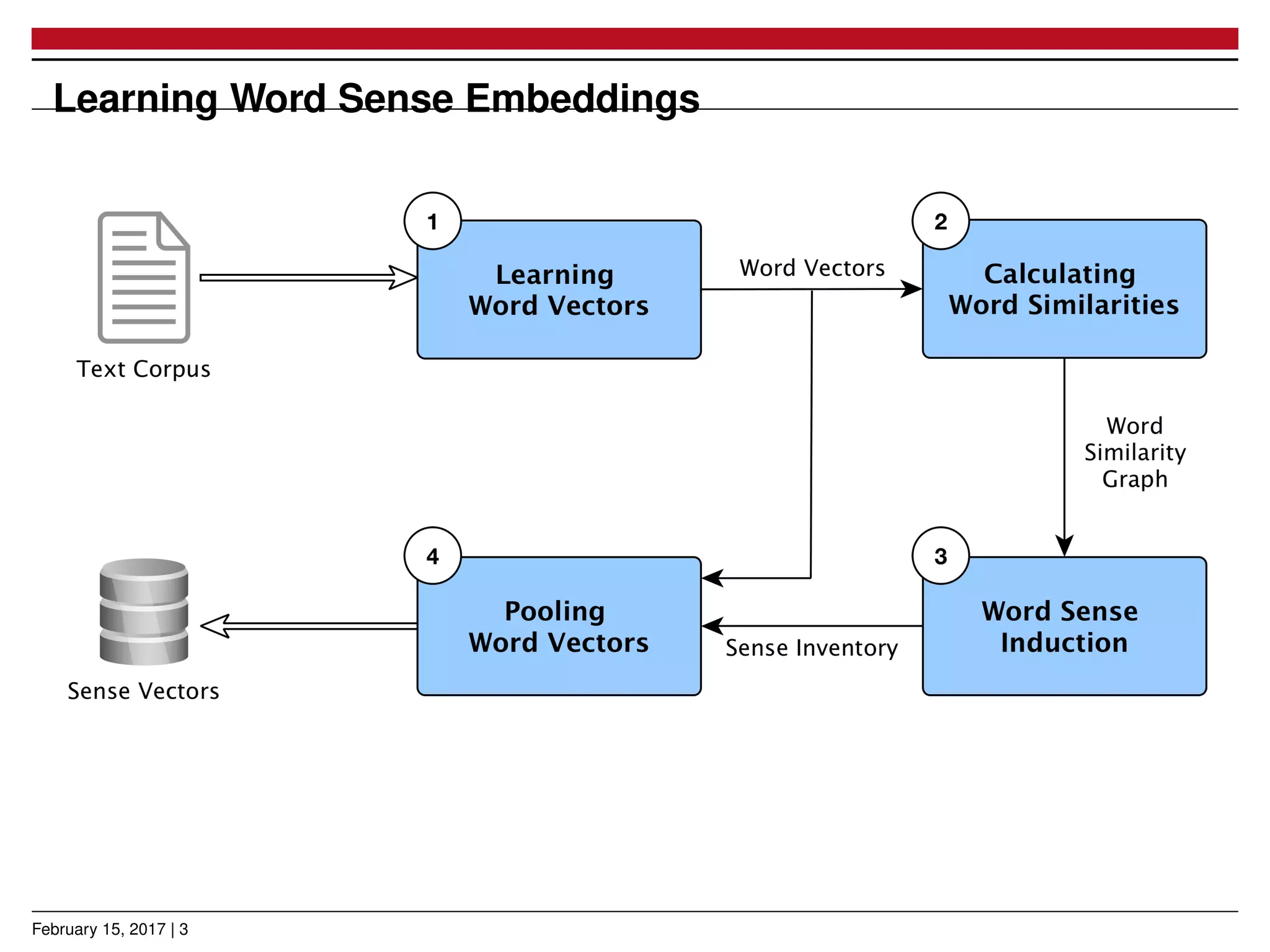
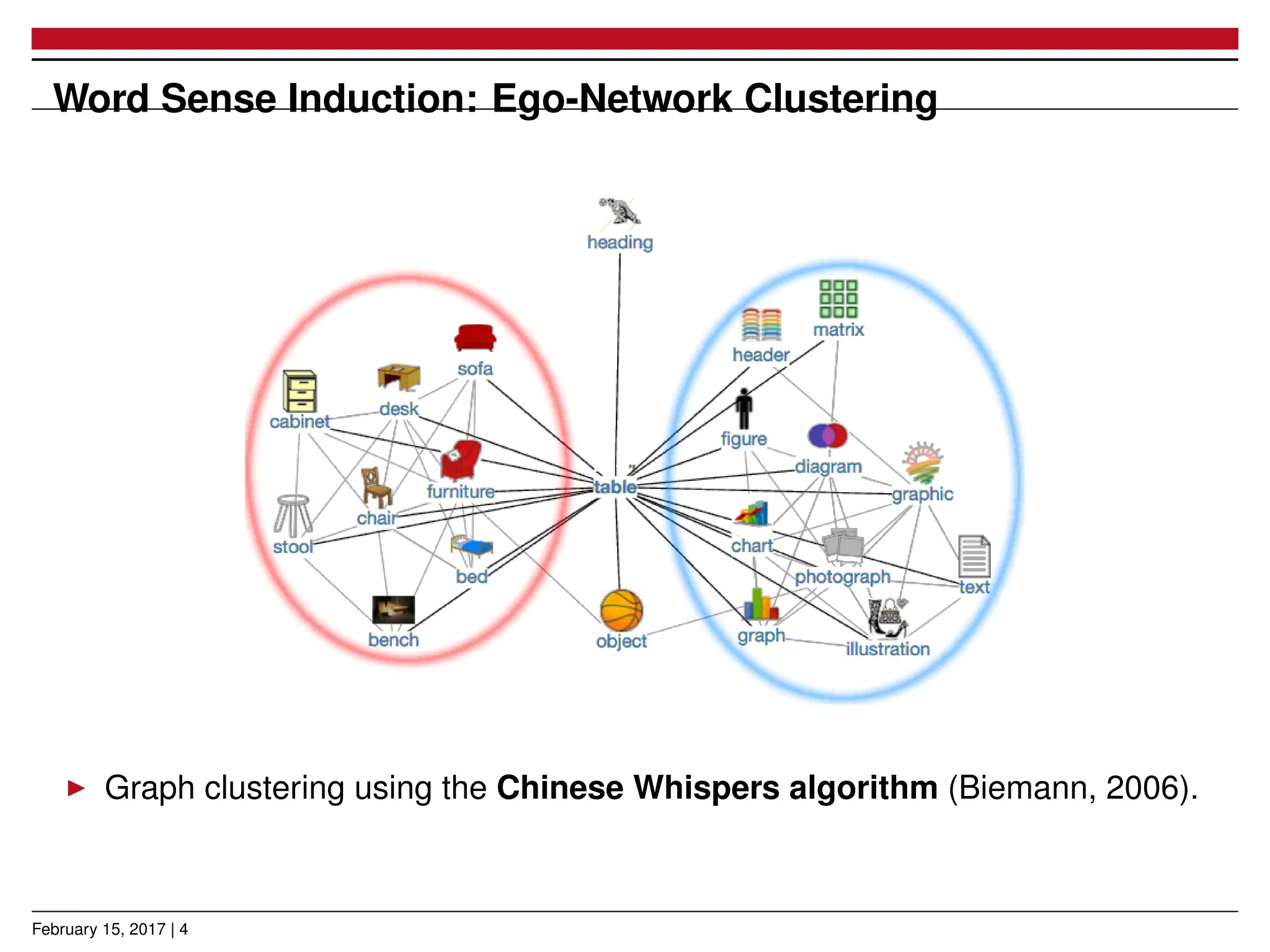
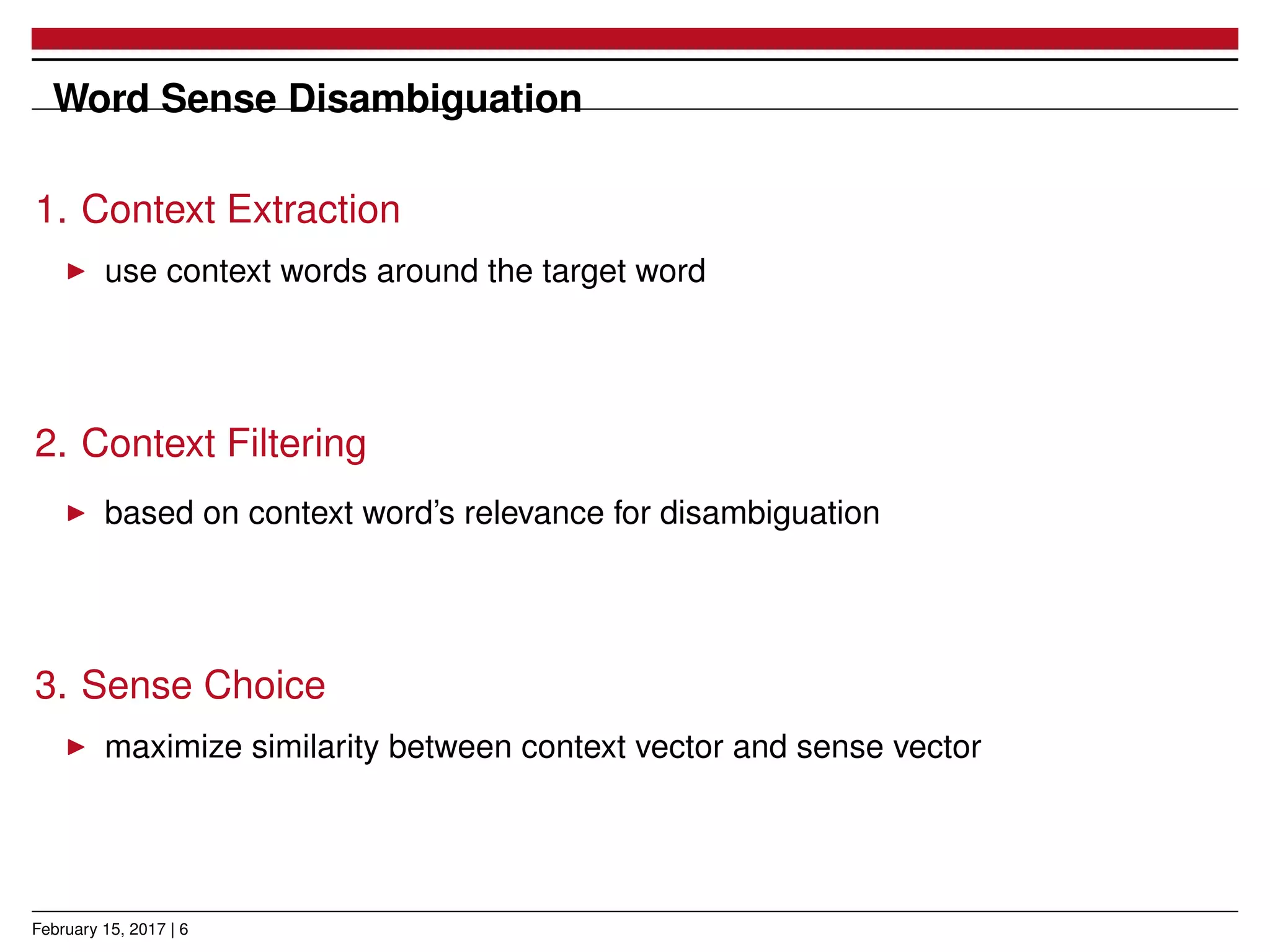
