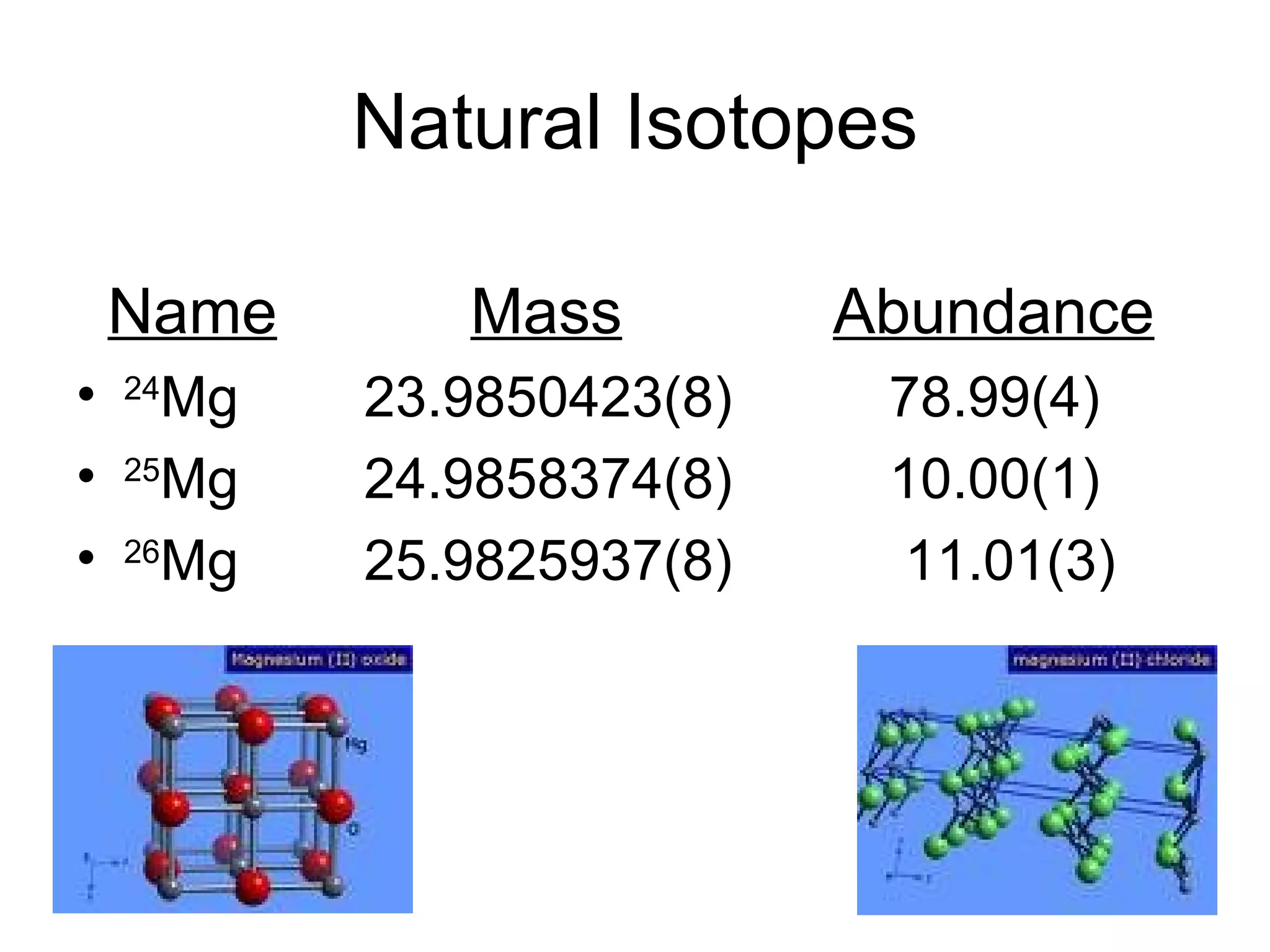
Magnesium is a metallic element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It was discovered in 1755 and isolated in 1808. Magnesium occurs naturally as the minerals dolomite and carnallite, and is most abundant in seawater. It has a silvery-white color, is fairly tough yet elastic, and poses a major fire risk. Common uses of magnesium include flares, reducing agent for uranium production, and as an alloy in computers and radios.