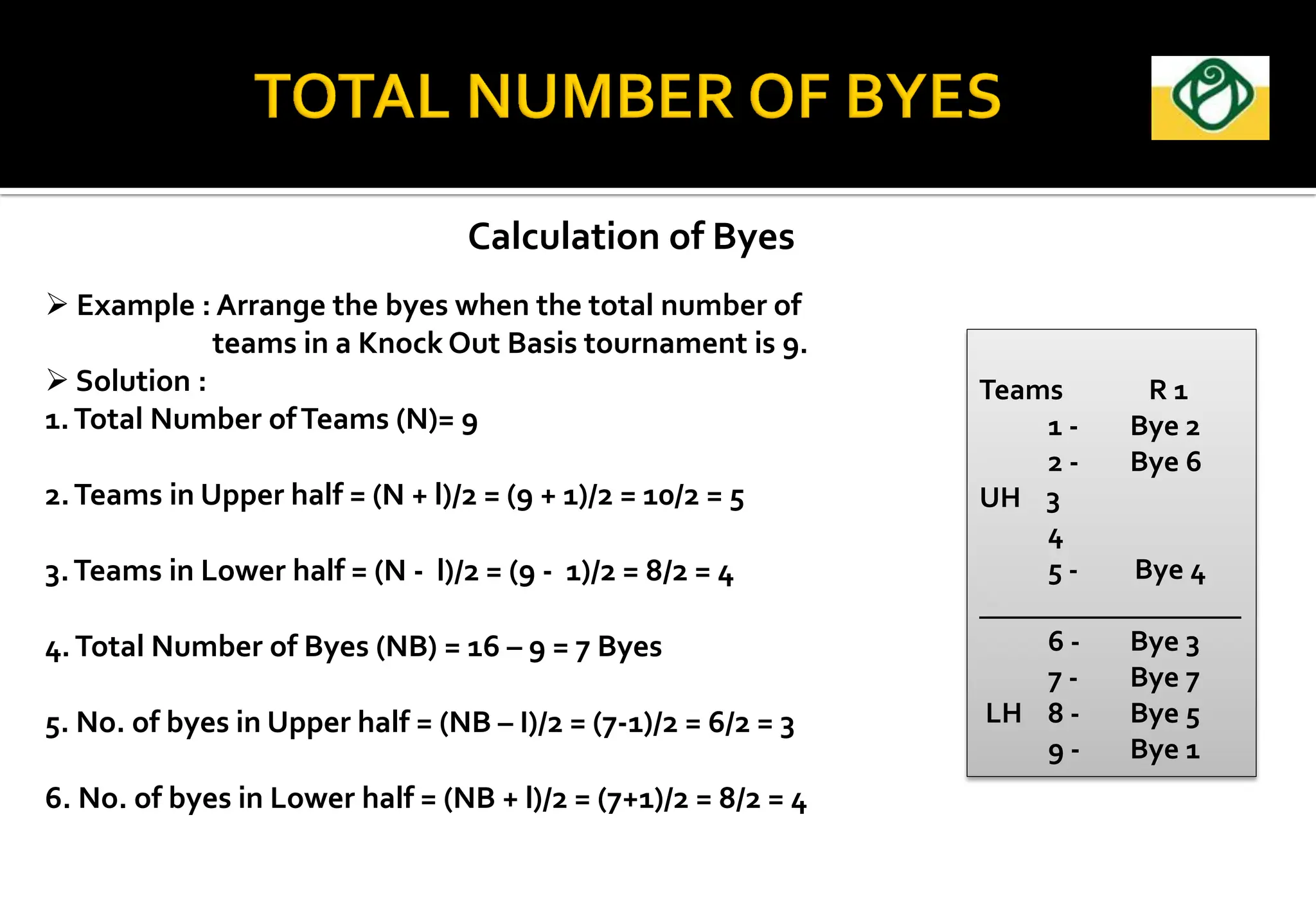
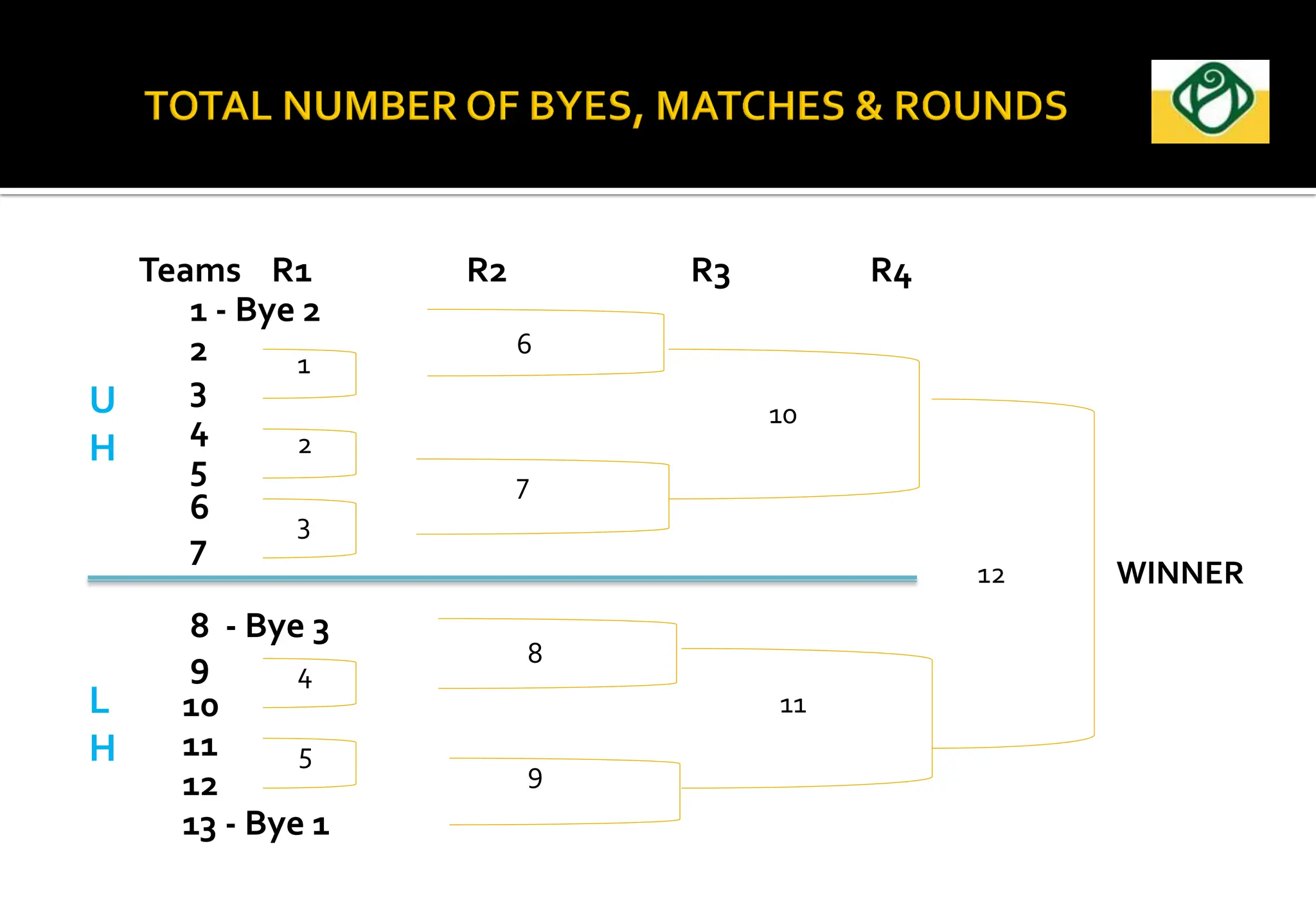
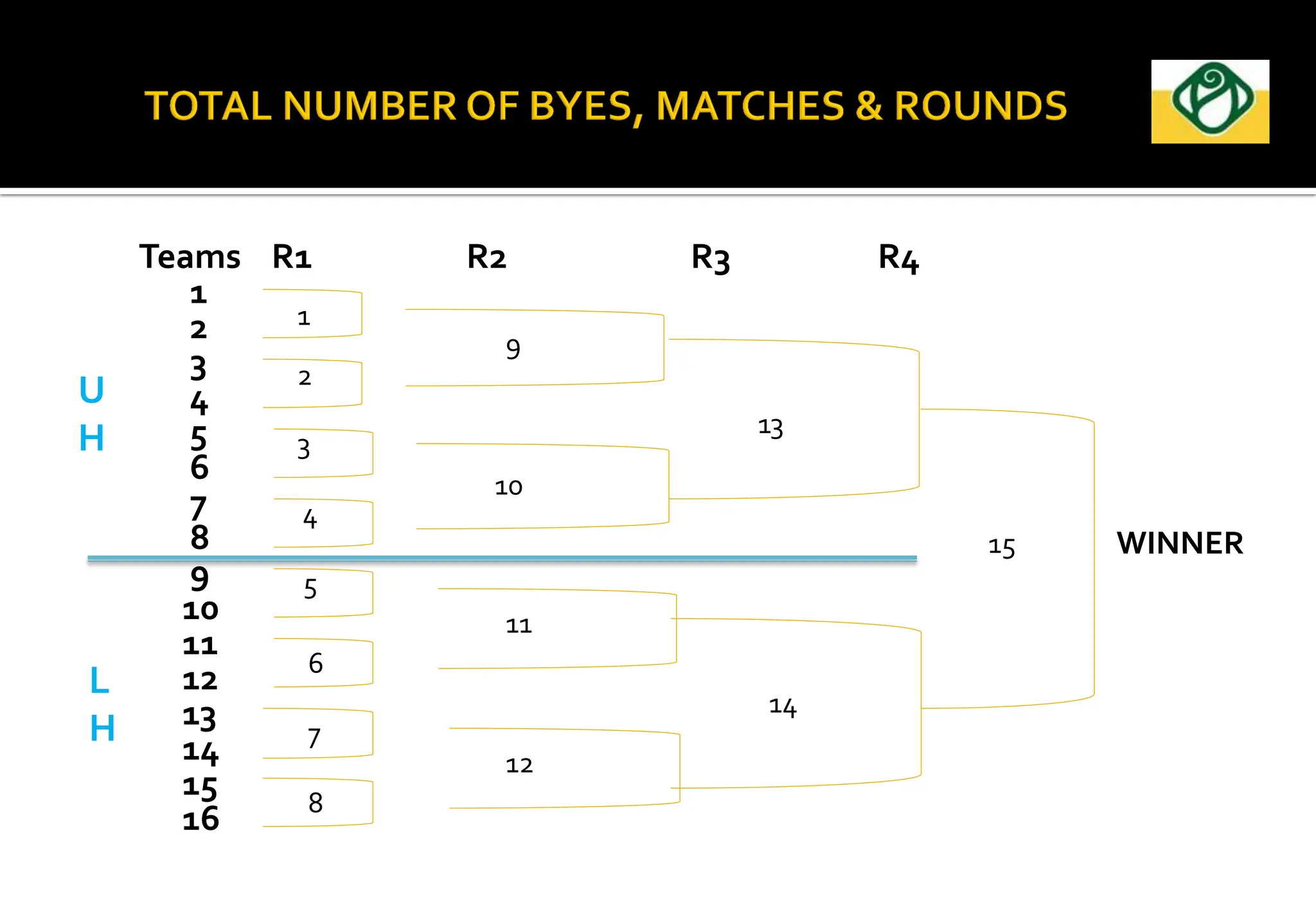
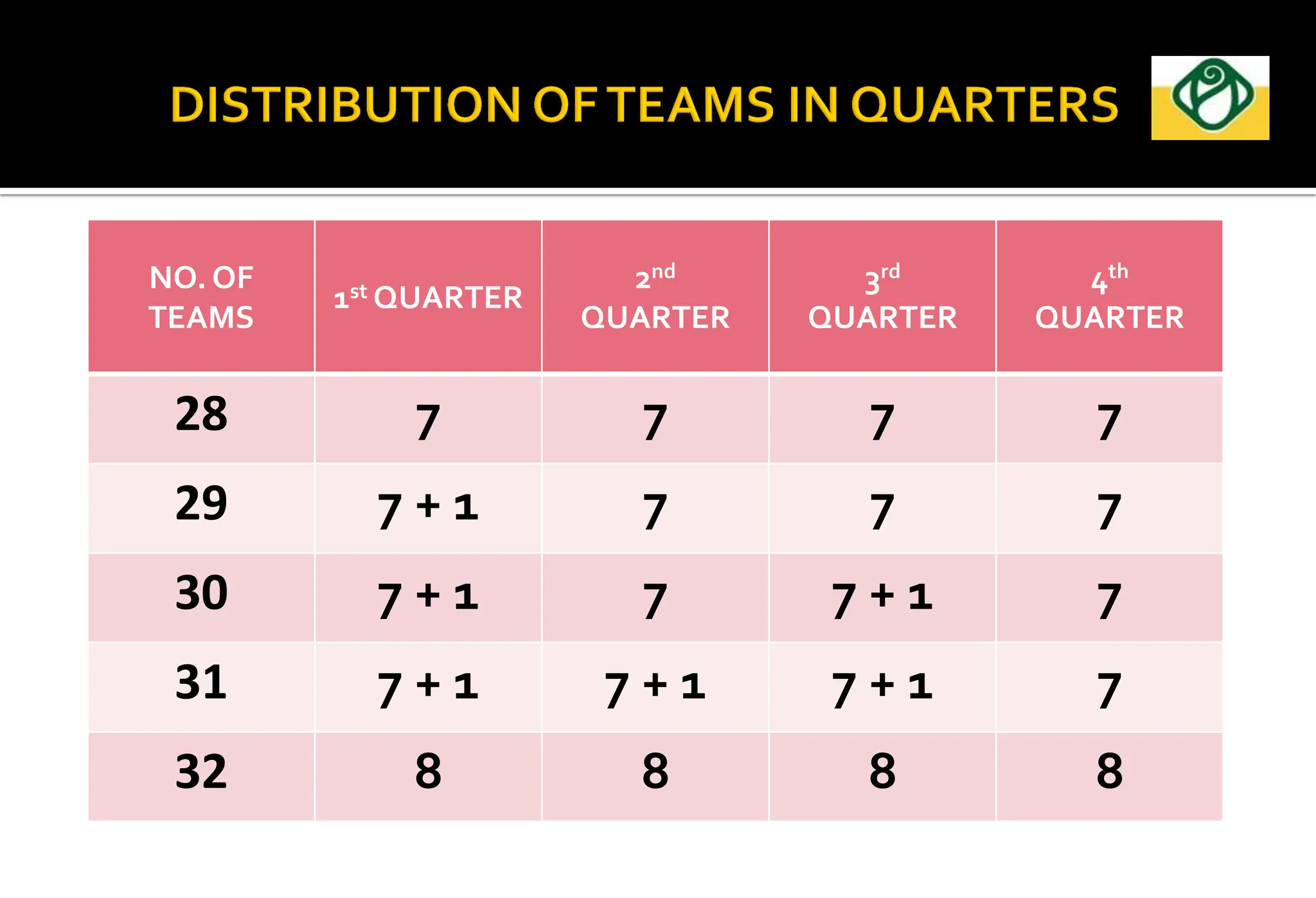
