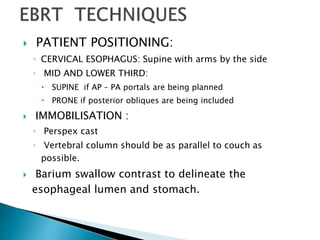
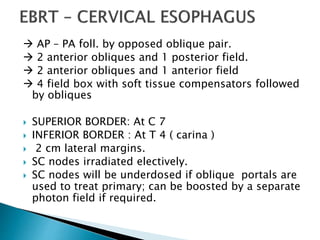
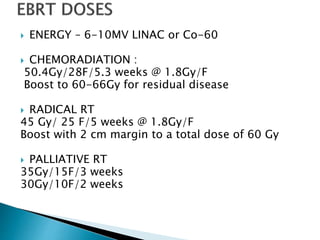
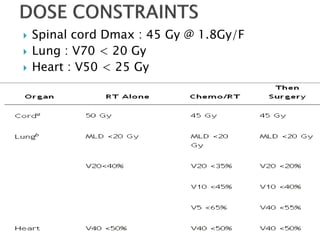
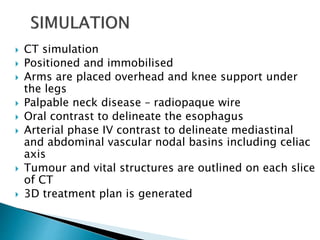
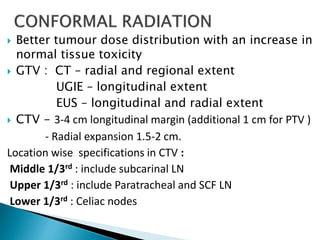
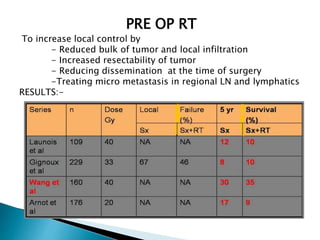
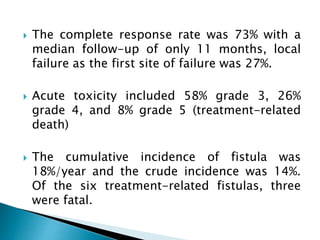
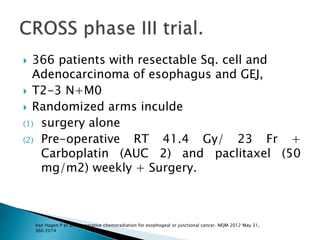
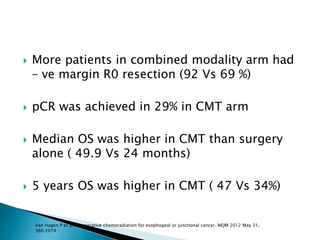
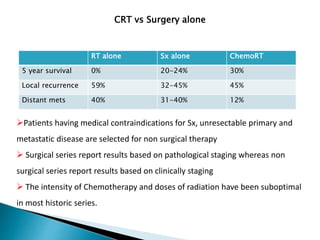
This document discusses esophageal cancer. Some key points:
- Squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma are the most common histologies. Risk factors include smoking, alcohol, obesity, and Barrett's esophagus.
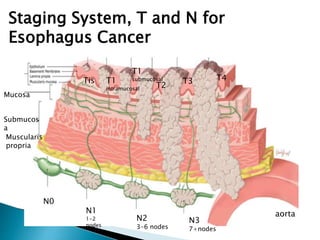
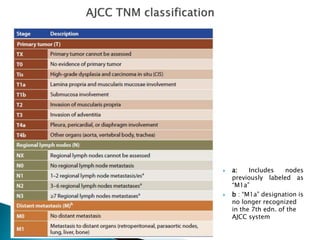
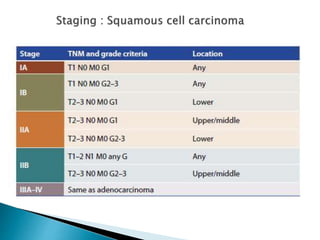
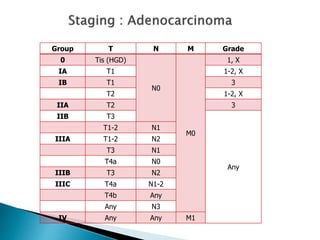
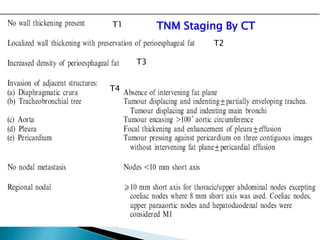
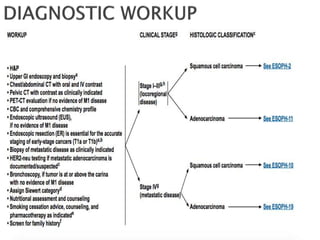
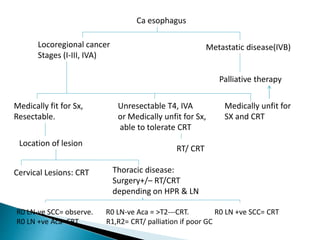
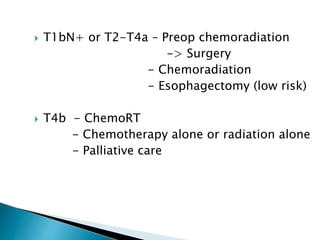
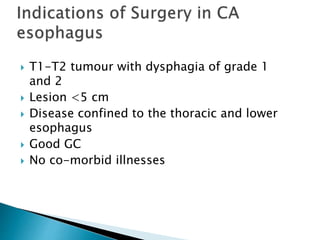
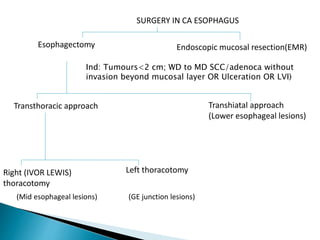
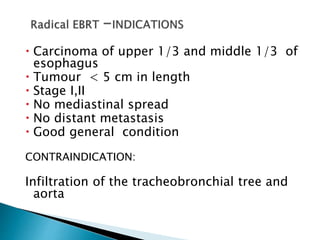
- Staging uses the TNM system. Treatment depends on stage but may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination.
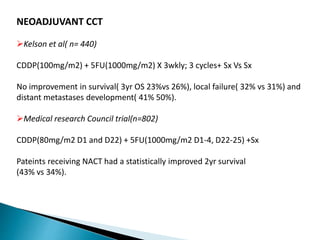
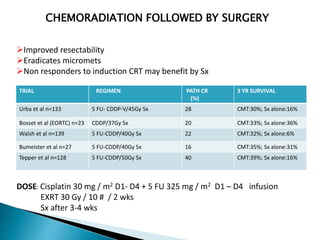
- For locally advanced stages, neoadjuvant chemoradiation can improve resectability and survival compared to surgery alone. The MAGIC trial showed improved survival with perioperative chemotherapy compared to surgery alone.
- Prognosis remains poor with 5-year survival rates of 15-20%, though outcomes have improved with multimod