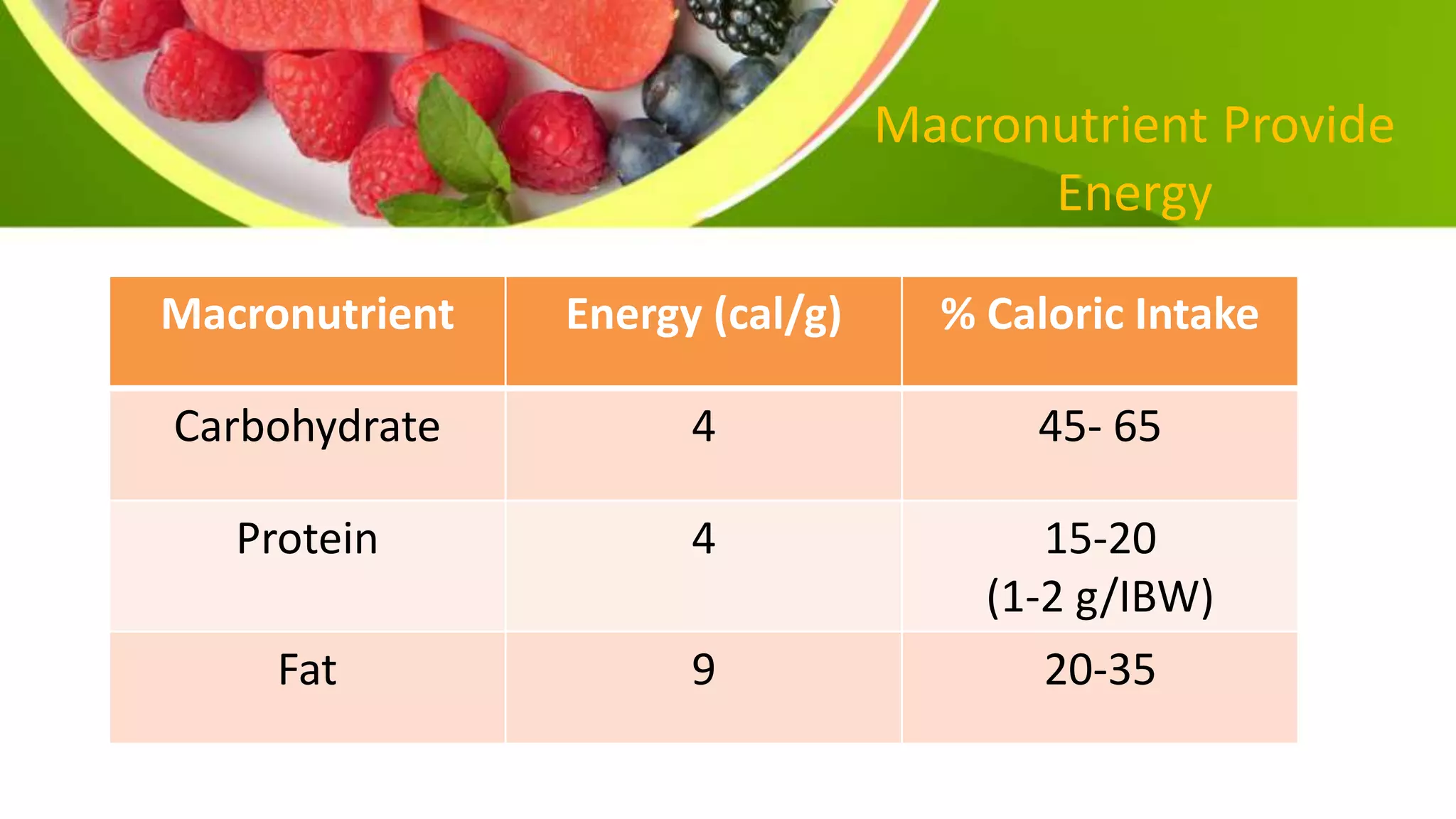
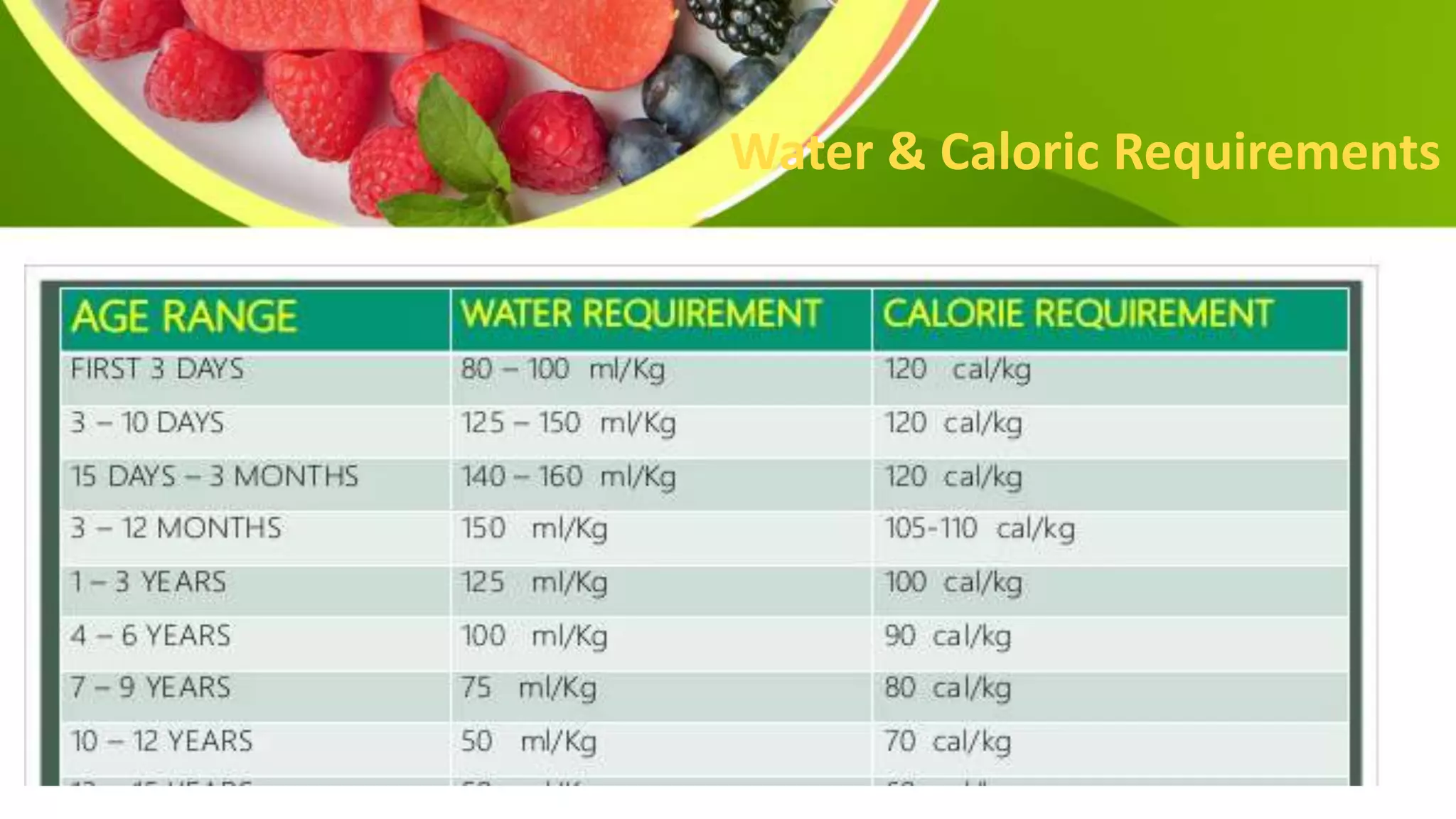
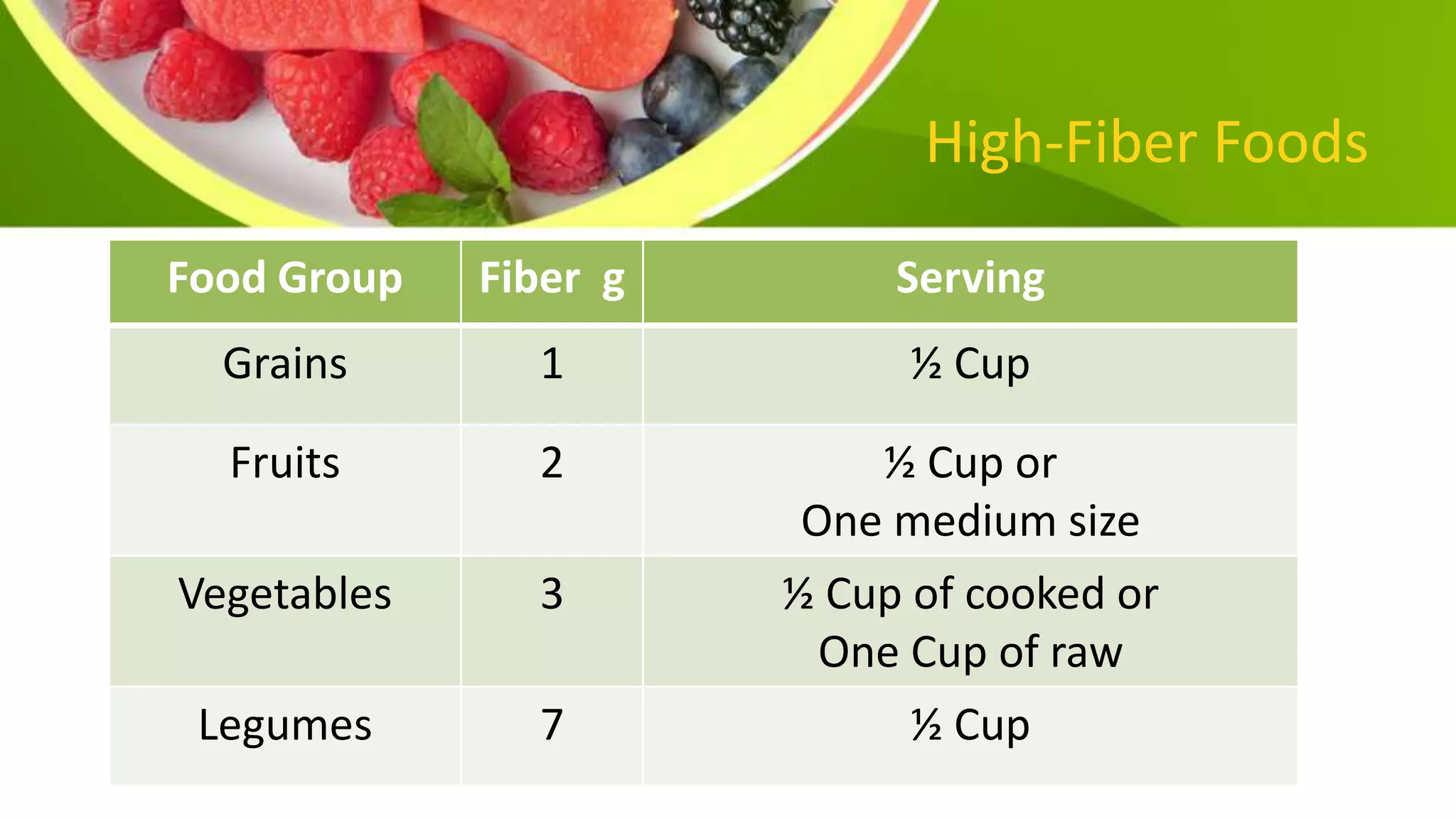