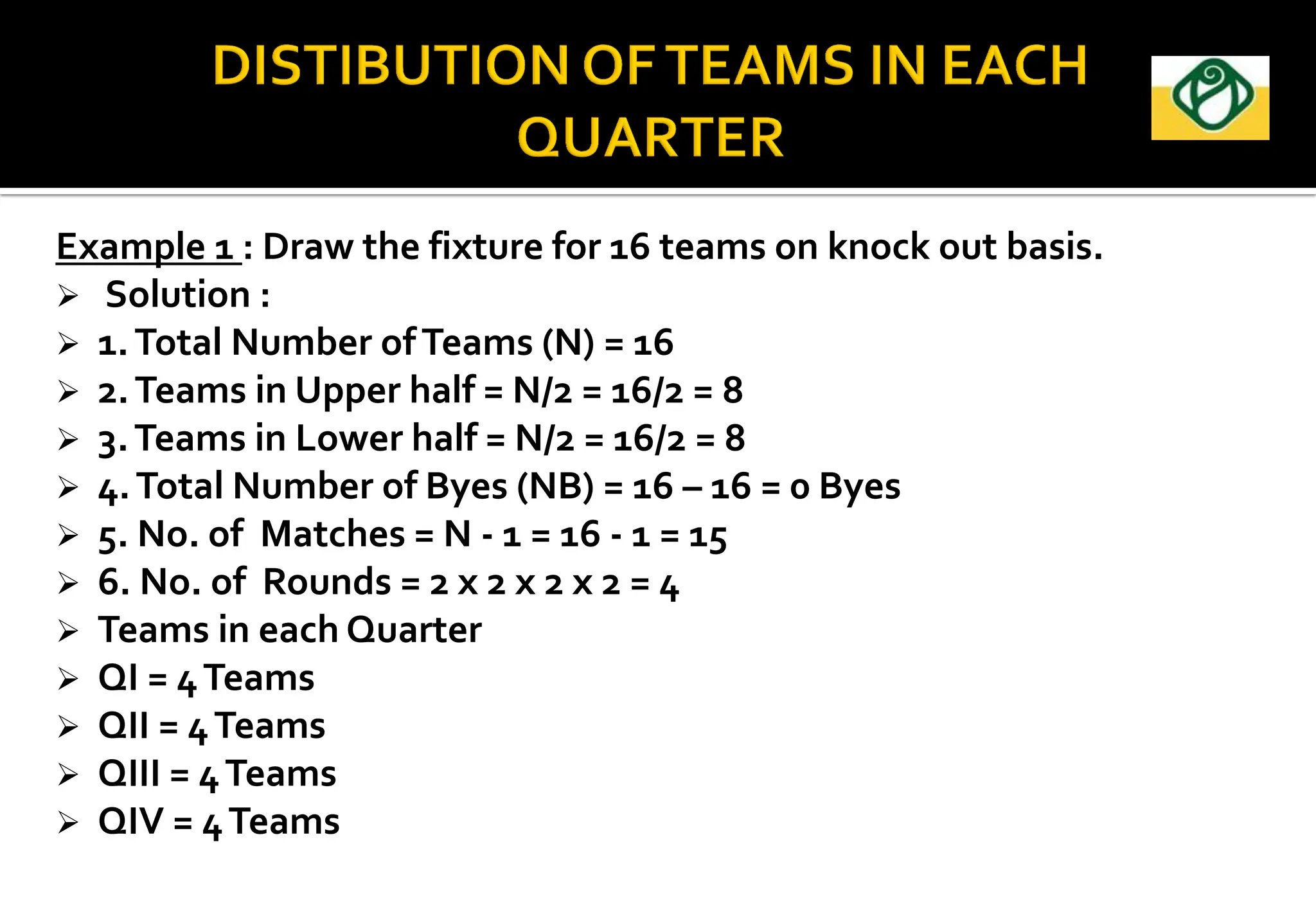
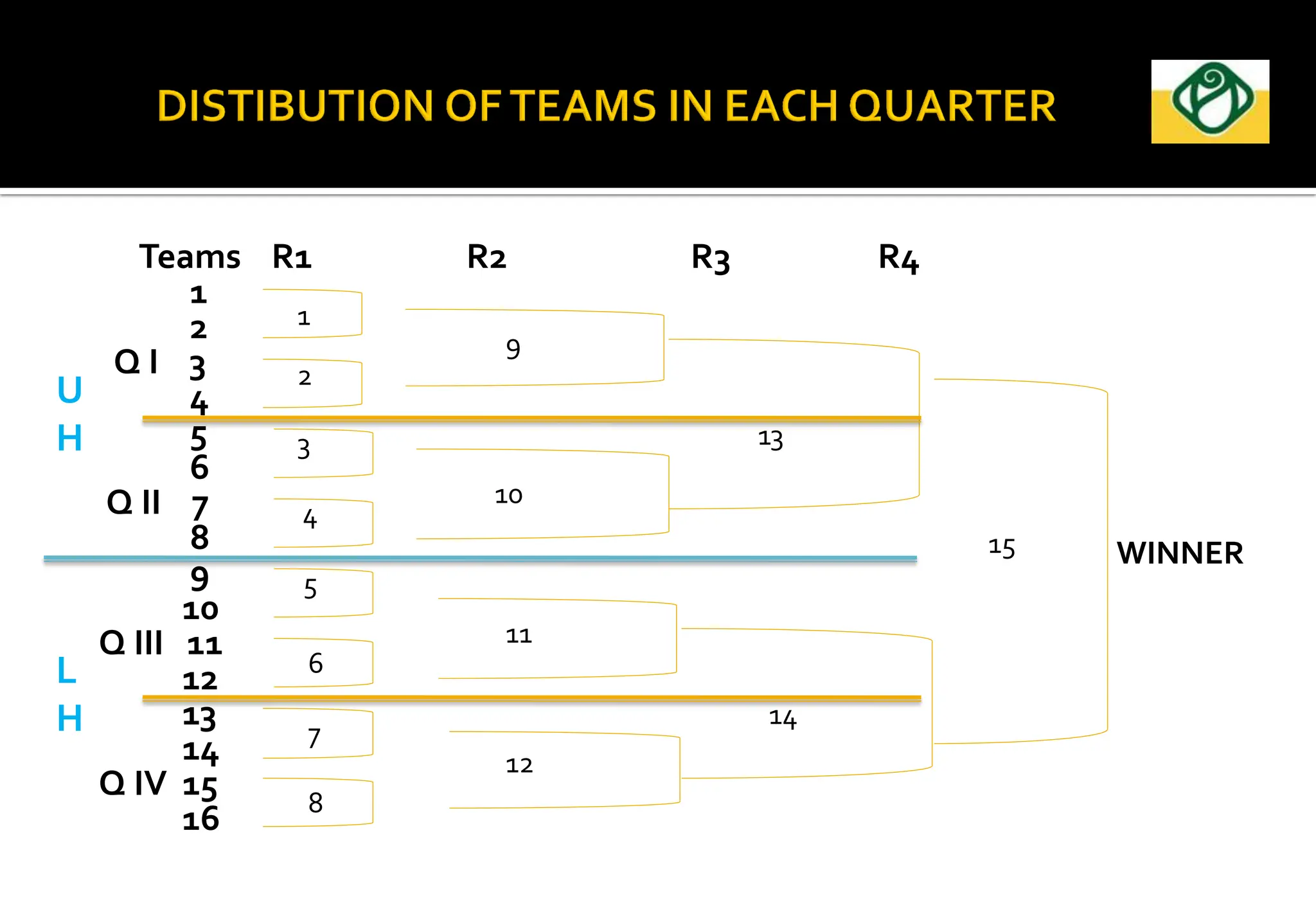
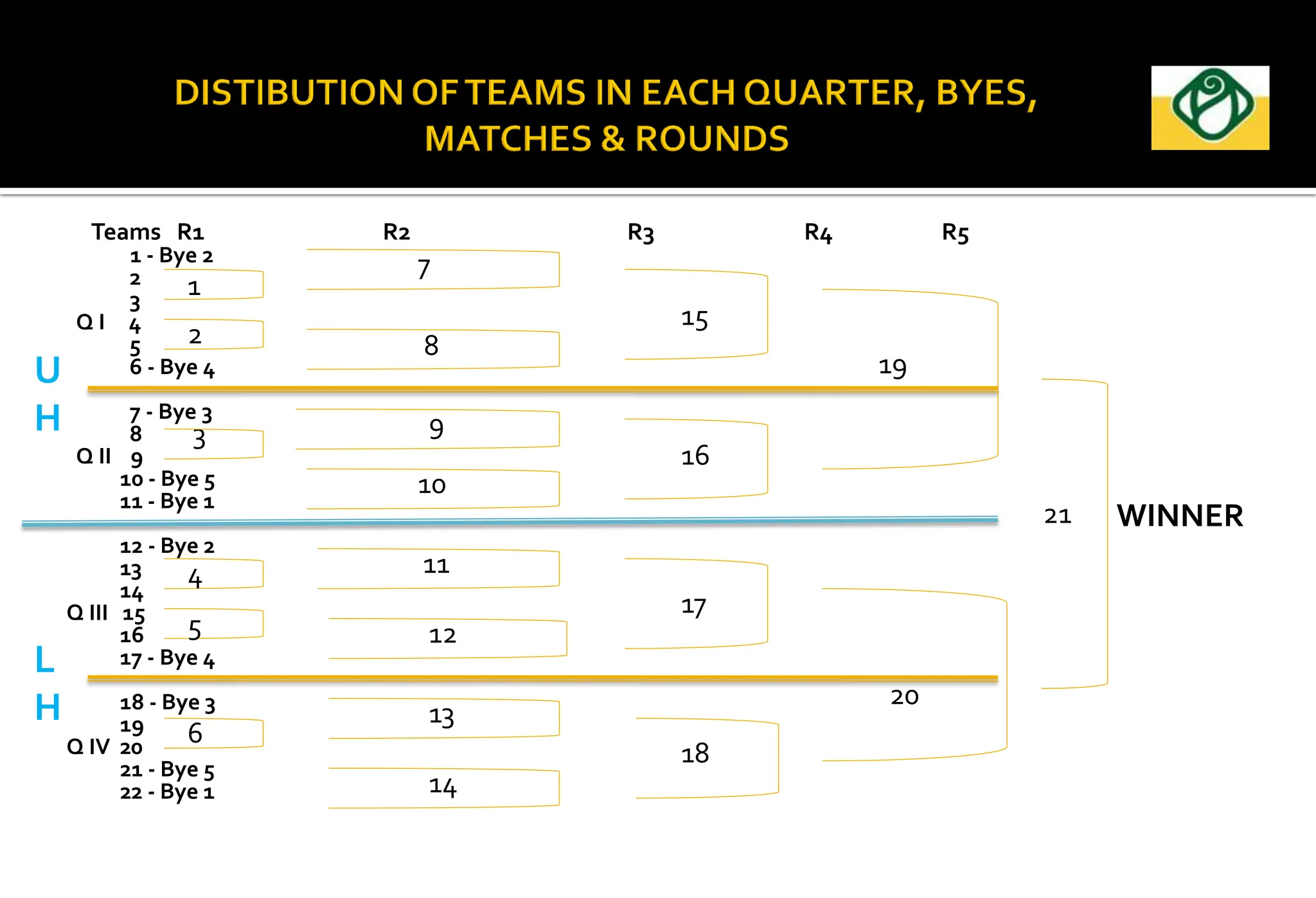
