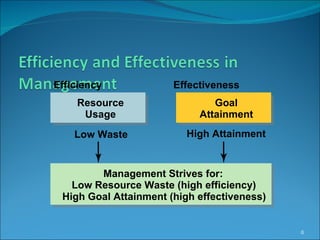
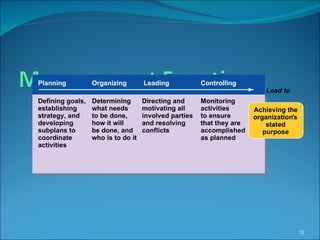
The document provides an overview of management principles, defining management as the coordination of group activities to achieve objectives. It outlines different managerial levels (first-line, middle, and top managers) and emphasizes key functions such as planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Additionally, it discusses Mintzberg's management roles, including interpersonal, informational, and decisional roles that managers embody to ensure organizational effectiveness.