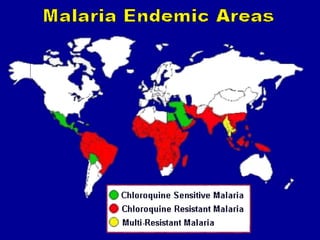
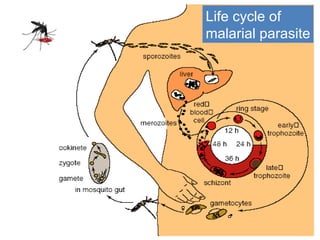
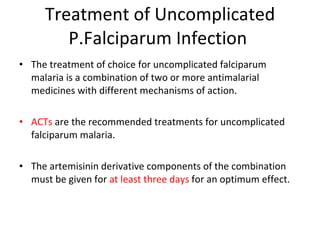
Malaria remains a major global health problem, infecting over 240 million people annually and killing over 1 million, mostly children in Africa. It is caused by Plasmodium parasites and transmitted via mosquito bites. Diagnosis and treatment of both uncomplicated and severe malaria is discussed. Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) are the recommended treatments. For severe malaria, artesunate is the treatment of choice due to its superiority over quinine in clinical trials. Malaria control efforts aim to expand access to effective prevention and treatment.