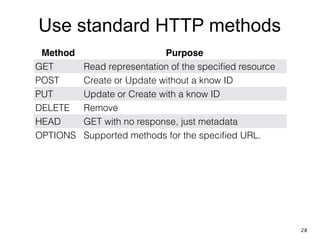
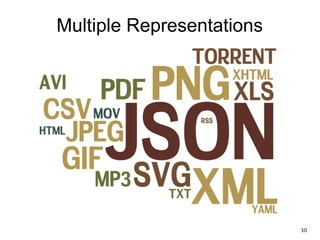
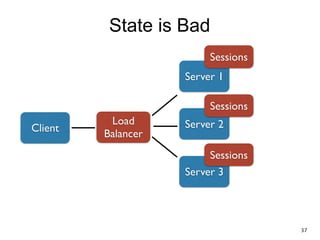
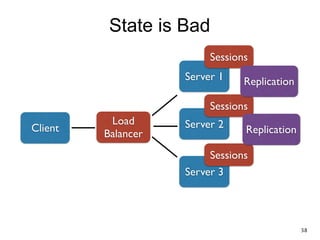
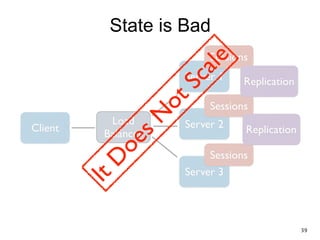
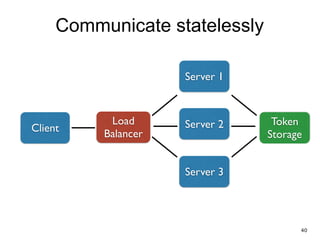
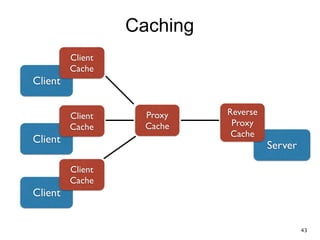
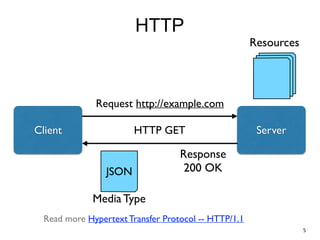
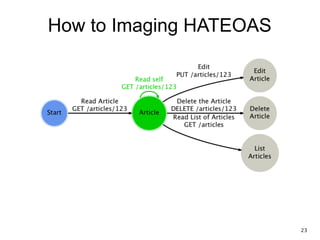
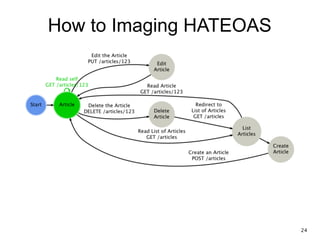
The document discusses REST and JAX-RS 2.0. It defines REST as an architectural style for building lightweight web services using HTTP. The key REST principles include giving everything a unique ID, linking resources together, using standard HTTP methods, supporting multiple representations, communicating statelessly, and enabling caching. JAX-RS 2.0 is a Java specification that makes it easy to build RESTful web services by using annotations to define resources and HTTP methods. It supports the REST principles and features like content negotiation, hypermedia links, and caching controls.
















![Let's try
$ curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/articles/7!
{!
"id": 7,!
"title": "REST Individual Resource",!
"content": "REST Individual Resource example"!
}
$ curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/articles/!
[!
{!
"id": 7,!
"title": "REST Individual Resource",!
"content": "REST Individual Resource example"!
}!
]
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/making-java-rest-with-jax-rs-2-140426073202-phpapp01/85/Making-Java-REST-with-JAX-RS-2-0-18-320.jpg)




![JAX-RS 2.0 HATEOAS
@POST
@Consumes({"application/json", "application/xml"})
@Produces({"application/json", "application/xml"})
public Response create(Article article) {
Article created = articleDao.create(article);
return Response
.ok(created)
.link("link-URI", “link-rel")
.links(produceLinks(created))
.build();
}
!
private Link[] produceLinks(Article article) {...}
Read more javax.ws.rs.core.Link
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/making-java-rest-with-jax-rs-2-140426073202-phpapp01/85/Making-Java-REST-with-JAX-RS-2-0-25-320.jpg)

![Let's try
$ curl -X GET “http://localhost:8080/articles/123"
{
"id": 123,
"title": "Hypermedia and JAX-RS 2.0",
"content": "JAX-RS 2.0 supports Hypermedia …",
"links": [
{ "uri": "/articles/",
"rel": "self" },
{ "uri": "/articles/",
"rel": "edit" },
{ "uri": "/articles/",
"rel": "delete" },
{ "uri": "/articles",
"rel": “list"}]
}
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/making-java-rest-with-jax-rs-2-140426073202-phpapp01/85/Making-Java-REST-with-JAX-RS-2-0-27-320.jpg)