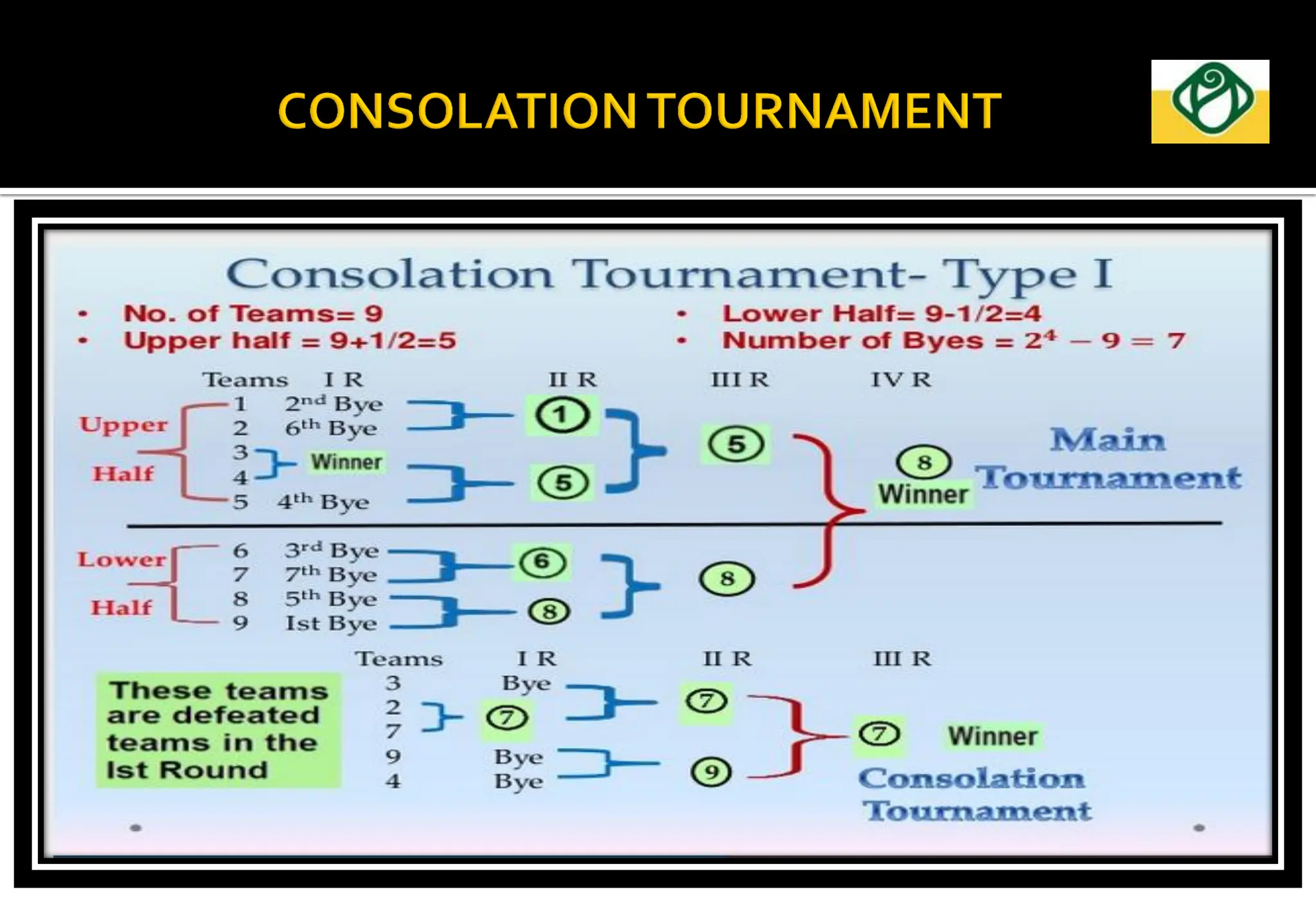
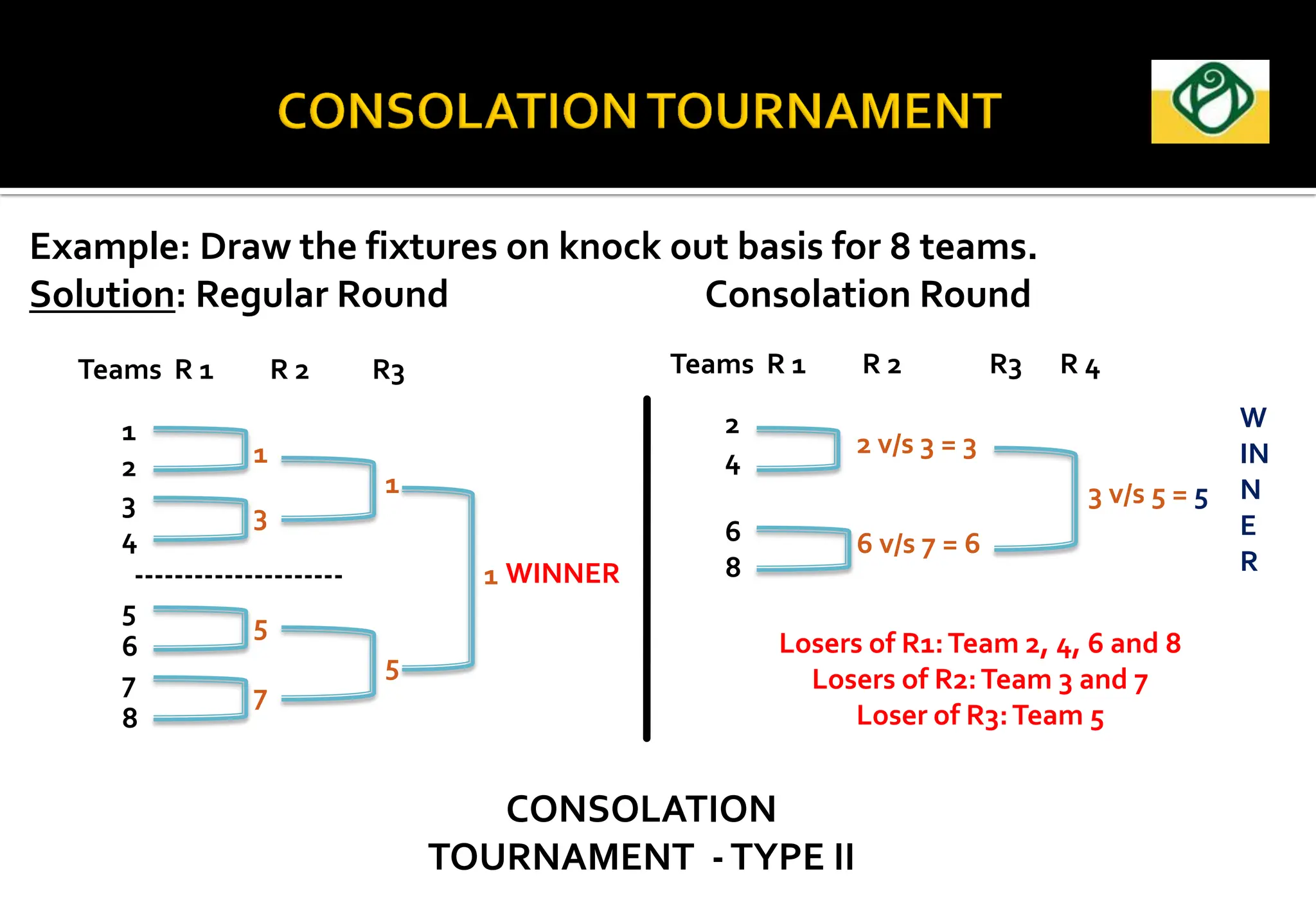
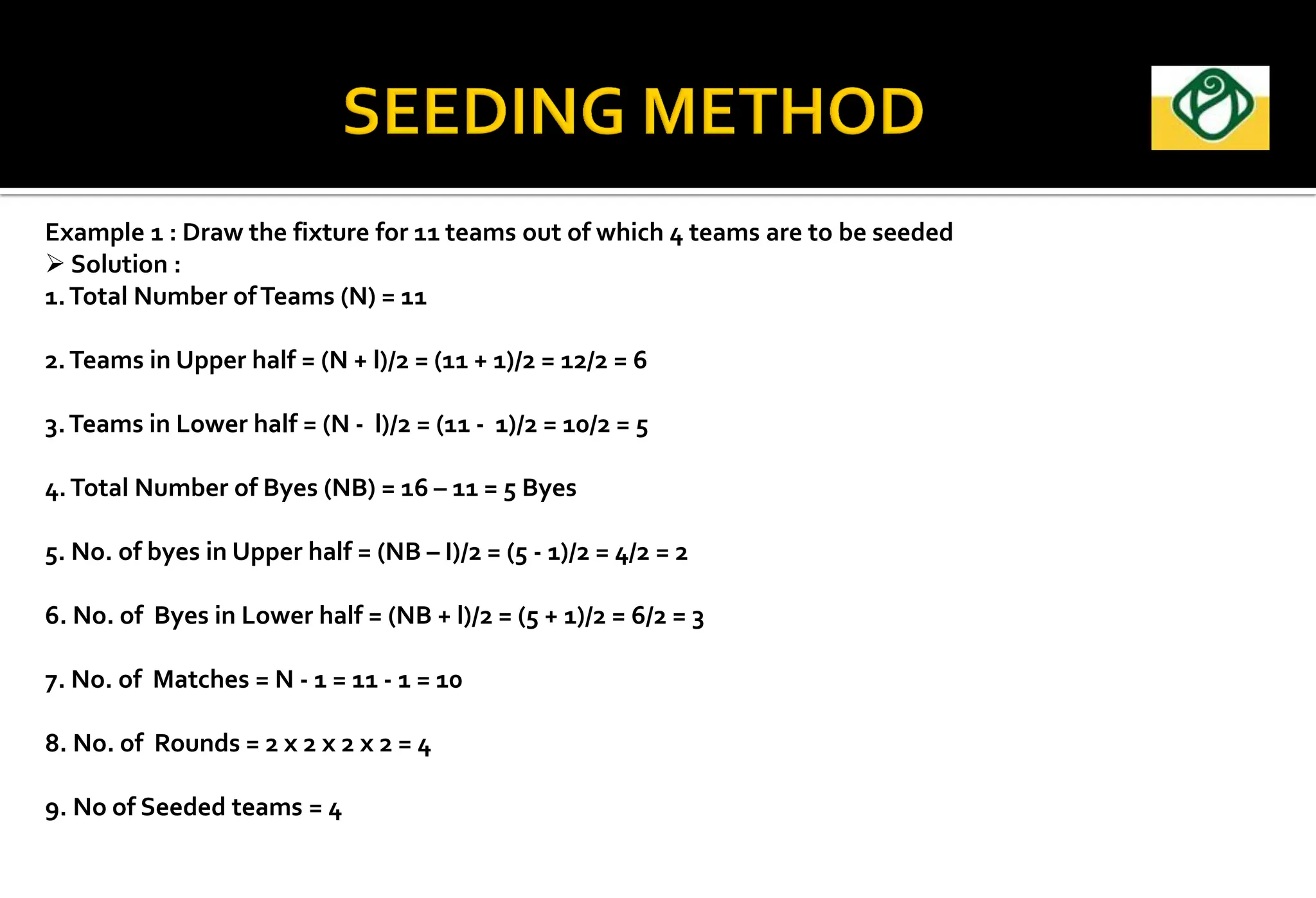
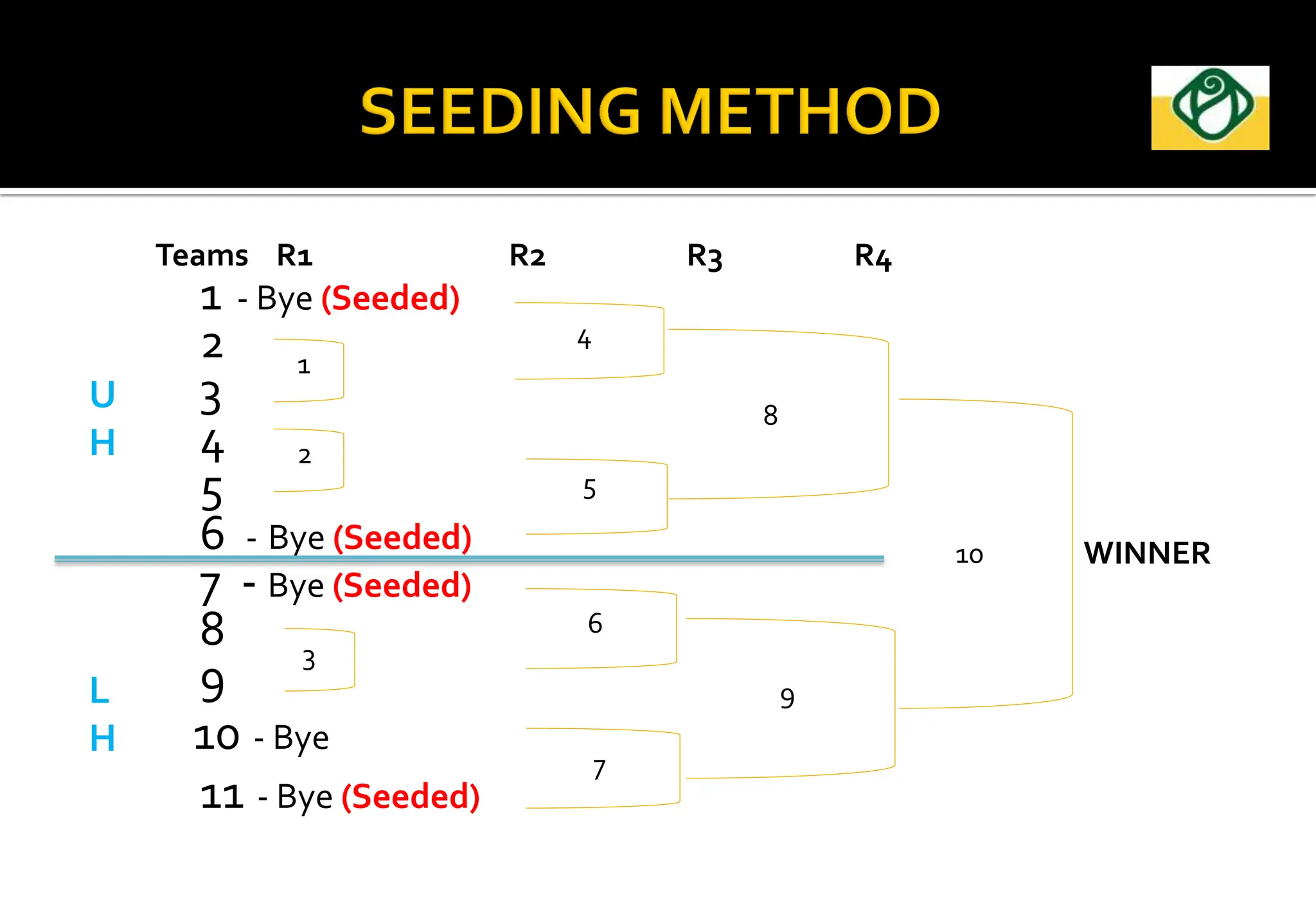