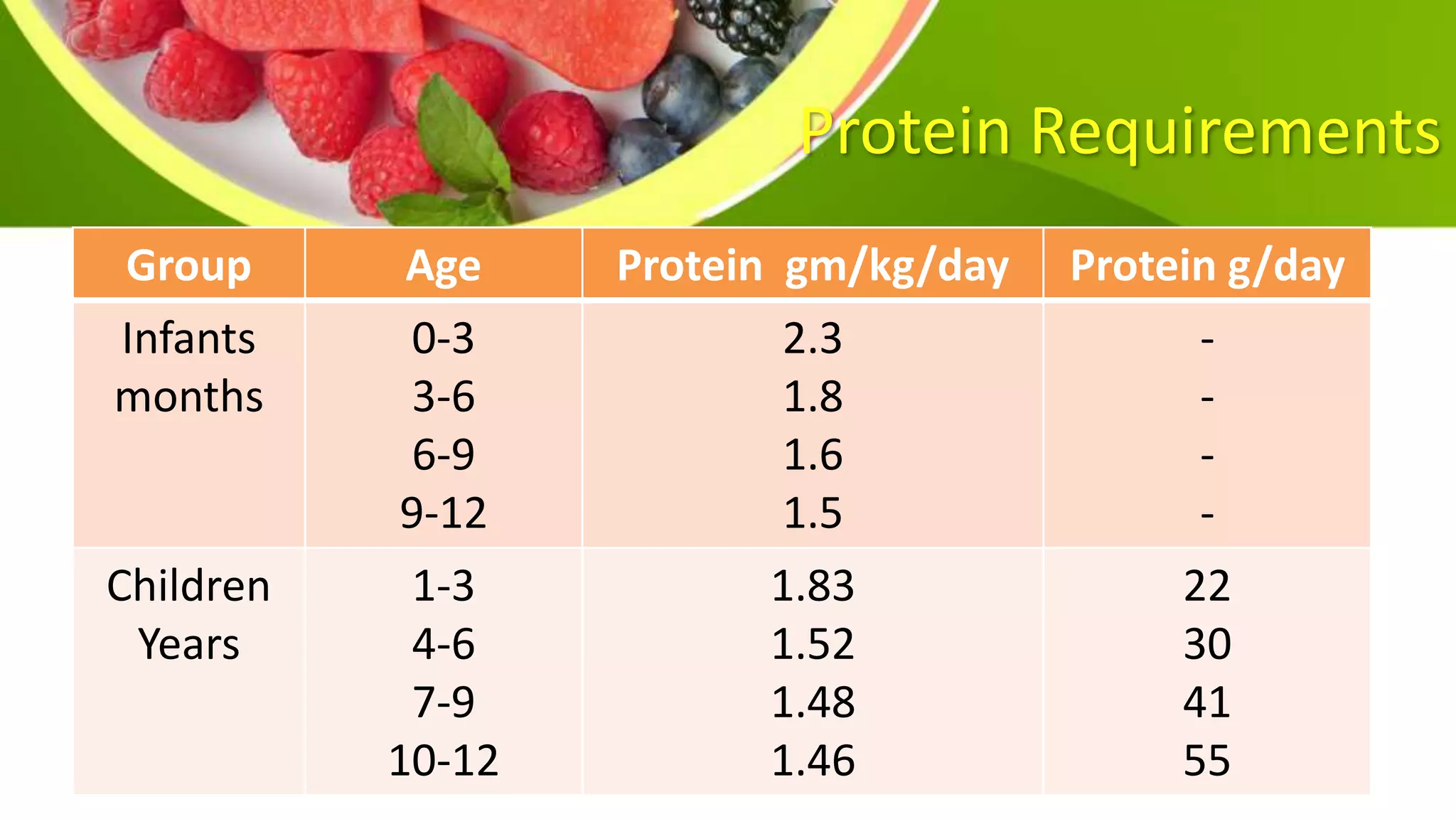
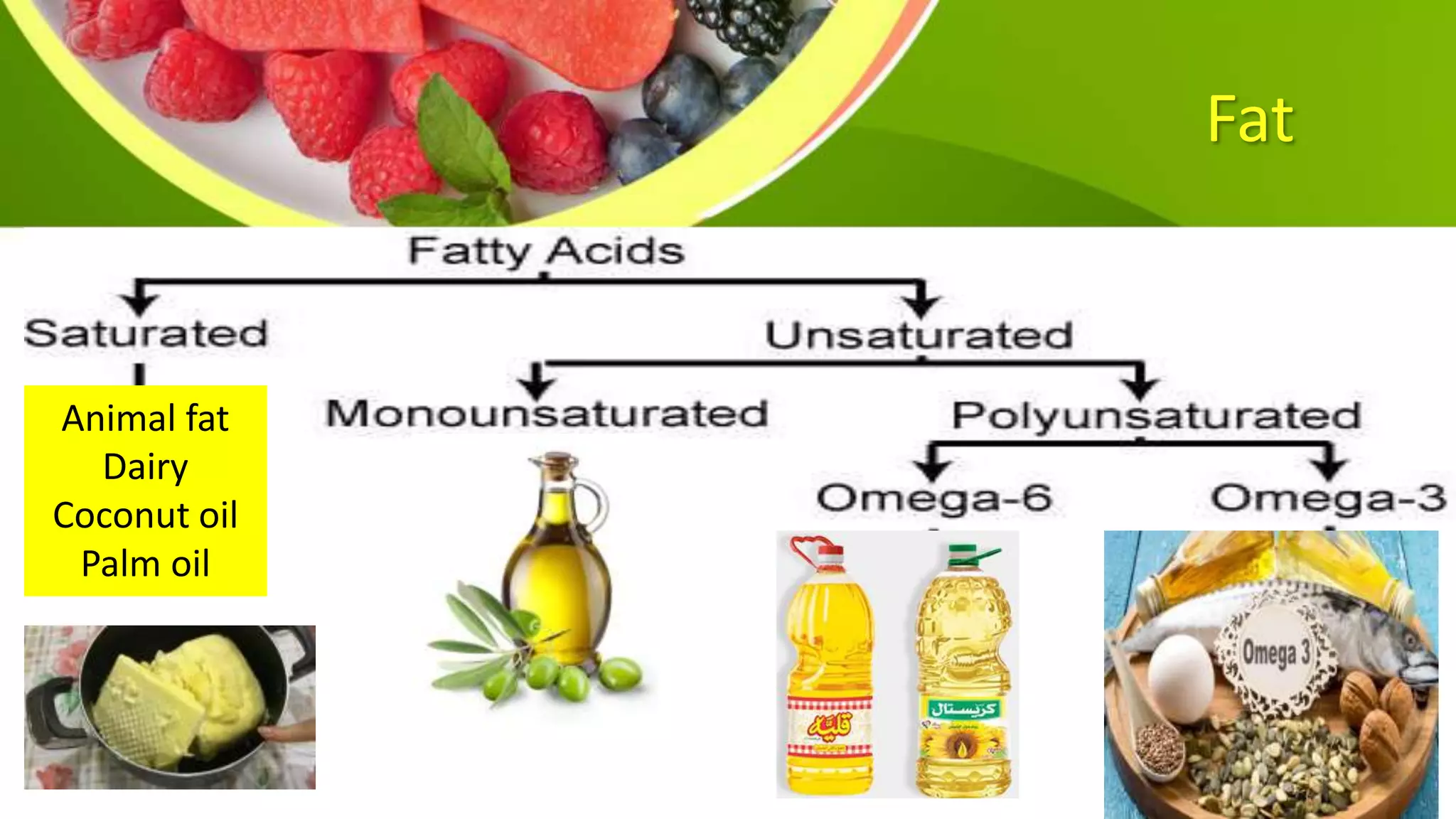
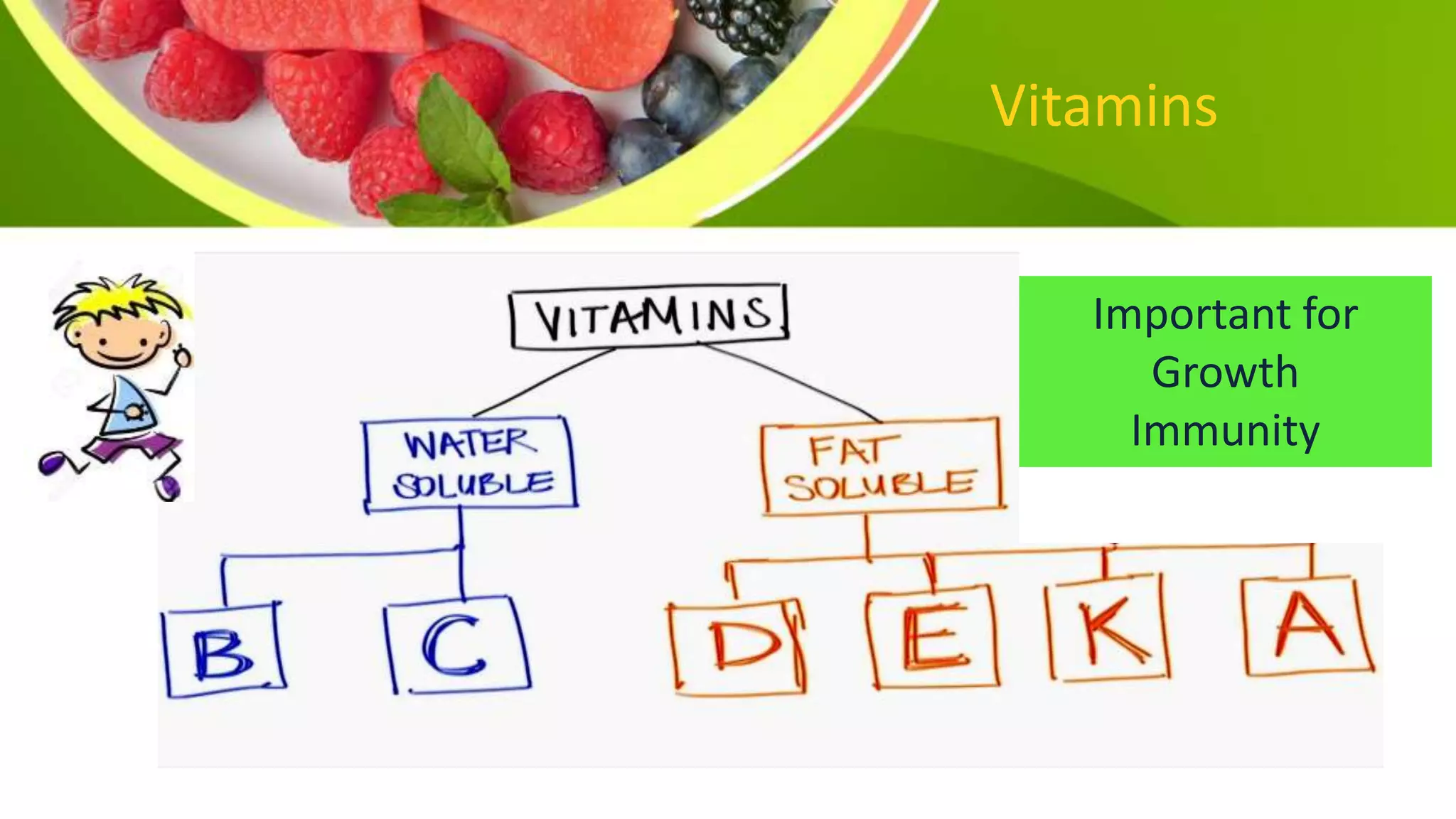
