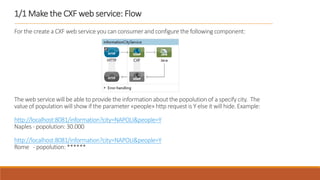
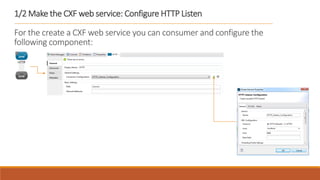
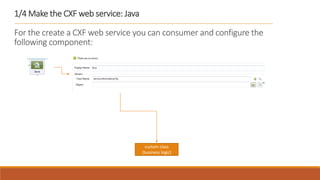
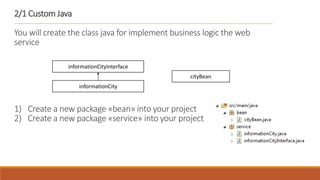
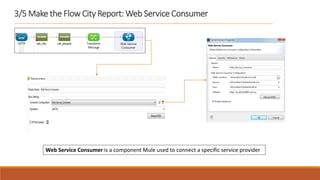
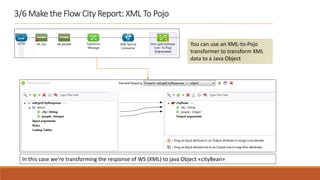
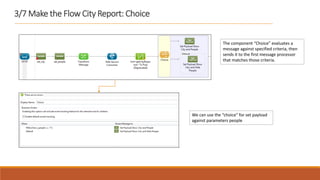
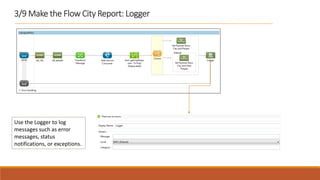
1. The document describes how to build a flow in Anypoint Studio that provides population statistics for different cities based on HTTP request parameters. It involves creating a CXF web service, custom Java classes, and a flow that uses components like Set Variable, Transform Message, Choice, and Logger.
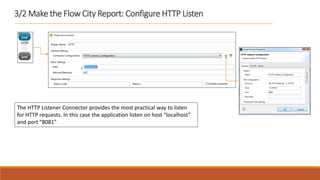
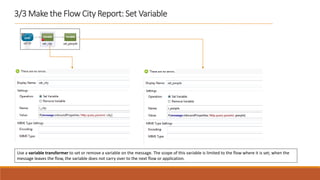
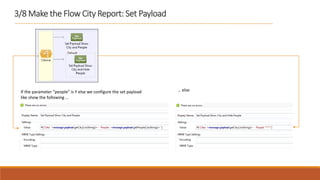
2. The flow listens for HTTP requests on port 8081 and routes the request to the CXF web service. Based on the "people" parameter, it either sets the response payload to include the population or hides it.
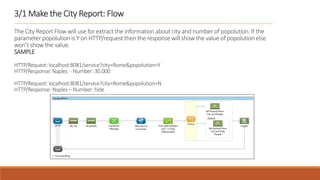
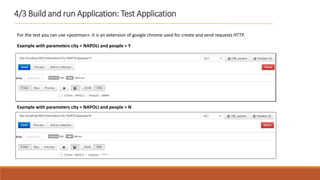
3. The application can be tested using Postman by sending sample requests with different city/people parameter combinations.