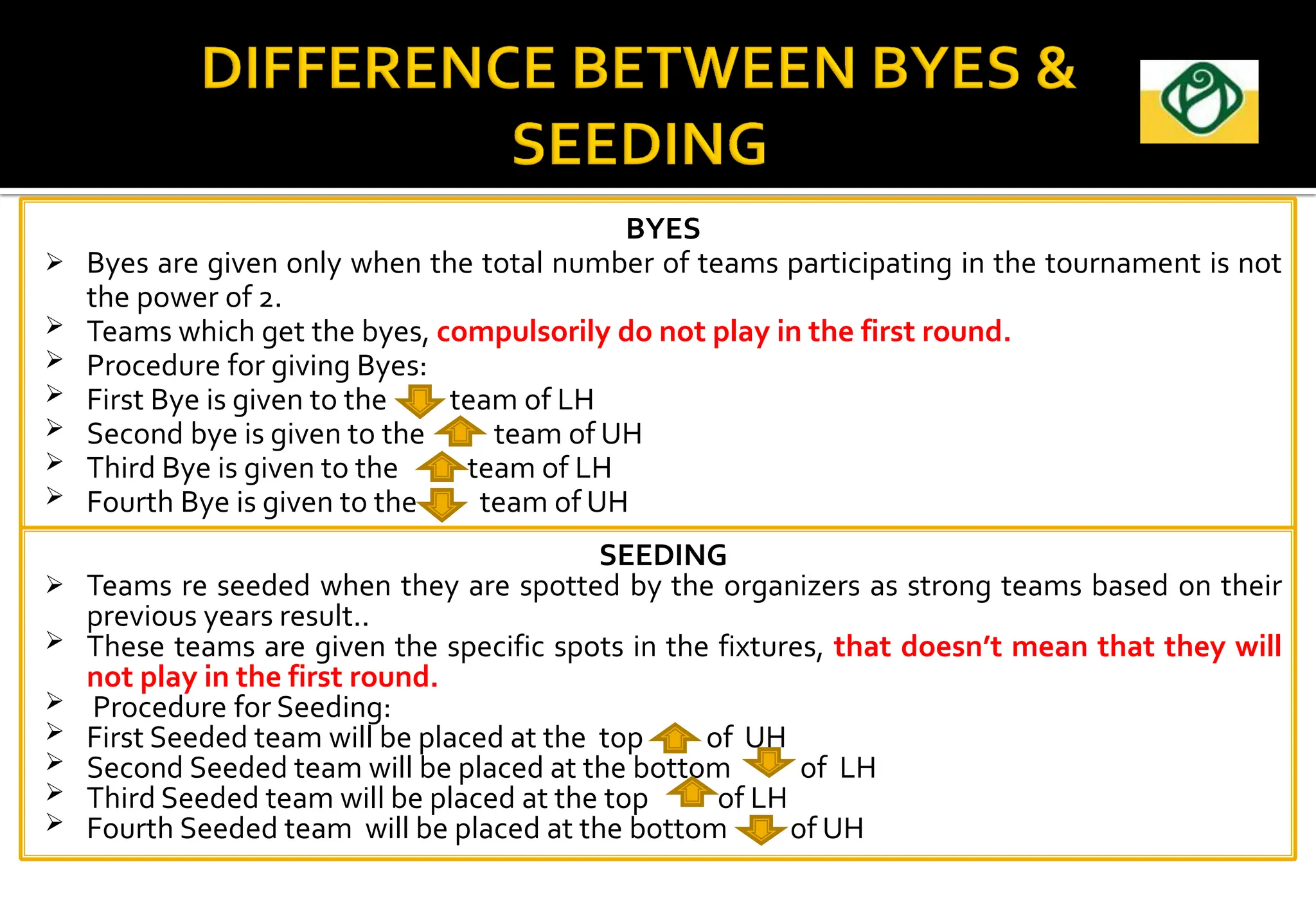
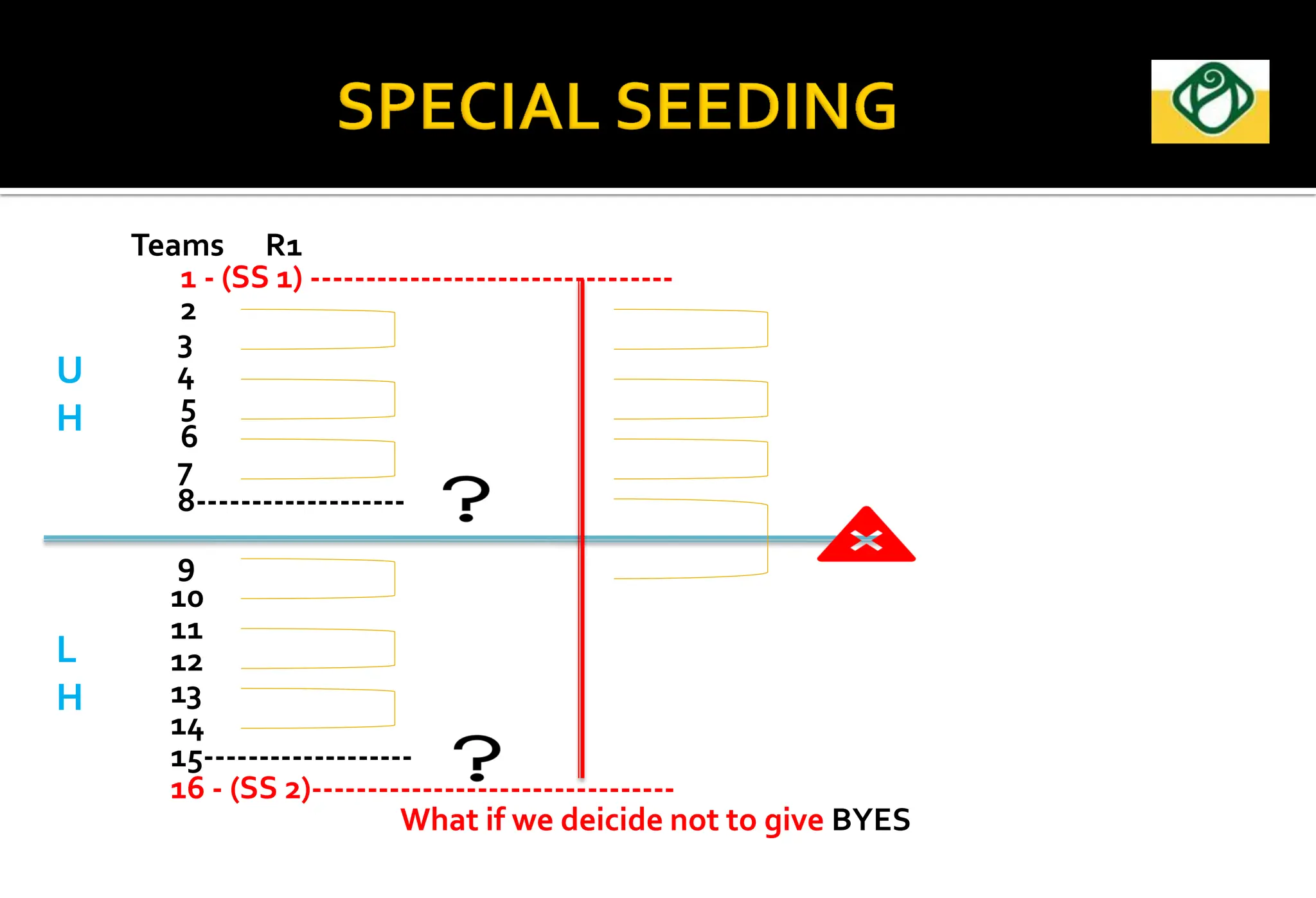
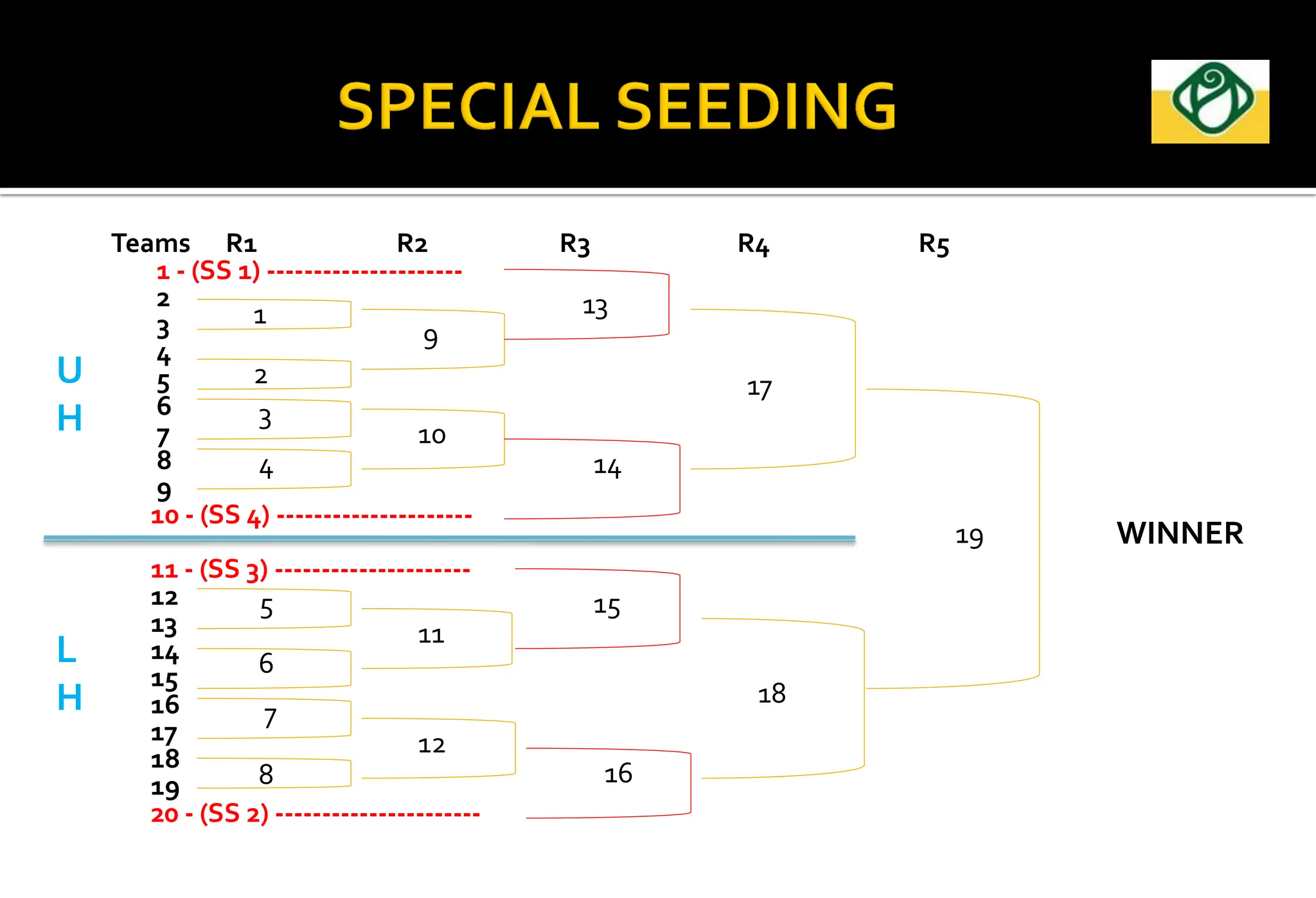