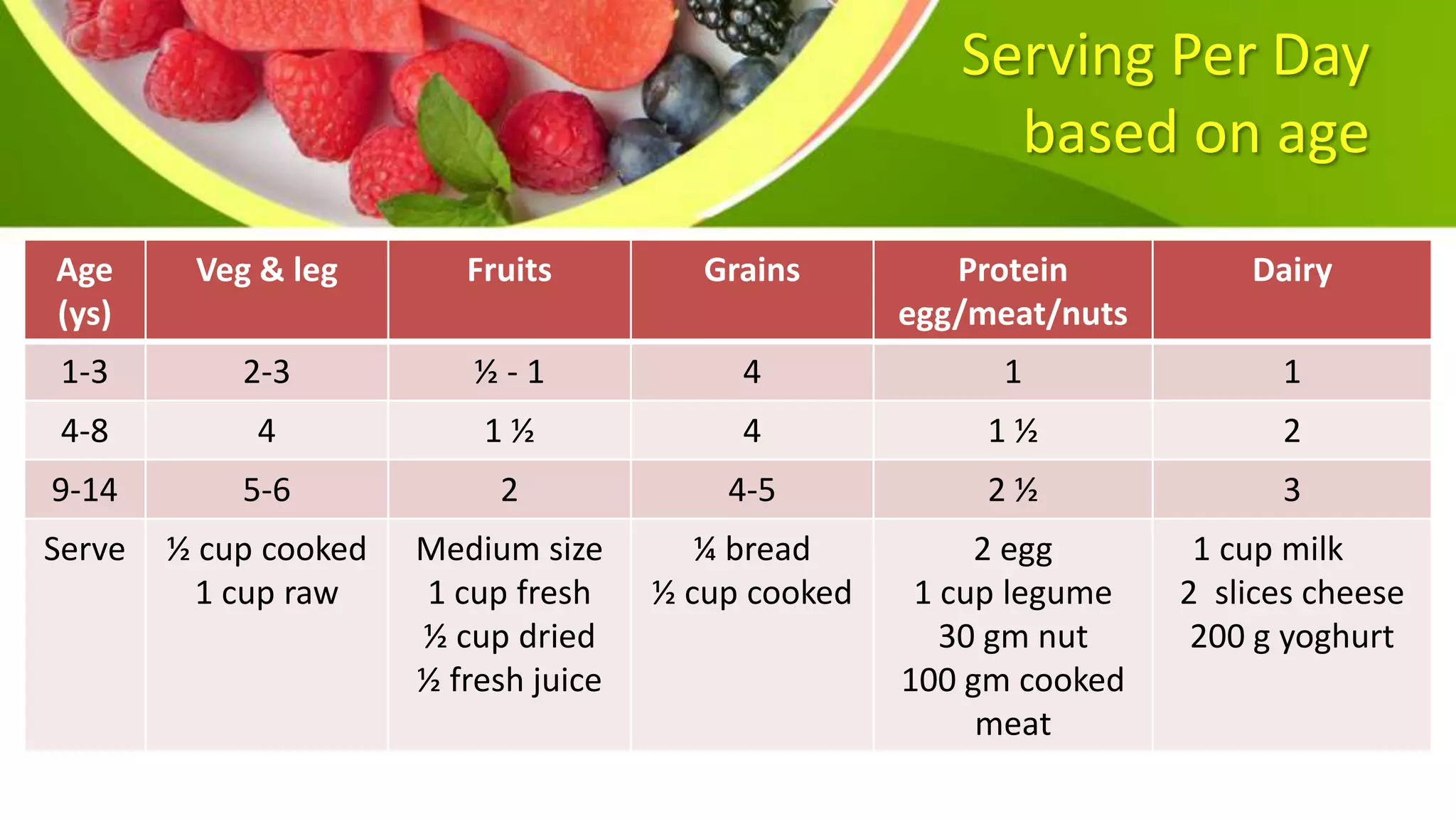
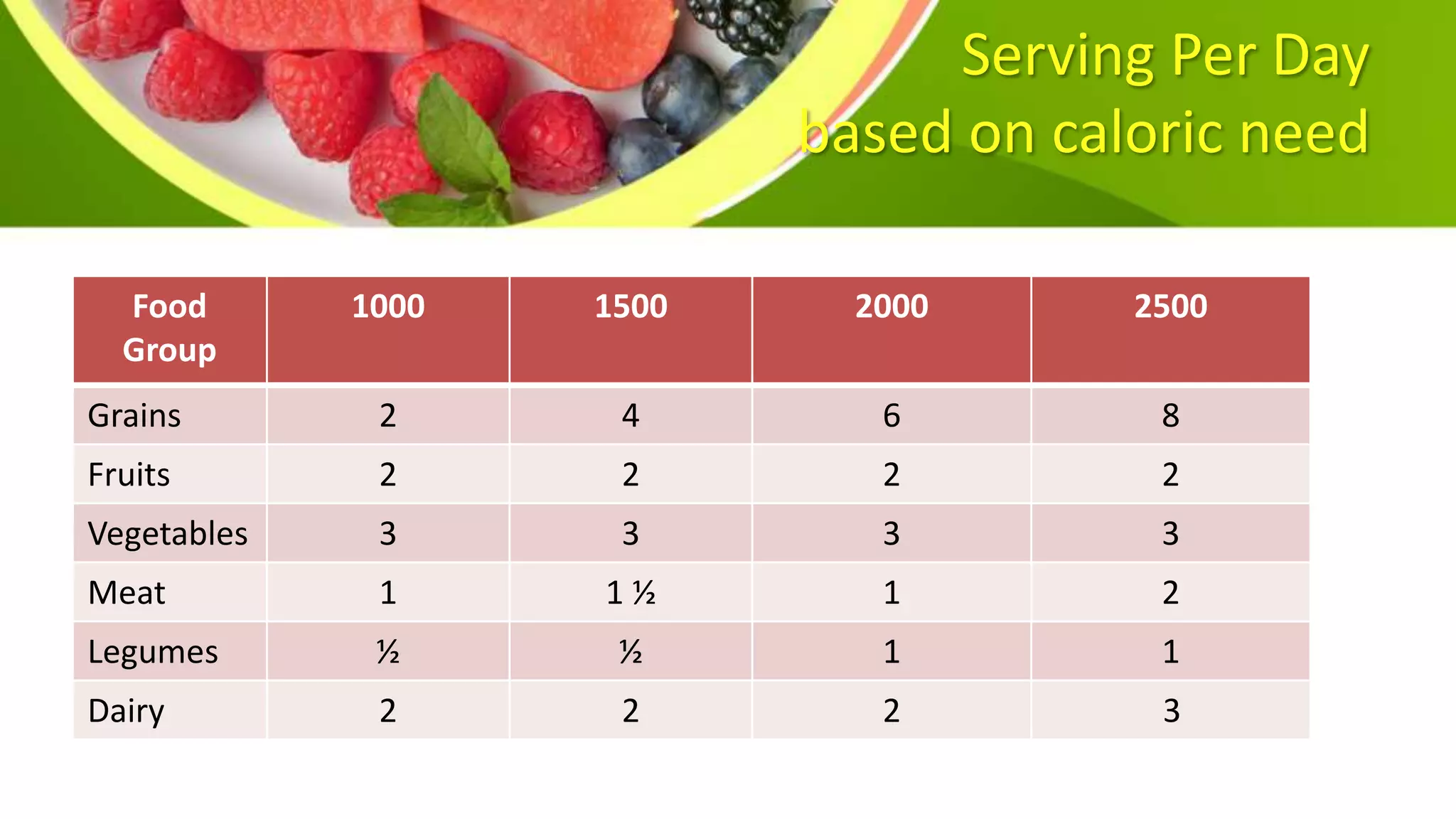
This document provides information on planning a balanced diet and nutritional requirements. It discusses dietary goals such as promoting growth and maintaining ideal body weight. Key terminology is defined, such as RDA, nutrient deficiency, and nutrient density. Macronutrients that provide energy like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are examined. Water and caloric requirements are addressed as well as fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Guidelines are given for daily servings based on age and caloric needs. The importance of a balanced diet with a variety of nutrient-dense foods is emphasized.