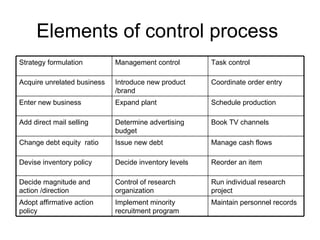
Management control systems (MCS) involve hierarchical control at three levels - strategic, business unit, and operational. Strategic control deals with long-term planning over 3 years, business unit control with annual plans and budgets, and operational control with monthly/quarterly operating plans. MCS define objectives, key performance factors, measure deviations, and evolve alternative action plans. They are a problem-solving and decision-making process involving managerial judgment. MCS evaluate, monitor, and control sub-units to efficiently allocate resources and achieve goals. Actual performance is compared to plans/budgets to identify gaps and provide managers with resources. MCS are not idealistic and do not require strict adherence to plans, instead focusing on discovering better