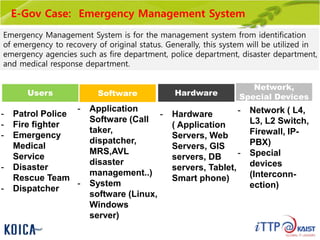
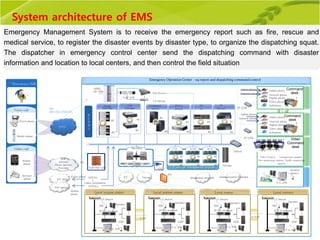
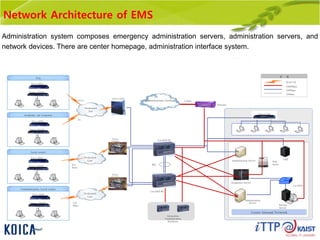
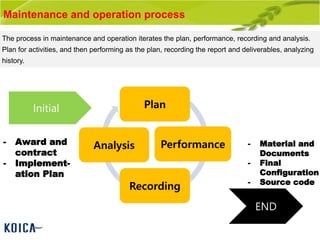
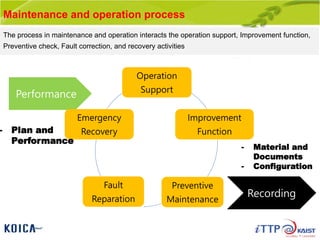
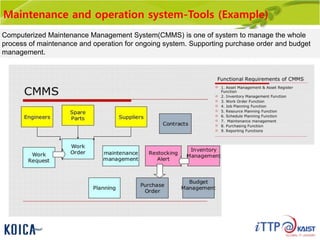
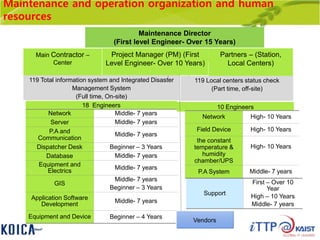
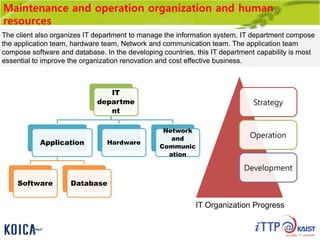
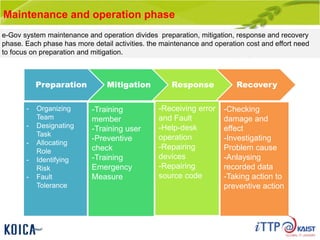
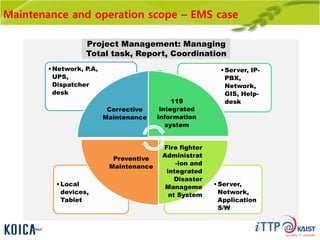
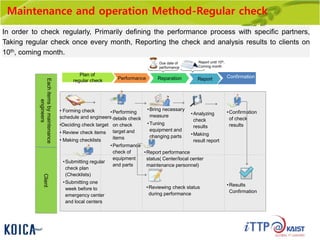
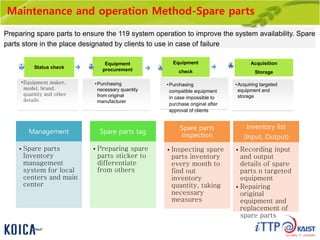
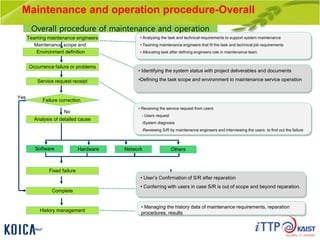
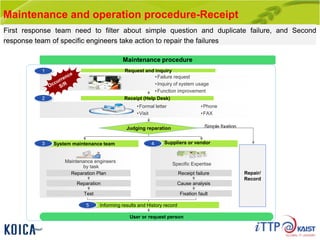
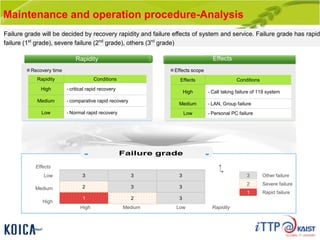
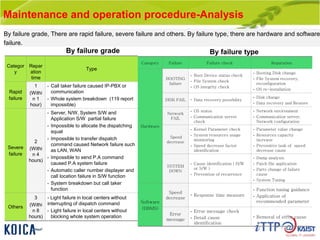
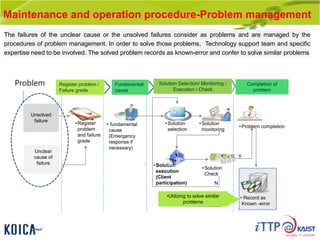
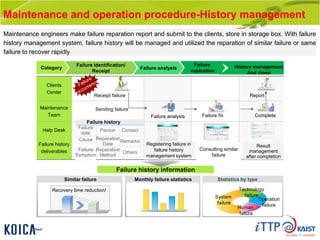
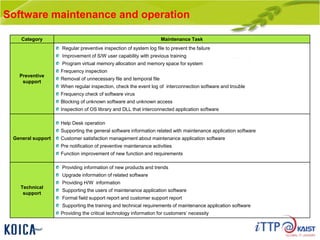
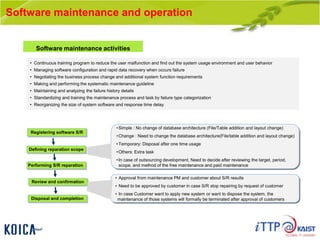
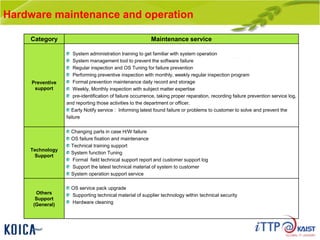
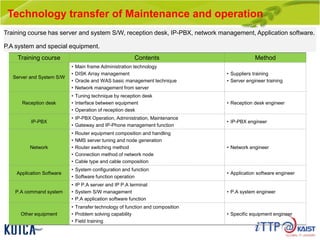
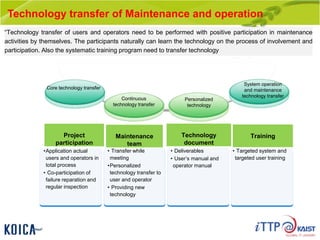
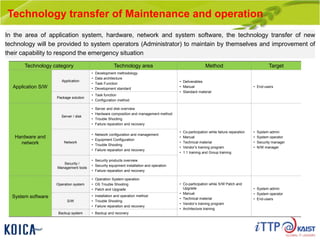
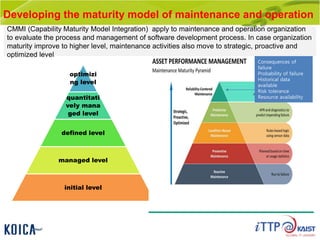
This document provides an overview of maintenance and operation for an Emergency Management System (EMS) case study in Bangladesh. It describes the key components of an EMS including software, hardware, network architecture and users. It then covers various aspects of maintaining and operating the EMS such as defining maintenance and operations, the management process, necessary systems and tools, required organization and human resources, different phases and types of maintenance. It also discusses methods, procedures and checks for regular and special maintenance of the EMS.