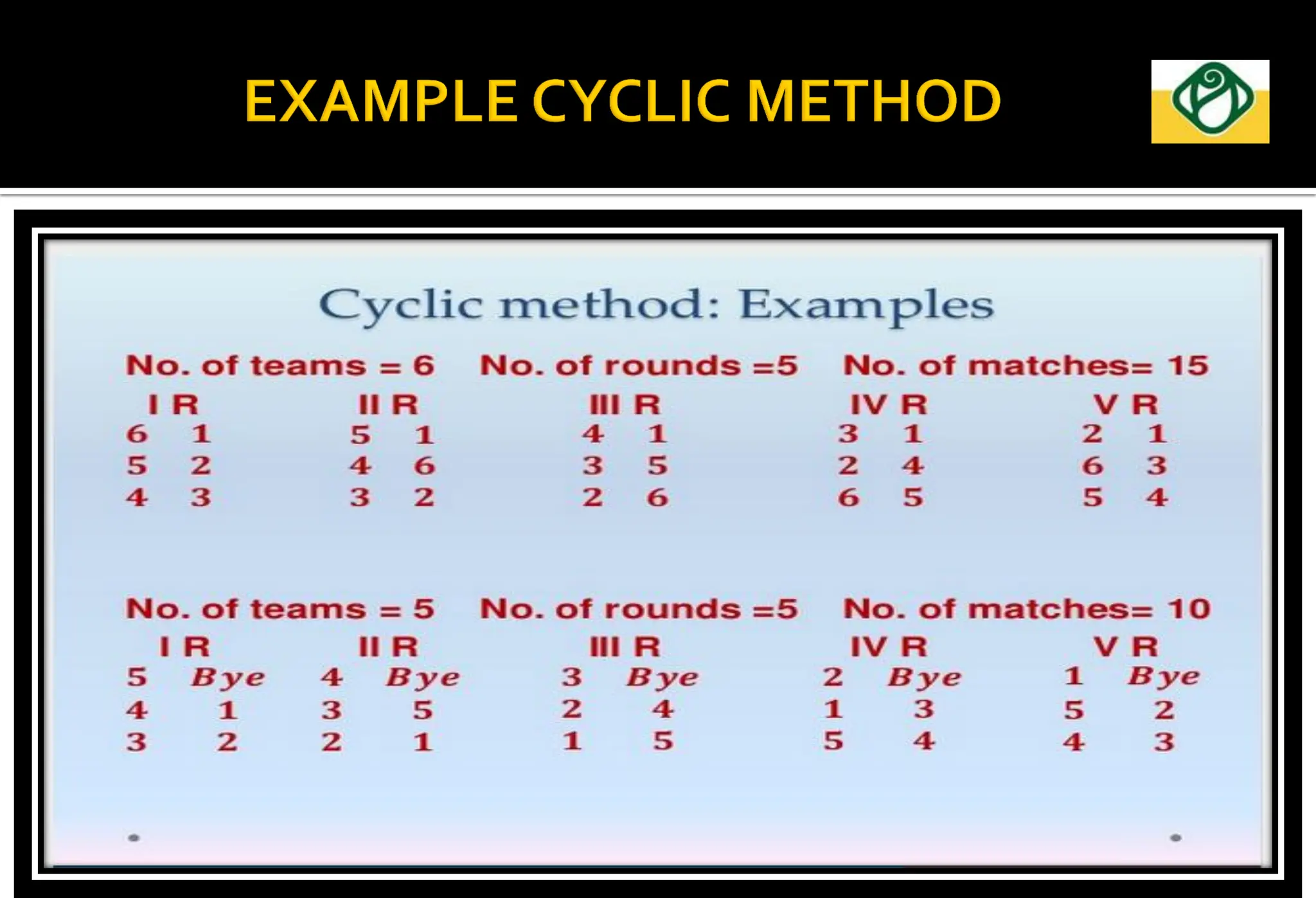
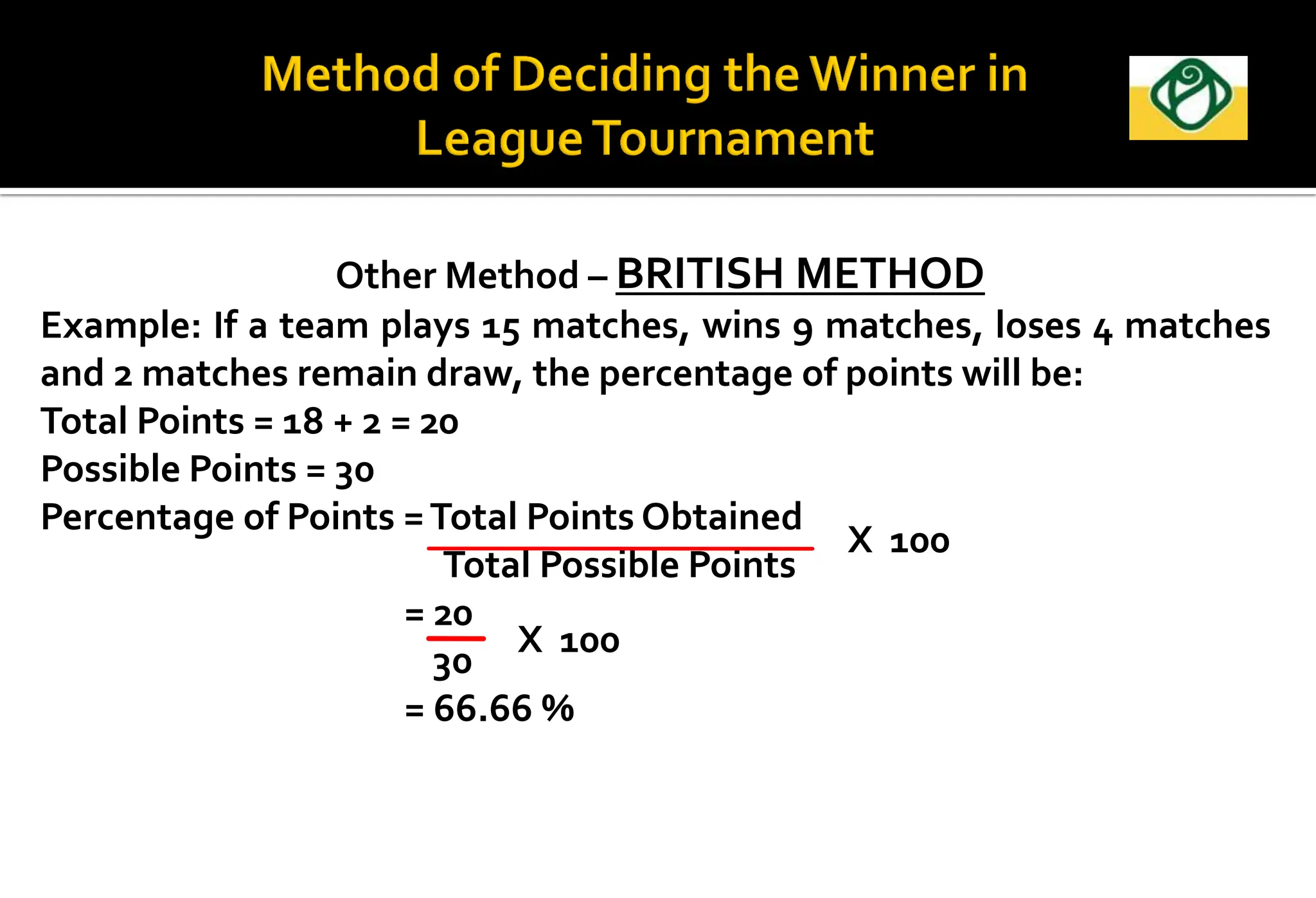
The document covers the essential aspects of planning and managing sporting events, including definitions, objectives, and the functions of management such as planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling. It details various types of tournaments, such as knock-out and league formats, and outlines the responsibilities of different committees involved in event management. Effective planning is emphasized as crucial for the success of sports events, impacting organization and execution.