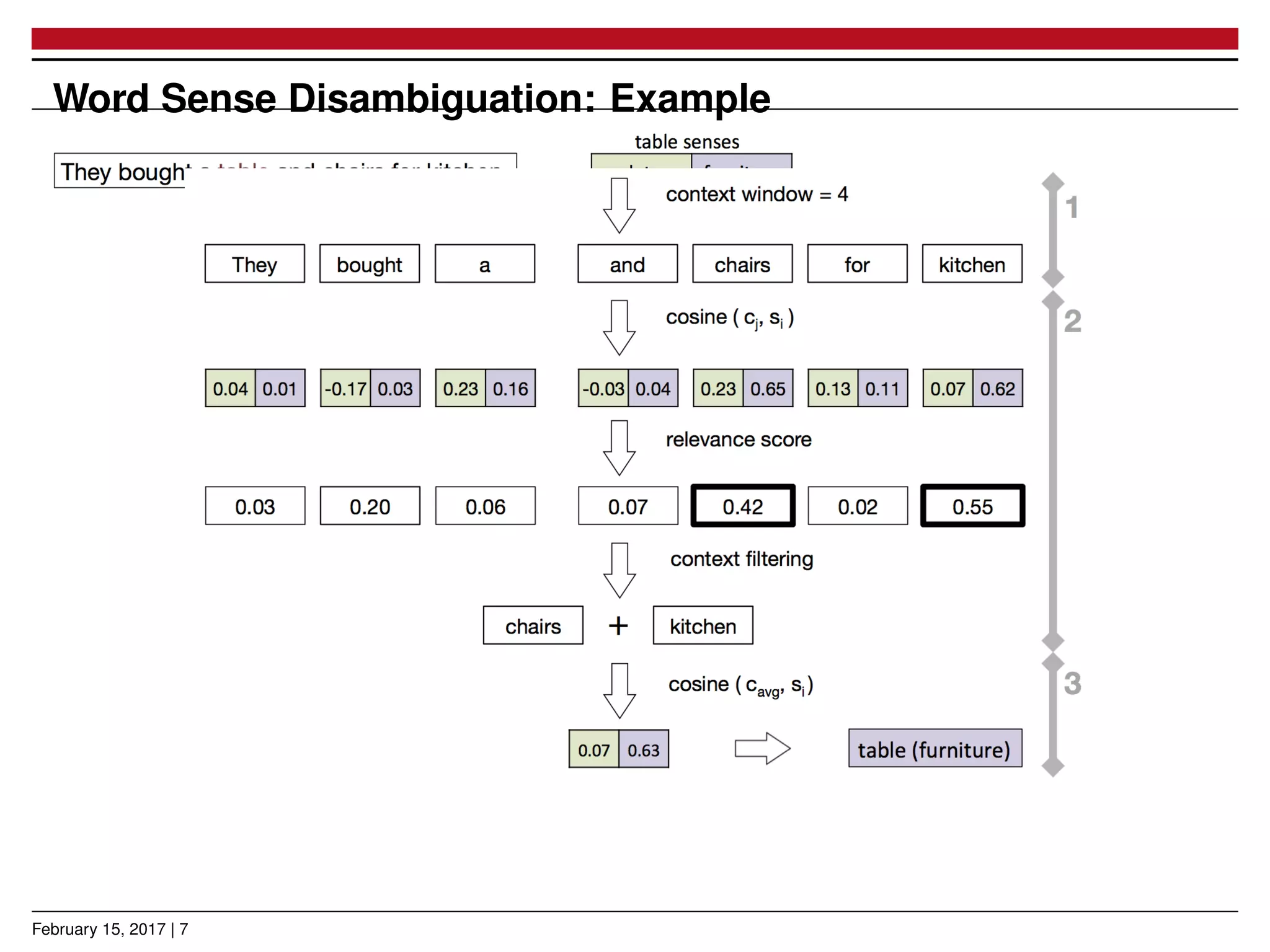
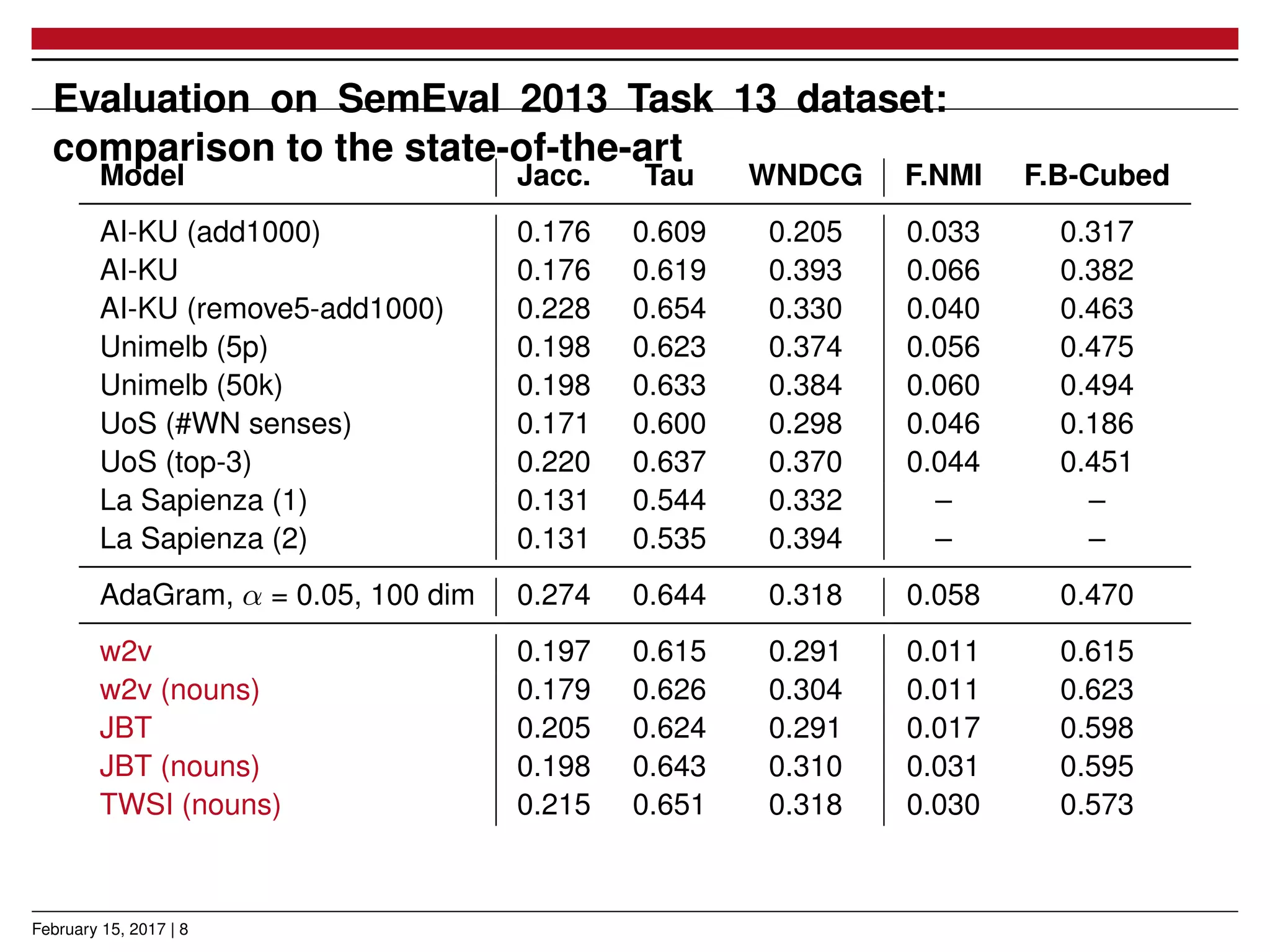
