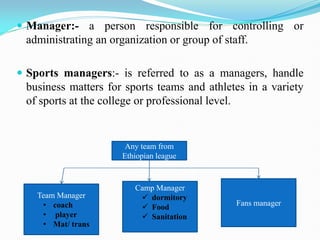
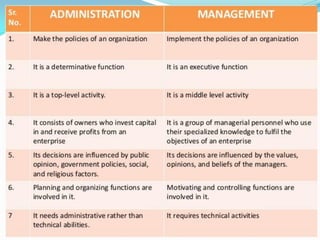
The document discusses the organization and management of the sports industry, highlighting that it encompasses a broad range of entities including venues, teams, and various organizations involved in sports-related activities. It defines key concepts such as organization, sports management, administration, and the functions and roles of managers within sports entities. Additionally, it touches upon the importance of planning, organizing, staffing, and leadership styles in achieving organizational goals while emphasizing the need for ethical practices in sports management.