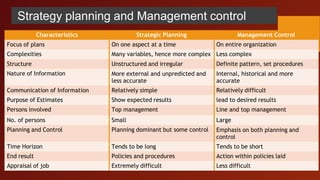
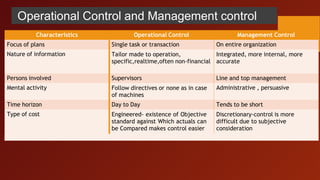
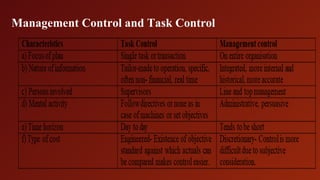
Management Control Systems (MCS) are processes through which management influences organizational members to effectively execute strategies, involving aspects such as planning, coordinating, communicating, and evaluating performance. MCS operates between strategy formulation and operational control, emphasizing the alignment of individual goals with corporate objectives, and relies on both formal systems like budgets and informal factors such as organizational culture. The document outlines the importance of strategic planning, the characteristics of effective MCS, and the need for motivation and information systems to ensure success in achieving organizational goals.