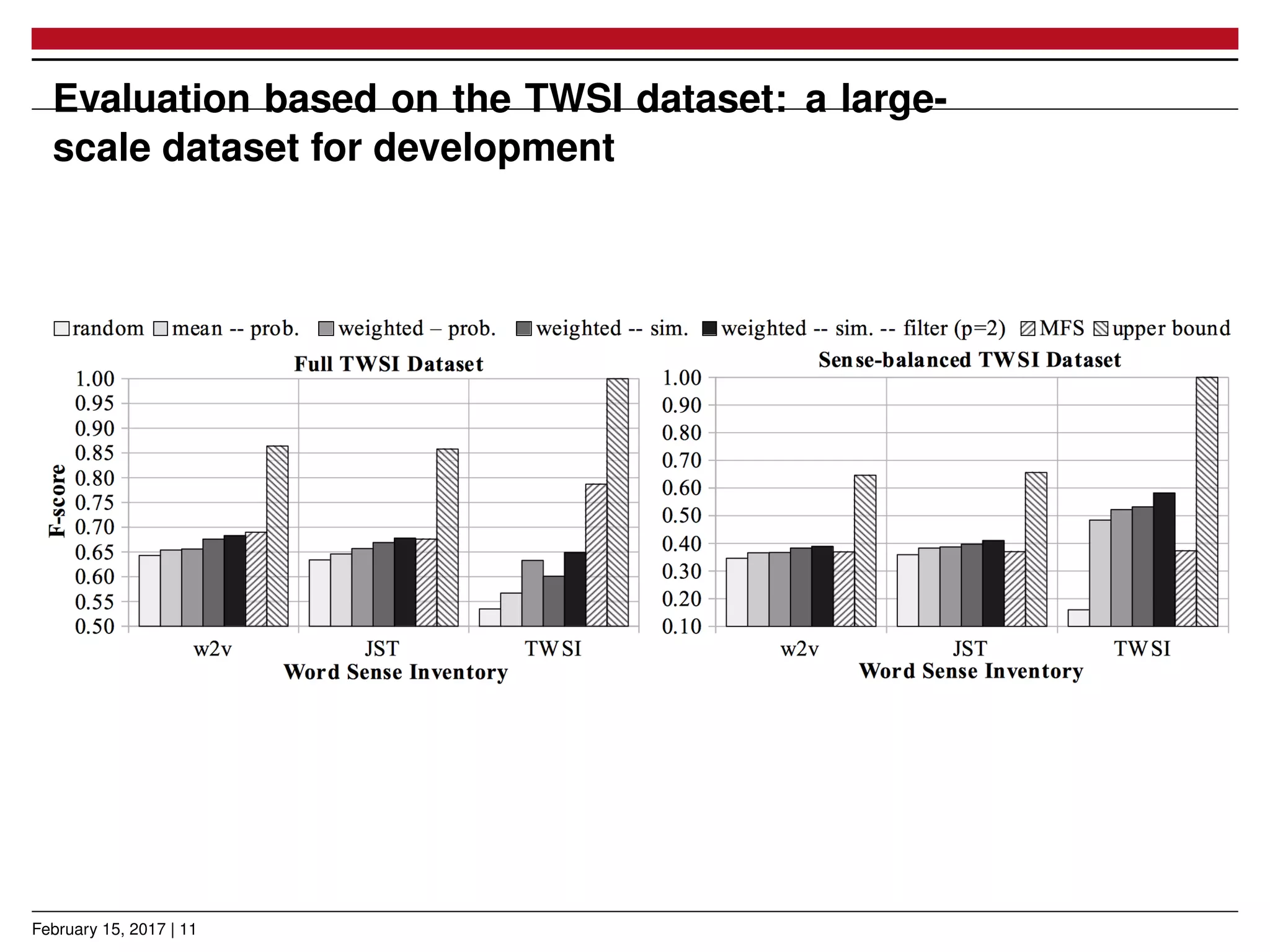
The document presents a novel approach for learning word sense embeddings using existing word embeddings as input, which involves ego-network clustering for word sense induction and a method for word sense disambiguation. The evaluation of the method on the SemEval 2013 task 13 dataset shows performance comparable to state-of-the-art systems. Source code and pre-trained models are available at the provided GitHub link.